
中国农学通报 ›› 2021, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (15): 128-136.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0328
所属专题: 植物保护
王群1( ), 毕云青1, 何成兴1, 郭志祥1, 钟德卫2, 李君洪3, 陈乾昭2, 游继华2, 黄正会2, 李进斌1(
), 毕云青1, 何成兴1, 郭志祥1, 钟德卫2, 李君洪3, 陈乾昭2, 游继华2, 黄正会2, 李进斌1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-20
修回日期:2020-11-13
出版日期:2021-05-25
发布日期:2021-05-18
通讯作者:
李进斌
作者简介:王群,女,1970年出生,四川资阳人,副研究员,博士,研究方向:生物多样性及植物病害研究。通信地址:650205 云南省昆明市北京路2238号 云南省农科院环资所,Tel:15288249540,E-mail: 基金资助:
Wang Qun1( ), Bi Yunqing1, He Chengxing1, Guo Zhixiang1, Zhong Dewei2, Li Junhong3, Chen Qianzhao2, You Jihua2, Huang Zhenghui2, Li Jinbin1(
), Bi Yunqing1, He Chengxing1, Guo Zhixiang1, Zhong Dewei2, Li Junhong3, Chen Qianzhao2, You Jihua2, Huang Zhenghui2, Li Jinbin1( )
)
Received:2020-08-20
Revised:2020-11-13
Online:2021-05-25
Published:2021-05-18
Contact:
Li Jinbin
摘要:
探明绥江半边红李炭疽病为害程度及病原菌的种类,可为李树炭疽病的防控提供依据。以绥江县2个主要种植区会仪镇和新滩镇的6个半边红李果园为研究对象,对炭疽病为害状况进行了调查,并对炭疽病原菌进行分离保存;利用病原菌分生孢子形态及核糖体ITS序列对绥江半边红李树炭疽病致病菌进行了种类鉴定和分析。病害调查表明,新滩镇比会仪镇的危害程度严重。单孢分离获得15株分离株,各分离株平板菌落形态略有差异,获得4类不同的分生孢子,经回接验证均致病。rDNA ITS序列系统进化分析初步推定半边红李炭疽病的病原菌为胶孢炭疽复合群(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex)和暹罗炭疽复合群C. siamense species complex。该研究探查了半边红李炭疽病的为害状况,获得了李炭疽菌的单胞分离菌株,初步鉴定了半边红李炭疽菌归属的复合群。
中图分类号:
王群, 毕云青, 何成兴, 郭志祥, 钟德卫, 李君洪, 陈乾昭, 游继华, 黄正会, 李进斌. 半边红李炭疽病病害调查及病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(15): 128-136.
Wang Qun, Bi Yunqing, He Chengxing, Guo Zhixiang, Zhong Dewei, Li Junhong, Chen Qianzhao, You Jihua, Huang Zhenghui, Li Jinbin. Anthracnose Disease on Prunus salicina ‘Banbianhong’: Investigation and Pathogen Identification[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(15): 128-136.
| 果园 | 海拔/m | 发病率/% | 病情指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 会仪镇黄坪村1 | 380~500 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 会仪镇黄坪村2 | 500~700 | 30 | 31.1 |
| 会仪镇黄坪村3 | 700~900 | 30 | 30.0 |
| 合计 | 20 | 20.4 | |
| 新滩镇鲢鱼10队 | 380~500 | 40 | 41.1 |
| 新滩镇鲢鱼12队 | 500~700 | 70 | 70.0 |
| 新滩镇鲢鱼17队 | 700~900 | 40 | 63.3 |
| 合计 | 50 | 78.5 |
| 果园 | 海拔/m | 发病率/% | 病情指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 会仪镇黄坪村1 | 380~500 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 会仪镇黄坪村2 | 500~700 | 30 | 31.1 |
| 会仪镇黄坪村3 | 700~900 | 30 | 30.0 |
| 合计 | 20 | 20.4 | |
| 新滩镇鲢鱼10队 | 380~500 | 40 | 41.1 |
| 新滩镇鲢鱼12队 | 500~700 | 70 | 70.0 |
| 新滩镇鲢鱼17队 | 700~900 | 40 | 63.3 |
| 合计 | 50 | 78.5 |
| 菌株 | 长度/μm | 宽度/μm | 长宽比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-4-C2 | 18.35±1.70(15.9~21.6) B | 4.72±0.64(4.0~6.1) A | 3.94±0.58(3.0~4.8) B |
| 18-8-C1 | 13.35±1.14(11.9~15.1) C | 4.00±0.55(3.3~4.8) B | 3.40±0.62(2.9~4.6) B |
| 18-8-D1 | 21.94±2.25(18.2~26.1) A | 2.62±0.52(2.1~3.5) C | 8.65±1.91(6.7~12.2) A |
| 18-5-B1 | 14.65±1.94(12.8~19.1) C | 4.35±0.53(3.6~5.2) AB | 3.44±0.82(2.5~5.4) B |
| 菌株 | 长度/μm | 宽度/μm | 长宽比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-4-C2 | 18.35±1.70(15.9~21.6) B | 4.72±0.64(4.0~6.1) A | 3.94±0.58(3.0~4.8) B |
| 18-8-C1 | 13.35±1.14(11.9~15.1) C | 4.00±0.55(3.3~4.8) B | 3.40±0.62(2.9~4.6) B |
| 18-8-D1 | 21.94±2.25(18.2~26.1) A | 2.62±0.52(2.1~3.5) C | 8.65±1.91(6.7~12.2) A |
| 18-5-B1 | 14.65±1.94(12.8~19.1) C | 4.35±0.53(3.6~5.2) AB | 3.44±0.82(2.5~5.4) B |
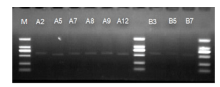
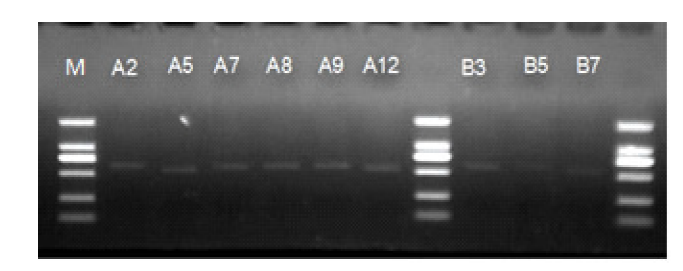
| [1] | 成策, 陆俊, 韩文琪, 等. 李子果粒果汁饮料加工工艺研究[J]. 食品与机械, 2015,31(6):215-218. |
| [2] | Cannon P F, Buddie A G, Bridge P D. The typification of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides[J]. Mycotaxon, 2008,104(2):189-204. |
| [3] | Sutton B C. The genus Glomerella and its anamorph Colletotrichum[M]// Bailey J A and Jeger M J. Colletotrichum: biology, pathology control. Wallingford: CABI, 1992:1-26. |
| [4] | Corda A C I. Die Pilze Deutschlands[M] // Sturm J. Deutschlands flora in Abbildungen nach der Natur mit Beschreibungen. Nürnberg: Sturm, 1831:33-64. |
| [5] | Arx J V. Die Arten der Gattung Colletotrichum Cda[J]. Phytopathologische Zeitschrift, 1957,29:413-468. |
| [6] | Sutton B C. The Coelomycetes[M]// Fungi imperfecti with pycnidia acervuli and stromata. Kew, UK: CABI, 1980:523-537. |
| [7] |
Cannon P F, Damm U, Johnston P R, et al. Colletotrichum - current status and future directions[J]. Studies in Mycology, 2012,73(1):181-213.
doi: 10.3114/sim0014 pmid: 23136460 |
| [8] |
Damm U, Cannon P F, Liu F, et al. The Colletotrichum orbiculare species complex: important pathogens of field crops and weeds[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2013,61(1):29-59.
doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0255-4 URL |
| [9] |
Damm U, Cannon P F, Woudenberg J H C, et al. The Colletotrichum acutatum species complex[J]. Studies in Mycology, 2012,73(73):37-113.
doi: 10.3114/sim0010 URL |
| [10] |
Damm U, Cannon P F, Woudenberg J H C, et al. The Colletotrichum boninense species complex[J]. Studies in Mycology, 2012,73(1):1-36.
doi: 10.3114/sim0002 pmid: 23136457 |
| [11] |
Damm U, O'Connell R J, Groenewald J Z, et al. The Colletotrichum destructivum species complex-hemibiotrophic pathogens of forage and field crops[J]. Studies in Mycology, 2014,79(79):49-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2014.09.003 URL |
| [12] | Hyde K D, Cai L, Cannon P F, et al. Colletotrichum - names in current use[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2009,39:147-182. |
| [13] |
Liu F, Cai L, Crous P W. The Colletotrichum gigasporum species complex[J]. Persoonia, 2014,33(1):83-97.
doi: 10.3767/003158514X684447 URL |
| [14] |
Sharma G, Kumar N, Weir B, et al. The ApMat marker can resolve Colletotrichum species: a case study with Mangifera indica[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2013,61(1):117-138.
doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0247-4 URL |
| [15] |
Weir B S, Johnston P R, Damm U. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex[J]. Studies in Mycology, 2012,73(1):115-180.
doi: 10.3114/sim0011 pmid: 23136459 |
| [16] |
Crouch J A. Colletotrichum caudatum s.l. is a species complex[J]. IMA Fungus, 2014,5(1):17-30.
doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2014.05.01.03 URL |
| [17] |
Lee H D, Kim D H, Jeon Y A, et al. Molecular and cultural characterization of Colletotrichum spp. causing bitter rot of apples in Korea[J]. The Plant Pathology Journal, 2007,23(2):37-44.
doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2007.23.2.037 URL |
| [18] | 侯丽冰, 贺伟, 刘小勇, 等. 我国几种松干锈菌亲缘关系的ITS 序列分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2002,24(Z1):175-182. |
| [19] | Schoch C L, Seifert K A, Sabine H, et al. Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for Fungi[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012,109(16):6241-6246. |
| [20] |
Dresler-Nurmi A, Kaijalainen S, LindstrÖM K, et al. Grouping of lignin degrading corticioid fungi based on RFLP analysis of 18S rDNA and ITS regions[J]. Mycological Research, 1999,103(8):990-996.
doi: 10.1017/S0953756298008156 URL |
| [21] |
Freeman S, Minz D, Jurkevitch E, et al. Molecular analyses of Colletotrichum species from almond and other fruits[J]. Phytopathology, 2000,90(6):608-614.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2000.90.6.608 pmid: 18944540 |
| [22] | 邓先琼, 郭立中, 张天晓. 布朗李炭疽病的病原鉴定及药效试验[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2004,23(6):626-630. |
| [23] | Hassan O, Lee Y S, Chang T. Colletotrichum Species Associated with Japanese Plum (Prunus salicina) Anthracnose in South Korea[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019,9(1):1-12. |
| [24] |
Montri P, Taylor P W J, Mongkolporn O. Pathotypes of Colletotrichum capsici, the causal agent of chili anthracnose, in Thailand[J]. Plant Disease, 2009,93:17-20.
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-93-1-0017 URL |
| [25] | Awa O C, Samuel O, Oworu O O, et al. First report of fruit anthracnose in Mango caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in Southwestern Nigeria[J]. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 2012,1(4):30-34. |
| [26] | 曹若彬. 果树病理学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1992. |
| [27] |
Li Z, Liang Y M, Tian C M. Characterization of the causal agent of poplar anthracnose occurring in the Beijing region[J]. Mycotaxon, 2012,120(1):277-286.
doi: 10.5248/120.277 URL |
| [28] | 方中达. 植物病理研究方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1979. |
| [29] |
Tai T H, Tanksley S D. A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 1990,8(4):297-303.
doi: 10.1007/BF02668766 URL |
| [30] | White T J, Bruns T, Lee S, et al. Analysis of phylogenetic relationships by amplification and direct sequencing of ribosomal RNA genes[M] // Innis MA, Gelfand D H, Sninsky J J, et al. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. San Diego, USA: Academic Press, 1990:315-322. |
| [31] |
Thompson J D, Gibson T J, Plewniak F, et al. The CLUSTALX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1997,25(24):4876-4882.
doi: 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876 URL |
| [32] |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolutionary 2016,33(7):1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 URL |
| [33] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, et al. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0[J]. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 2013,30(4):2725-2729. |
| [34] | Prihastuti H, Cai L, Chen H, et al. Characterization of Colletotrichum species associated with coffee berries in northern Thailand[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2009,39:89-109. |
| [35] | Yang Y L, Liu Z Y, Cai L, et al. Colletotrichum anthracnose of Amaryllidaceae[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2009,39(2):123-146. |
| [36] |
Chen Y, Qiao W, Zeng L, et al. Characterization, pathogenicity, and phylogenetic analyses of Colletotrichum species associated with brown blight disease on Camellia sinensis in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2017,101(6):1022-1028.
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-12-16-1824-RE URL |
| [37] |
Grammen A, Wenneker M, Van Campenhout J, et al. Identification and pathogenicity assessment of Colletotrichum isolates causing bitter rot of apple fruit in Belgium[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2019,153(1):47-63.
doi: 10.1007/s10658-018-1539-z pmid: WOS:000484796700003 |
| [38] |
Diao Y Z, Zhang C, Liu F, et al. Colletotrichum species causing anthracnose disease of chili in China[J]. Persoonia, 2017,38:20-37.
doi: 10.3767/003158517X692788 URL |
| [39] |
Diao Y Z, Zhang C, Xu J P, et al. Genetic differentiation and recombination among geographic populations of the fungal pathogen Colletotrichum truncatum from chili peppers in China[J]. Evolutionary Applications, 2015,8:108-118.
doi: 10.1111/eva.2015.8.issue-1 URL |
| [40] |
Kanto T, Uematsu S, Tsukamoto T, et al. Anthracnose of sweet pepper caused by Colletotrichum scovillei in Japan[J]. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 2014,80:73-78.
doi: 10.1007/s10327-013-0496-9 URL |
| [41] |
Liao C Y, Chen M Y, Chen Y K, et al. Characterization of three Colletotrichum acutatum isolates from Capsicum spp.[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2012,133:599-608.
doi: 10.1007/s10658-011-9935-7 URL |
| [42] |
Sharma G, Shenoy B D. Colletotrichum fructicola and C. siamense are involved in chilli anthracnose in India[J]. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 2014,47(10):1179-1194.
doi: 10.1080/03235408.2013.833749 URL |
| [43] |
Than P P, Prihastuti H, Phoulivong S, et al. Chilli anthracnose disease caused by Colletotrichum species[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 2008,9(10):764-778.
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0860007 URL |
| [44] | 向梅梅, 张云霞, 刘霄. 炭疽菌属真菌分类的研究进展[J]. 仲恺农业工程学院学报, 2017,30(1):59-66. |
| [45] |
Sharma G, Pinnaka A K, Shenoy B D. Resolving the Colletotrichum siamense species complex using ApMat marker[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2015,71(1):247-264.
doi: 10.1007/s13225-014-0312-7 URL |
| [1] | 孙博, 刘闰, 王占斌, 陈黄欣, 阎肃. 桃叶蓼白粉菌的显微观察及进化关系分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 130-136. |
| [2] | 侯世星, 胡娜, 张继明, 张国新, 吴芳. 染井吉野樱花腐烂病病原菌鉴定及其致病性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(35): 76-82. |
| [3] | 魏日凤, 彭成彬, 陈美霞, 张政雄, 阮俊峰, 刘伟. 柳叶蜡梅真菌病害分离鉴定及生物学特性[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(3): 127-133. |
| [4] | 宋垚, 王辉. 基于DNA序列的‘和田’玫瑰遗传背景分析研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(28): 36-40. |
| [5] | 宋晓兵, 黄峰, 罗小玲, 林培华, 彭埃天, 凌金锋, 崔一平. 吡唑醚菌酯对两种优稀水果病原菌的毒力测定及田间防治效果[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(27): 125-128. |
| [6] | 李瑜, 覃剑锋, 刘运华, 孙莹莹, 唐晓东. 一种绞股蓝根结线虫的研究初报[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(22): 110-114. |
| [7] | 尤梦瑶, 闫佳佳, 万璐, 张赫, 郑春英. 甘草产香内生真菌RP2的初步鉴定及挥发性成分分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(12): 138-145. |
| [8] | 黄蔚, 崔丽红, 谢王超, 肖国强. 西瓜新炭疽病病原菌分子鉴定及其生物学特性初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(1): 131-136. |
| [9] | 王占斌, 周暄, 马鑫博, 王靖琳. 药用植物内生真菌的分离及拮抗菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(1): 75-81. |
| [10] | 张亚楠, 陈新慧, 张杰. 苹果炭疽病抗性miRNA的筛选[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(7): 106-111. |
| [11] | 曾华兰, 蒋秋平, 叶鹏盛, 何炼, 华丽霞, 刘勇, 王明娟, 张敏, 曾静, 何晓敏. 种苗处理对麦冬生长的影响及其控病效果研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(6): 137-141. |
| [12] | 韩帅, 吴婕, 张河庆, 梁根云, 席亚东. 黄瓜新炭疽病原的鉴定及生物学特性初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(28): 96-108. |
| [13] | 元超, 舒雪纯, 张影波, 王凯, 谢小丽, 徐子琪, 袁媛. 艾纳香内生真菌抗细菌和炭疽菌的活性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(23): 38-44. |
| [14] | 李维蛟, 任可, 浦仕彪. 栽培三七内生真菌优势种群分离鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(18): 102-108. |
| [15] | 袁国徽, 田志慧, 李涛, 钱振官, 沈国辉. 稗属植物DNA条形码研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(15): 106-111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||