
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (23): 153-164.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0800
• 水产·渔业 • 上一篇
廖设国( ), 赖福香, 刘玓玓, 郑弘朝, 郑然, 林慷祺, 范兰芬(
), 赖福香, 刘玓玓, 郑弘朝, 郑然, 林慷祺, 范兰芬( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-21
修回日期:2024-02-28
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-08-09
通讯作者:
作者简介:廖设国,男,2000年出生,本科,研究方向:水产健康养殖。通信地址:510642 广东省广州市五山路483号 华南农业大学海洋学院, E-mail:2219108489@qq.com。
基金资助:
LIAO Sheguo( ), LAI Fuxiang, LIU Didi, ZHENG Hongchao, ZHENG Ran, LIN Kangqi, FAN Lanfen(
), LAI Fuxiang, LIU Didi, ZHENG Hongchao, ZHENG Ran, LIN Kangqi, FAN Lanfen( )
)
Received:2023-11-21
Revised:2024-02-28
Published:2024-08-15
Online:2024-08-09
摘要:
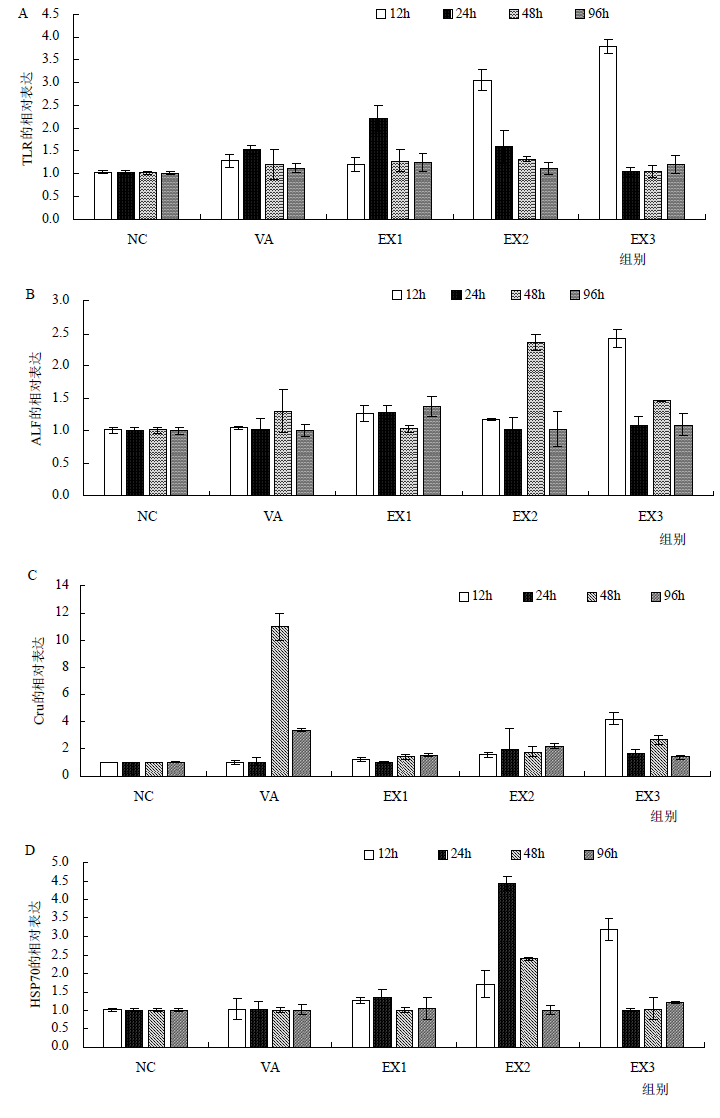
本研究旨在评估仙鹤草醇提取物对高致病性弧菌感染的凡纳滨对虾的防治效果。通过在饲料中添加90%含量的仙鹤草醇提取物,分析投喂3、6、9 d后,感染高致病性弧菌的凡纳滨对虾的肠道微生物、免疫相关基因和肠道组织。结果表明,在病虾肠道内,菌群种类与数量增加,其中希瓦氏菌属、弧菌属和海绵假单胞菌属等致病菌的数量均显著高于健康对虾,且菌群的组成与健康对虾的菌群组成差异较大,对投喂仙鹤草醇提取物添加剂饲料再攻菌的凡纳滨对虾,以上致病菌群的相对丰度显著降低,而有益菌群的溶杆菌属有了大幅的提升。另外,仙鹤草醇提取物还可以保护对虾的肠道组织,提高对虾免疫相关基因TLR、ALF、Crustin与HSP70的表达。饲料中添加仙鹤草醇提取物,能够显著提高对虾感染高致病性弧菌后的免疫力,增强对虾抗菌能力。
廖设国, 赖福香, 刘玓玓, 郑弘朝, 郑然, 林慷祺, 范兰芬. 仙鹤草醇提取物对高致病性弧菌感染凡纳滨对虾的防治效果探究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(23): 153-164.
LIAO Sheguo, LAI Fuxiang, LIU Didi, ZHENG Hongchao, ZHENG Ran, LIN Kangqi, FAN Lanfen. The Prevention and Control Effect of Ethanol Extract from Agrimonia pilosa on Highly Pathogenic Vibrio Infection in Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(23): 153-164.
| 基因 | 核酸序列(5′-3′) | GenBank登录号 |
|---|---|---|
| Crustin | F:AACCAGAGACACCTGTTGGC | AY48497.1 |
| R:AGTCACCTCCTTCGGCTCTC | ||
| ALF | F:TGTTCCTGGTGGCACTCTTC | GQ227486.1 |
| R:GTCTCCTCGTTCCTCCACAG | ||
| TLR | F:TGCCAAGCAGTGATGTGA | KC660103.1 |
| R:GCGGGAAGGAAGTGATGT | ||
| HSP70 | F:CCTCCAGGACTTCTTCAACG | EF495128 |
| R:GGTCACGTCCAACAGCAAC | ||
| β-actin | F:GACTACCTGATGAAGATCC | AF300705 |
| R:TCGTTGCCGATGGTGATCA |
| 基因 | 核酸序列(5′-3′) | GenBank登录号 |
|---|---|---|
| Crustin | F:AACCAGAGACACCTGTTGGC | AY48497.1 |
| R:AGTCACCTCCTTCGGCTCTC | ||
| ALF | F:TGTTCCTGGTGGCACTCTTC | GQ227486.1 |
| R:GTCTCCTCGTTCCTCCACAG | ||
| TLR | F:TGCCAAGCAGTGATGTGA | KC660103.1 |
| R:GCGGGAAGGAAGTGATGT | ||
| HSP70 | F:CCTCCAGGACTTCTTCAACG | EF495128 |
| R:GGTCACGTCCAACAGCAAC | ||
| β-actin | F:GACTACCTGATGAAGATCC | AF300705 |
| R:TCGTTGCCGATGGTGATCA |
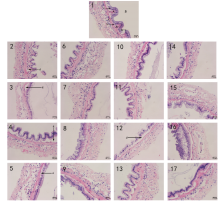


| [1] |
刘庆明, 骆大鹏, 赵志英, 等. 罗氏沼虾与凡纳滨对虾池塘生态混养技术[J]. 现代农业科技, 2022(23):175-180.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
王天艺. 南美白对虾养殖中存在的问题及其对策探讨[J]. 南方农业, 2021, 15(11):197-198.
|
| [5] |
罗红, 赵永锋, 魏友海. 罗氏沼虾产业发展现状及面临的主要问题[J]. 科学养鱼, 2022(2):20-23.
|
| [6] |
李钫. 海洋科技助力抗“玻璃苗”疫病对虾种苗选育[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(2):372.
|
| [7] |
王印庚, 于永翔, 刘潇, 等. 凡纳滨对虾虾苗细菌性玻化症(BVS)的病原、病理分析[J]. 水产学报, 2021, 45(9):1563-1573.
|
| [8] |
魏大伟. 中国沿海地区副溶血弧菌流行病学调查及遗传多样性分析[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2024.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
冯博. 引起对虾早期死亡综合征的副溶血性弧菌的分离鉴定及发病机理研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2017.
|
| [12] |
孔嘉明, 戴习林, 黎兰诗, 等. 副溶血弧菌对罗氏沼虾肝胰腺和鳃组织中呼吸相关酶活性及抗氧化酶基因表达的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(12):3294-3302.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
周疆, 郑凯妮, 朱斐. 中草药在水产动物免疫上的应用[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(2):406-414.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
余文兰, 梁柏, 刘忠华. 猪亚硝酸盐中毒模型复制与诊疗[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2017(24):104-106.
|
| [18] |
康林之, 袁敏, 邵峰, 等. 仙鹤草不同提取物抗疲劳抗氧化及免疫调节作用研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2016, 27(5):1079-1081.
|
| [19] |
钟希琼, 邓定波, 熊秋洁, 等. 紫甘薯花色苷对亚硝化反应的抑制作用[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2015(6):120-123.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
吕玲. 仙鹤草提取物具有广谱抗流感病毒活性[J]. 中国家禽, 2010, 32(2):74.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
张家松, 段亚飞, 张真真, 等. 对虾肠道微生物菌群的研究进展[J]. 南方水产科学, 2015, 11(6):114-119.
|
| [25] |
孔祎頔, 田佳鑫, 陈秀梅, 等. 水产动物益生菌及其对肠道菌群影响的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2019, 55(1):29-33.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: S0882-4010(18)31695-4 pmid: 30503960 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00899-14 pmid: 24727271 |
| [32] |
杨慧婷. 对虾肠道菌群动态平衡的免疫调控研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
李晶晶, 李云, 刘红, 等. 感染溶藻弧菌及白斑综合症病毒后凡纳滨对虾不同组织的Toll样受体基因表达变化研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(2):476-483.
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00872 pmid: 31110504 |
| [37] |
|
| [1] | 周文川, 王芸, 段亚飞, 王珺, 周传朋, 黄忠. 饲料中添加红景天对凡纳滨对虾抗氧化功能及盐度骤变适应性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(14): 144-151. |
| [2] | 樊英, 王晓璐, 王友红, 刘洪军, 刁菁, 李乐, 王淑娴, 于晓清, 盖春蕾, 叶海斌, 许拉, 穆川川, 马星坤. 益生菌制剂和抗生素对凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)非特异性免疫及肠道微生物的影响比较[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(33): 138-146. |
| [3] | 代君君, 舒蕊, 刘健, 章玉萍, 张丽丽, 陈明, 赵萍, 刘震. 苯菌灵胁迫对蜜蜂肠道微生物菌群结构的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(26): 136-140. |
| [4] | 郑文涌, 杨涛, 李双全, 吕常旭, 石敏, 马立保, 晏向华. 新型酿酒酵母培养物对育肥猪生产性能、肌肉品质和肠道微生物的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(21): 145-154. |
| [5] | 黄永春,杨宏磊,张哲,黎中宝,郑伟刚,邓超准,陈辉辉,何晓雄,杨章武. 选育对虾形态性状对体质量的通径分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(11): 11-16. |
| [6] | 樊英,李乐,于晓清,刘恩孚,李天保,叶海斌. 免疫增强剂对仿刺参肠道微生物的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(2): 91-96. |
| [7] | 叶宁 陈文霞 申玉春 李再亮. 日粮水平对凡纳滨对虾生长、消化酶和免疫酶活力以及氮收支的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(20): 26-29. |
| [8] | 刘婷 李宗军 廖勇 邹晓卓 李华丽. 饲喂乳酸菌和茶多酚对肉鸡生长及生理生化的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(11): 6-10. |
| [9] | 鲁梅 许传田 胡北侠 张秀美 鲁清贵. 诺维康对肉鸡免疫器官和及血液中T淋巴细胞数量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(2): 57-59. |
| [10] | 许传田. 中药产品甙肽对猪高热病防治效果分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(22): 16-19. |
| [11] | 王兴强,曹 梅,马 甡,董双林,阎斌伦. 密度对凡纳滨对虾存活、生长和能量收支的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(8): 409-409. |
| [12] | 曹 梅,王兴强,阎斌伦. 密度和碳水化合物水平对凡纳滨对虾存活和生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(12): 435-435. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||