
中国农学通报 ›› 2020, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (30): 91-97.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0011
所属专题: 生物技术
曹德宸1,2( ), 叶磊1,2, 李维庆1,2, 李赛男1,2, 高冬妮1,2(
), 叶磊1,2, 李维庆1,2, 李赛男1,2, 高冬妮1,2( ), 葛菁萍1,2(
), 葛菁萍1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2019-04-16
修回日期:2020-05-24
出版日期:2020-10-25
发布日期:2020-10-16
通讯作者:
高冬妮,葛菁萍
作者简介:曹德宸,男,1994年出生,黑龙江牡丹江人,硕士研究生,研究方向:生物学。通信地址:150080 黑龙江省哈尔滨市南岗区学府路74号,Tel:0451-86609016,E-mail: 基金资助:
Cao Dechen1,2( ), Ye Lei1,2, Li Weiqing1,2, Li Sainan1,2, Gao Dongni1,2(
), Ye Lei1,2, Li Weiqing1,2, Li Sainan1,2, Gao Dongni1,2( ), Ge Jingping1,2(
), Ge Jingping1,2( )
)
Received:2019-04-16
Revised:2020-05-24
Online:2020-10-25
Published:2020-10-16
Contact:
Gao Dongni,Ge Jingping
摘要:
为了提高基因工程疫苗对新城疫病毒F蛋白的表达能力,从而为研制高效基因工程疫苗奠定了基础。利用Western blot技术检测含有不同启动子与表达元件的重组杆状病毒,在中国仓鼠卵巢细胞中其F蛋白的表达量的差异。Western blot结果显示,含有CMV立即早期增强子区与鸡肌动蛋白启动子区的复合启动子的质粒表达F蛋白量较含人巨细胞病毒立即早期启动子(CMV)的质粒提高了24.52%~231.18%,含有土拨鼠肝炎病毒转录后调控元件(WPRE)能够提高F蛋白表达量2.9~8.6倍,而腺伴随病毒末端反向重复序列(ITRs)对质粒F蛋白表达量提高1.95%~9.27%。CBA启动子的启动能力远高于CMV的启动能力,调控元件WPRE能够显著提高F蛋白的表达量,而ITRs元件对于F蛋白的表达量未产生显著提高。
中图分类号:
曹德宸, 叶磊, 李维庆, 李赛男, 高冬妮, 葛菁萍. 含有不同启动子、WPRE以及ITRs对重组杆状病毒表达新城疫F蛋白的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(30): 91-97.
Cao Dechen, Ye Lei, Li Weiqing, Li Sainan, Gao Dongni, Ge Jingping. Effects of Different Promoters, WPRE and ITRs on Recombinant Baculovirus Expression of Newcastle Disease F Protein[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(30): 91-97.
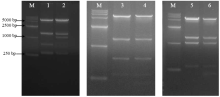
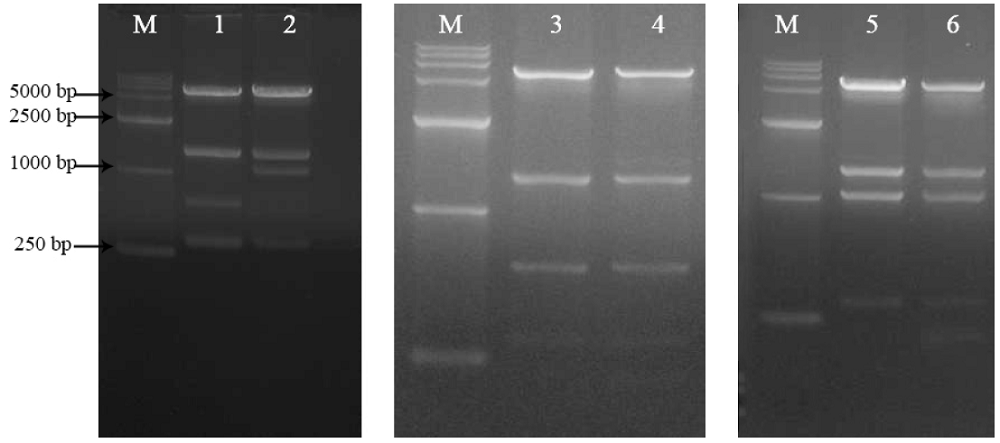
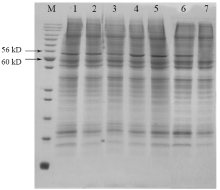
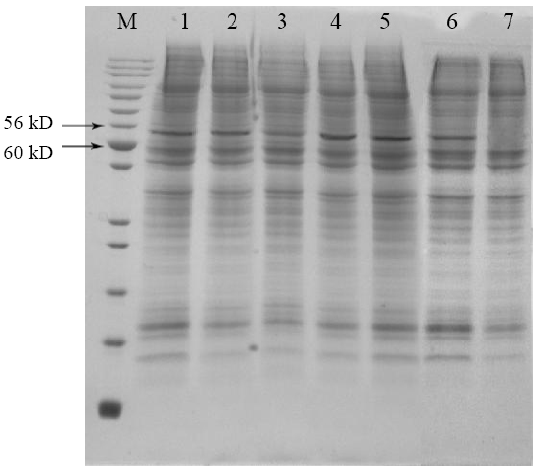
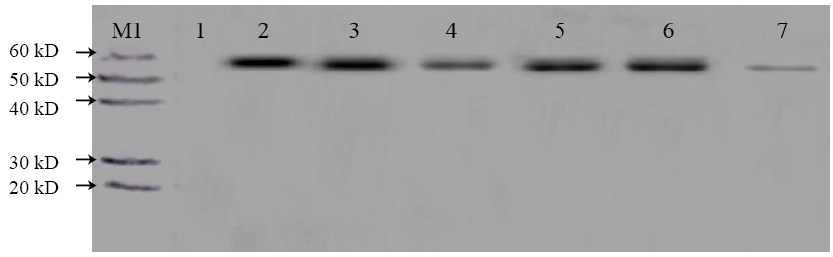
| 组一 | 分子量 | 强度 | 组二 | 分子量 | 强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 泳道2 vYL-SD | 57.48 | 1109.7 | 泳道5 vYL-LM | 55.661 | 831.52 |
| 泳道3 vYL-SD-ITRs | 56.563 | 1015.6 | 泳道6 vYL-LMI | 55.661 | 815.61 |
| 泳道4 vYL-SD(-) | 56.563 | 285.69 | 泳道7 vYL-LM(-) | 54.772 | 86.264 |
| 泳道1 空白细胞对照 | 0 | 0 |
| 组一 | 分子量 | 强度 | 组二 | 分子量 | 强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 泳道2 vYL-SD | 57.48 | 1109.7 | 泳道5 vYL-LM | 55.661 | 831.52 |
| 泳道3 vYL-SD-ITRs | 56.563 | 1015.6 | 泳道6 vYL-LMI | 55.661 | 815.61 |
| 泳道4 vYL-SD(-) | 56.563 | 285.69 | 泳道7 vYL-LM(-) | 54.772 | 86.264 |
| 泳道1 空白细胞对照 | 0 | 0 |
| [1] | B.W.卡尔尼克. 禽病学[M].第十版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1999: 691-726. |
| [2] | Pitt J J, Da Silva EGerman J J. Determination of the disulfide bond arrangement of Newcastle disease virus hemaggulutinon neuraminidase[J]. J Bio Chem, 2000,275(9):6469-6478. |
| [3] |
Palmieri S, Michael L P. An alternative method of oligonucleotide finger printing for resulting Newcastle disease virus specific RNA fragments[J]. Avian Disease, 1988,33:345-350.
doi: 10.2307/1590854 URL |
| [4] |
Peeters B P, De Leeuwenhoek O S, Koch G. Rescue of Newcastle disease virus from cloned cDNA: evidence that cleavability of the fusion protein is a major determinant for virulence[J]. J Virol, 1999,73(6):5001-5009.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.5001-5009.1999 URL pmid: 10233962 |
| [5] | 田夫林, 陈静, 马惠玲, 等. 10株新城疫病毒分离F基因的克隆及遗传变异分析[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2004(01):31-34. |
| [6] |
Leilei D, Pucheng C, Xingzhi B, et al. Recombinant duck enteritis viruses expressing the Newcastle disease virus (NDV) F gene protects chickens from lethal NDV challenge[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2019,232:146-150.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.04.022 URL pmid: 31030839 |
| [7] | 刘长梅. 新城疫病毒的研究现状[J]. 山东家禽, 2002(3):22-24. |
| [8] |
Ding L, Chen P, Bao X. Recombinant duck enteritis viruses expressing the Newcastle disease virus (NDV) F gene protects chickens from lethal NDV challenge[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2019,232:146-150.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.04.022 URL pmid: 31030839 |
| [9] | 谢青梅, 封柯宇, 沈勇. 动物病毒重组活载体疫苗研究进展[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019(5). |
| [10] |
Ebadat S, Ahmadi S, Ahmadi M, et al. Evaluating the efficiency of CHEF and CMV promoter with IRES and Furin/2A linker sequences for monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells[J]. Plos One, 2017,12(10):e0185967.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185967 URL pmid: 29023479 |
| [11] |
James G. Ackford, Juan C. Corredor, Yanlong Pei a. et al. Foreign gene expression and induction of antibody response by recombinant fowl adenovirus-9-based vectors with exogenous promoters[J]. Vaccine, 2017,35(37):4974-4982.
URL pmid: 28780115 |
| [12] | Makrides S C. Components of vectors for gene transfer and expression in mammalian cells[J]. Protein ExprPurif, 1999,(17):183-202. |
| [13] |
Powell S K, Rivera-Soto R, Gray S J. Viral Expression Cassette Elements to Enhance Transgene Target Specificity and Expression in Gene Therapy[J]. Discovery medicine, 2015,19(102):49-57.
URL pmid: 25636961 |
| [14] | 高冬妮, 平文祥, 金丽颖, 等. 以具有WPRE调控元件的杆状病毒为载体在鸡胚原代细胞中表达新城疫病毒F基因[J]. 微生物学报, 2014,54(4):455-462. |
| [15] |
Lizheng W, Zixuan W, Fangfang Z, et al. Enhancing Transgene Expression from Recombinant AAV8 Vectors in Different Tissues Using Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Post-Transcriptional Regulatory Element[J]. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 2016,13(4):286-291.
URL pmid: 27076785 |
| [16] |
Savy A, Dickx Y, Nauwynck L. Impact of Inverted Terminal Repeat Integrity on rAAV8 Production Using the Baculovirus/Sf9 Cells System[J]. Human gene therapy methods, 2017.
doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2018.211 URL pmid: 30727774 |
| [17] |
Want C Y, Li F, Yang Y. Recombinant baculoviruses containing the Diphtheria toxin a gene for malignant glioma therapy[J]. Cancer Research, 2006,66:5798-5806.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4514 URL pmid: 16740719 |
| [18] | 高冬妮, 金丽颖, 葛菁萍, 等. EF1α启动的高效重组杆状病毒载体的构建及其表达效果[J]. 微生物学报, 2014(6). |
| [19] |
Zhou Q, Tian W, Liu C, et al. Deletion of the B-B’ and C-C’ regions of inverted terminal repeats reduces rAAV productivity but increases transgene expression[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017,7(1):5432.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04054-4 URL pmid: 28710345 |
| [20] |
Bello M B, Yusoff K, Ideris A, et al. Diagnostic and Vaccination Approaches for Newcastle Disease Virus in Poultry: The Current and Emerging Perspectives[J]. Biomed Res Int., 2018,2018:7278459.
doi: 10.1155/2018/7278459 URL pmid: 30175140 |
| [21] |
Absalón A E, Cortés-Espinosa D V, Lucio E, et al. Epidemiology, control, and prevention of Newcastle disease in endemic regions: Latin America[J]. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2019,51(5):1033-1048.
doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-01843-z URL pmid: 30877525 |
| [22] |
Firouzamandi M, Moeini H, Hosseini D, et al. Improved immunogenicity of Newcastle disease virus fusion protein genes[J]. Journal of Veterinary Science, 2016,17(1):21-26.
doi: 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.1.21 URL pmid: 27051336 |
| [23] |
Das A T, Tenenbaum L, Berkhout B. Tet-On Systems For Doxycycline-inducible Gene Expression[J]. Curr Gene Ther., 2016,16(3):156-67.
doi: 10.2174/1566523216666160524144041 URL pmid: 27216914 |
| [24] |
Chen B D, He C H, Chen X C, et al. Targeting transgene to the heart and liver with AAV9 by different promoters[J]. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 2015,42(10):1108-1117.
URL pmid: 26173818 |
| [25] |
Zufferey R, Donello J E, Trono D, et al. Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Posttranscriptional Regulatory Element Enhances Expression of Transgenes Delivered by Retroviral Vectors[J]. Journal of Virology, 1999,73(4):2886-2892.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.2886-2892.1999 URL pmid: 10074136 |
| [26] | Hu Y C. Baculoviral Vectors for Gene Delivery: A Review. Current Gene Therapy, 2008(8):54-65. |
| [27] |
Wang C Y, Li F, Yang Y, et al. Recombinant baculovirus containing the Diphtheria toxin a gene for malignant glioma therapy[J]. Cancer Research, 2006,66:5798-5806.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4514 URL pmid: 16740719 |
| [1] | 王贝贝,宋丽丽,马德慧,毛景东,王学理. 中药鱼腥草注射液鸡胚接种抗新城疫病毒的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(2): 95-97. |
| [2] | 于 航,高冬妮,田兆峰,平文祥,葛菁萍. 不同启动子对HA-VP2重组杆状病毒蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(23): 100-105. |
| [3] | 葛菁萍,白程乐,高冬妮,申 艳,于 航,平文祥. 鸡IL-2重组杆状病毒的构建及其病理组织学研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(21): 142-148. |
| [4] | 刘 颖,金丽颖,申 燕,高冬妮,平文祥,葛菁萍. 新城疫病毒La Sota株HN基因的克隆与序列分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(14): 89-95. |
| [5] | 安琦 申燕 原韬 刘颖 金丽颖 高冬妮 葛菁萍 平文祥. 鸡新城疫病毒F基因的克隆及序列分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(26): 11-16. |
| [6] | 唐晓艳 高冬妮 李梅 葛菁萍 平文祥 楼庄伟. 昆虫细胞中表达eGFP基因的重组杆状病毒的构建[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(8): 26-30. |
| [7] | 王立新,路振香,王金虎,王珊珊,胡静,戴四发. 新城疫病毒诱导黄粉虫抗病毒肽的效果分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(6): 37-39. |
| [8] | 王学兵,张红英,徐端红,崔保安,程晓静,李 欣,马 姣. 几种中药在鸡胚上对鸡常见病毒的作用效果试验[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(13): 5-9. |
| [9] | 崔斓斓. 麻杏石甘汤中抗新城疫病毒有效成分的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(10): 35-38. |
| [10] | 詹爱军 王新卫 谭婉明 马静云 毕英佐 于康振 曹永长. H9N2亚型AIV HA基因的克隆及其在昆虫细胞中的表达[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(1): 18-22. |
| [11] | 许信刚,张 琦,邢福珊,张耀相. Development and Application of a Diagnostic Kit for Detecting NDV[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(4): 30-30. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||