
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 148-157.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0110
王鹏翔( ), 陈翔宇, 魏春月, 马怡茹, 秦诗哲, 周泽轩, 张泽(
), 陈翔宇, 魏春月, 马怡茹, 秦诗哲, 周泽轩, 张泽( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-20
修回日期:2023-12-11
出版日期:2024-02-05
发布日期:2024-01-29
通讯作者:
作者简介:王鹏翔,男,1998年出生,新疆石河子人,硕士在读,研究方向为农业信息化。通信地址:832003 新疆石河子市北五路石河子大学北苑新区 石河子大学农学院,E-mail:17690591268@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Pengxiang( ), CHEN Xiangyu, WEI Chunyue, MA Yiru, QIN Shizhe, ZHOU Zexuan, ZHANG Ze(
), CHEN Xiangyu, WEI Chunyue, MA Yiru, QIN Shizhe, ZHOU Zexuan, ZHANG Ze( )
)
Received:2023-02-20
Revised:2023-12-11
Published-:2024-02-05
Online:2024-01-29
摘要:
地上部氮浓度是准确诊断作物氮素丰缺进而评价其生长状况的重要指标。通过构建基于高光谱的滴灌棉花地上部氮浓度估测模型,实现棉花氮素含量的实时、无损、精确获取,为精准施肥提供理论依据和技术支撑。以新疆北部主栽棉花‘新陆早45号’和‘新陆早53号’为供试品种,设置6个施纯氮处理(0、120、240、348、360、480 kg/hm2),测量棉花冠层高光谱信息,利用函数变换去除冗余,一阶与二阶导数筛选结果相似,倒数的对数筛选结果较为分散。采用机器学习权重排序进行特征筛选,共选出359、371、751、752、746、739、755 nm等7个特征波段。同时遍历波长组合,优化前人研究与氮素高相关的植被指数,共选出RVI′810,460、NDVI′811,856、NDVI′750,705、RVI′740,720、RVI′851,852、DVI′359,360、NDVI′851,852等7个光谱指数。将筛选得到的特征波段与植被指数分别利用岭回归、决策树、引导聚类、增强学习算法与棉花氮素建立养分估测模型,最终Adaboost迭代算法所建立滴灌棉花地上部氮浓度估测模型效果最优,模型精度R2达到0.911,RMSE为1.362。利用光谱信息可以有效反演棉花氮营养状态,基于植被指数构建的模型估测精度较特征波段更为稳定;对现有的植被指数特征波段进行优化,可以有效提升模型的估测精度;对比分析不同建模方式下模型精度,集成学习相比单机器学习在进行棉花氮营养估测时更有优势。
王鹏翔, 陈翔宇, 魏春月, 马怡茹, 秦诗哲, 周泽轩, 张泽. 基于机器学习算法的滴灌棉花地上部氮浓度估测模型研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(4): 148-157.
WANG Pengxiang, CHEN Xiangyu, WEI Chunyue, MA Yiru, QIN Shizhe, ZHOU Zexuan, ZHANG Ze. Research on Estimation Model of Aboveground Nitrogen Concentration in Drip Irrigation Cotton Based on Machine Learning Algorithm[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(4): 148-157.
| 植被指数 | 计算公式 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 简单比值植被指数 | R800/R680 | [ |
| 归一化植被指数 | (R690-R670)/(R690+R670) | [ |
| 优化归一化植被指数 | (R755-R711)/(R755+R711) | [ |
| 拔节比值植被指数 | R810/R460 | [ |
| 优化比值指数 | R761/R673 | [ |
| 优化比值植被指数 | R950/R710 | [ |
| 优化比值植被指数 | R950/R560 | [ |
| 绿色比值植被指数 | R786/R560 | [ |
| 优化归一化植被指数 | (R811-R856)/(R811+R856) | [ |
| 优化比值植被指数 | R895/R700 | [ |
| 红边归一化指数 | (R750-R705)/(R750+R705) | [ |
| Vogelmann红边指数 | R740/R720 | [ |
| 光化学反射指数 | (R531-R570)/(R531+R570) | [ |
| 植被指数 | 计算公式 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 简单比值植被指数 | R800/R680 | [ |
| 归一化植被指数 | (R690-R670)/(R690+R670) | [ |
| 优化归一化植被指数 | (R755-R711)/(R755+R711) | [ |
| 拔节比值植被指数 | R810/R460 | [ |
| 优化比值指数 | R761/R673 | [ |
| 优化比值植被指数 | R950/R710 | [ |
| 优化比值植被指数 | R950/R560 | [ |
| 绿色比值植被指数 | R786/R560 | [ |
| 优化归一化植被指数 | (R811-R856)/(R811+R856) | [ |
| 优化比值植被指数 | R895/R700 | [ |
| 红边归一化指数 | (R750-R705)/(R750+R705) | [ |
| Vogelmann红边指数 | R740/R720 | [ |
| 光化学反射指数 | (R531-R570)/(R531+R570) | [ |
| 方法 | 波长/nm | 相关性绝对值 |
|---|---|---|
| 一阶导数 | 359 | 0.675 |
| 二阶导数 | 371 | 0.653 |
| 倒数对数 | 752 | 0.551 |
| 仅平滑处理 | 751 | 0.548 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值1) | 739 | 0.545 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值2) | 746 | 0.549 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值3) | 751 | 0.556 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值4) | 755 | 0.561 |
| 方法 | 波长/nm | 相关性绝对值 |
|---|---|---|
| 一阶导数 | 359 | 0.675 |
| 二阶导数 | 371 | 0.653 |
| 倒数对数 | 752 | 0.551 |
| 仅平滑处理 | 751 | 0.548 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值1) | 739 | 0.545 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值2) | 746 | 0.549 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值3) | 751 | 0.556 |
| 根据重要性权重选择特征(阈值4) | 755 | 0.561 |
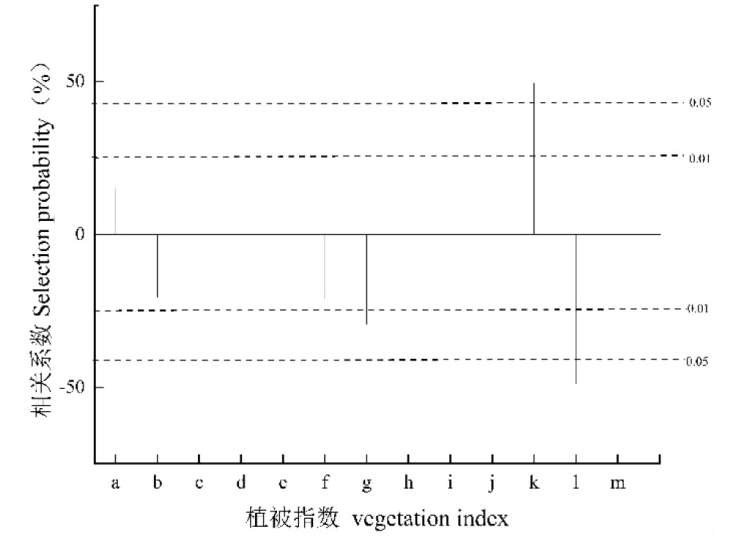
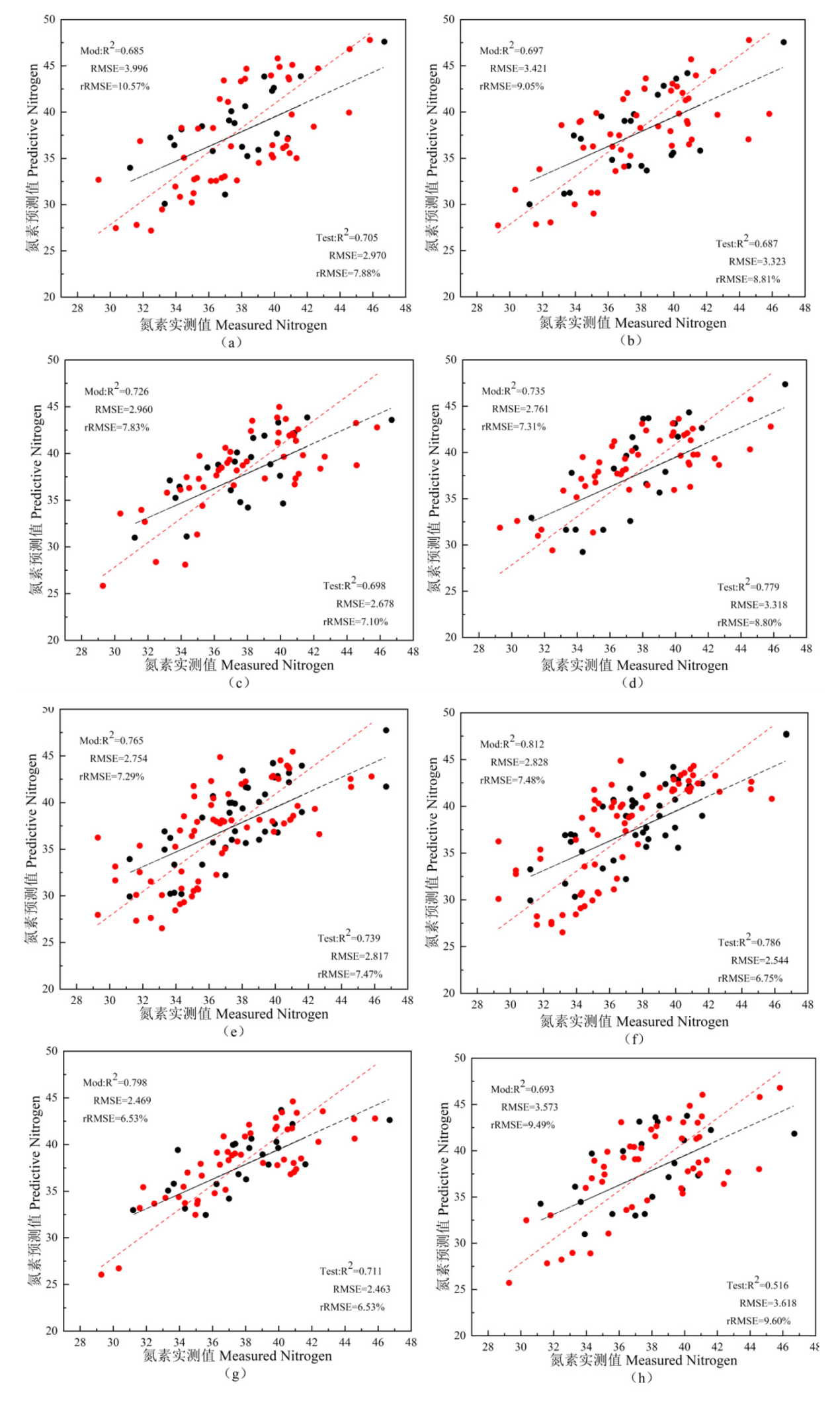
| [1] |
吴剑飞. 高光谱波段筛选技术在小麦含水率反演中的应用[J]. 南方农机, 2022, 53(8):23-27.
|
| [2] |
陈兵, 王方永, 韩焕勇, 等. 基于光谱红边参数的棉花黄萎病叶片氮素含量诊断研究[J]. 棉花学报, 2013, 25(3):254-261.
doi: 10.11963/cs130310 |
| [3] |
张文旭, 佟炫梦, 周天航, 等. 基于高光谱成像的棉花叶片氮素含量遥感估测[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2021, 52(5):586-596.
|
| [4] |
陈鹏飞, 梁飞. 基于低空无人机影像光谱和纹理特征的棉花氮素营养诊断研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(13):2220-2229.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.13.003 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.3390/rs11232838 URL |
| [6] |
doi: 10.3390/agronomy12061319 URL |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1007/s11119-019-09670-w |
| [9] |
马春艳, 王艺琳, 翟丽婷, 等. 冬小麦不同叶位叶片的叶绿素含量高光谱估算模型[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(16):217-225,358.
|
| [10] |
于丰华, 邢思敏, 郭忠辉, 等. 基于特征转移植被指数的水稻叶片氮素含量定量估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(2):175-182.
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1007/s11104-013-1937-0 URL |
| [12] |
孙小芳. 高光谱植被指数与水稻叶片叶绿素相关分析[J]. 闽江学院学报, 2013, 34(2):124-127.
|
| [13] |
赵佳佳, 冯美臣, 王超, 等. 基于光谱植被指数的冬小麦叶绿素含量反演[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(2):391-396.
|
| [14] |
赵明家. 东北春玉米冠层光谱特征与氮营养诊断依据的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2015.
|
| [15] |
田永超, 曹卫星, 姜东, 等. 不同水氮条件下水稻冠层反射光谱与植株含水率的定量关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(2):318-323.
|
| [16] |
黄春燕, 王登伟, 陈冠文, 等. 基于高光谱植被指数的棉花干物质积累估算模型研究[J]. 棉花学报, 2006, 18(2):115-119.
|
| [17] |
田永超, 朱艳, 曹卫星. 用冠层反射光谱预测小麦叶片糖氮量及糖氮比[J]. 作物学报, 2005(3):355-360.
|
| [18] |
杨玮, 孙红, 郑立华, 等. 冬枣光谱数据的灰色关联分析及叶片氮素含量预测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(11):3083-3087.
|
| [19] |
王巧男, 叶旭君, 李金梦, 等. 基于双波段植被指数(TBVI)的柑橘冠层含氮量预测及可视化研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(3):715-718.
|
| [20] |
王树文, 赵珊, 张长利, 等. 基于成像光谱技术的寒地玉米苗期冠层氮含量预测模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(13):149-154.
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00113-9 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.2135/cropsci2019.04.0227 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100369 URL |
| [24] |
pmid: 17711295 |
| [25] |
郭松, 常庆瑞, 张佑铭, 等. 连续投影与SSA-ELM结合的玉米氮平衡指数高光谱估测[J]. 西北农业学报, 2023, 32(1):130-138.
|
| [26] |
郭松, 常庆瑞, 崔小涛, 等. 基于光谱变换与SPA-SVR的玉米SPAD值高光谱估测[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(8):79-88.
|
| [27] |
张志勇, 樊泽华, 张娟娟, 等. 小麦籽粒蛋白质含量高光谱遥感预测模型比较[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2022, 56(2):188-198.
|
| [28] |
热依拉·艾合买提, 吾木提·艾山江, 阿不都艾尼·阿不里, 等. 基于机器学习的春小麦叶片水分含量高光谱估算[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(5):640-648.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
陈志超, 蒋贵印, 张正, 等. 基于无人机高光谱遥感的春玉米氮营养指数反演[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(3):81-89.
|
| [1] | 朱生翠, 李国婷, 魏永林, 马扶林, 金显玲, 曹迎敏. 青海湖北岸天然牧草产量预测模型研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(25): 109-115. |
| [2] | 孙博, 李靖, 王静. 机器学习在植物工厂中的研究现状与挑战[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(18): 142-150. |
| [3] | 陈桂良, 刘忠妹, 许木果, 黎小清, 丁华平, 杨春霞. 云南山地胶园土壤有机质高光谱估算[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(13): 87-94. |
| [4] | 马元花, 印彩霞, 王红玉, 刘宇轩, 刘前通, 张泽. 基于高光谱的棉花叶片磷含量估测模型[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 123-132. |
| [5] | 胡馨月, 孙倩, 古丽古丽·灭迪力哈孜. 新疆布尔津县五年间归一化植被指数时空演变[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(32): 6-11. |
| [6] | 周翔, 兴旺, 杨军, 孙来军, 王录红, 周婉婷, 王雪倩, 李思琪, 汪曼. 甜菜种子活力的测定——基于近红外高光谱技术[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(29): 7-12. |
| [7] | 纪树志. 极旱荒漠区湿地植被动态变化监测——以甘肃敦煌阳关国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(26): 105-109. |
| [8] | 吕小艳, 薛琳, 竞霞, 张超, 徐海清, 朱启法. 基于高光谱分数阶微分的烟叶SPAD值估测[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(24): 54-59. |
| [9] | 赵占辉, 张丛志, 张佳宝, 吴运金, 张宏敏, 鲁春阳. 基于回归分析的玉米冠层叶绿素含量高光谱反演分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(20): 7-16. |
| [10] | 王军, 姜芸. 基于无人机多光谱遥感的大豆叶面积指数反演[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(19): 134-142. |
| [11] | 姜蓝齐, 王萍, 姜丽霞, 宫丽娟, 于成龙, 李秀芬. 基于多时相MODIS数据监测水、旱作物种植面积及空间分布[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(16): 108-118. |
| [12] | 阳灵燕, 张红燕, 陈玉峰, 刘亚文. 机器学习在农作物品种识别中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(30): 158-164. |
| [13] | 杨红云, 罗建军, 万颖, 孙爱珍. 计算机视觉技术在水稻氮素营养诊断中应用的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(16): 149-155. |
| [14] | 翟浩然, 李西灿, 钟浩, 周钰. 耕层土壤含水量间接光谱估测模型[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(11): 86-91. |
| [15] | 刘佳,邵杰,王利民,杨福刚,杨玲波. 基于高光谱微分指数监测春玉米大斑病的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(6): 143-150. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||