
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (18): 125-134.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0573
黄勋1( ), 丰加文2, 何文睿2, 徐亚锦1, 邓琳梅1, 周昆燕1, 张潇方1, 杨艳丽1, 刘霞1(
), 丰加文2, 何文睿2, 徐亚锦1, 邓琳梅1, 周昆燕1, 张潇方1, 杨艳丽1, 刘霞1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-10
修回日期:2023-11-16
出版日期:2024-06-25
发布日期:2024-06-18
通讯作者:
作者简介:黄勋,男,1992年出生,云南玉溪人,博士研究生,研究方向:马铃薯土传病害。通信地址:650201 云南省昆明市盘龙区黑龙潭金黑公路95号 植物保护学院,E-mail:1214278318@qq.com。
基金资助:
HUANG Xun1( ), FENG Jiawen2, HE Wenrui2, XU Yajin1, DENG Linmei1, ZHOU Kunyan1, ZHANG Xiaofang1, YANG Yanli1, LIU Xia1(
), FENG Jiawen2, HE Wenrui2, XU Yajin1, DENG Linmei1, ZHOU Kunyan1, ZHANG Xiaofang1, YANG Yanli1, LIU Xia1( )
)
Received:2023-08-10
Revised:2023-11-16
Published:2024-06-25
Online:2024-06-18
摘要:
本研究旨在鉴定微型薯连作基质中疮痂病原菌的种类,筛选具有良好抑制活性的有机酸以利于控制疮痂病发生。研究从病薯上分离纯化病原菌,用薯片法、萝卜片法及温室盆栽接种法检测其致病性,结合形态学观察、生理生化特性测定及16S rRNA基因序列分析确定种类,对其耐盐性等生物学特性进行研究,用纸碟法测定甲酸等有机酸对疮痂链霉菌生长的影响。链霉菌19311具有致病性,其致病岛毒力相关基因型为txtAB+/tomA+/necI+,根据19311菌株培养特征、生理生化特性及16S rRNA序列分析结果鉴定为酸性疮痂链霉菌(Streptomyces acidiscabies)。甲酸、乙酸、丙酸、乳酸、柠檬酸、酒石酸可显著抑制S. acidiscabies的生长,甲酸抑菌效果最佳,抑菌圈直径为45.43 mm,抑菌最低有效浓度为1%,可通过增加细胞膜通透性抑制S. acidiscabies生长。综上所述,本研究明确了微型薯生产基质中疮痂链霉菌19311的种类及其生物学特性。未来可考虑使用1%甲酸进行疮痂病的控制试验,并评估其对原原种生产的潜在影响。
黄勋, 丰加文, 何文睿, 徐亚锦, 邓琳梅, 周昆燕, 张潇方, 杨艳丽, 刘霞. 马铃薯疮痂病菌Streptomyces acidiscabies鉴定及抑菌有机酸筛选[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 125-134.
HUANG Xun, FENG Jiawen, HE Wenrui, XU Yajin, DENG Linmei, ZHOU Kunyan, ZHANG Xiaofang, YANG Yanli, LIU Xia. Streptomyces acidiscabies: Identification and Screening of Antibacterial Organic Acids[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(18): 125-134.
| 试验类型 | 项目名称 | 试验现象 | Streptomyces strain 19311 | S. acidiscabies strain 44#[ | S. acidiscabies strain CPS-3[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糖酵解 | 葡萄糖 | 培养基变为黄色,无气泡 | + | / | / |
| 乳糖 | 培养基仍为紫色,无气泡 | - | / | / | |
| 大分子物质的 水解 | 淀粉水解 | 培养基平板颜色为紫色 | + | + | / |
| 明胶液化 | 培养基为液态 | + | + | / | |
| 牛奶石蕊 | 凝固胨化 | + | / | / | |
| 脲酶试验 | 试管颜色为红色 | + | / | / | |
| H2S产生 | 培养基中无黑色物质产生 | - | - | - | |
| IMViC试验 | 甲基红试验 | 试管颜色为红色 | + | / | / |
| VP试验 | 试管颜色为橘黄色 | - | / | / | |
| 柠檬酸盐利用 | 培养基颜色仍为黄绿色 | - | / | / | |
| 吲哚试验 | 加入吲哚试剂为黄色 | - | / | / |
| 试验类型 | 项目名称 | 试验现象 | Streptomyces strain 19311 | S. acidiscabies strain 44#[ | S. acidiscabies strain CPS-3[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糖酵解 | 葡萄糖 | 培养基变为黄色,无气泡 | + | / | / |
| 乳糖 | 培养基仍为紫色,无气泡 | - | / | / | |
| 大分子物质的 水解 | 淀粉水解 | 培养基平板颜色为紫色 | + | + | / |
| 明胶液化 | 培养基为液态 | + | + | / | |
| 牛奶石蕊 | 凝固胨化 | + | / | / | |
| 脲酶试验 | 试管颜色为红色 | + | / | / | |
| H2S产生 | 培养基中无黑色物质产生 | - | - | - | |
| IMViC试验 | 甲基红试验 | 试管颜色为红色 | + | / | / |
| VP试验 | 试管颜色为橘黄色 | - | / | / | |
| 柠檬酸盐利用 | 培养基颜色仍为黄绿色 | - | / | / | |
| 吲哚试验 | 加入吲哚试剂为黄色 | - | / | / |
| 项目 | 0 mm | 18 mm | 50 mm | 78 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 菌落生长面积/mm2 | 6062.15±155.42 a | 5971.94±241.38 a | 6004.53±96.66 a | 6172.56±212.28 a |
| 菌悬液浓度/OD600 | 0.248±0.015 d | 0.377±0.012 c | 0.638±0.016 b | 0.850±0.010 a |
| 项目 | 0 mm | 18 mm | 50 mm | 78 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 菌落生长面积/mm2 | 6062.15±155.42 a | 5971.94±241.38 a | 6004.53±96.66 a | 6172.56±212.28 a |
| 菌悬液浓度/OD600 | 0.248±0.015 d | 0.377±0.012 c | 0.638±0.016 b | 0.850±0.010 a |
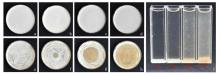

| 处理 | 抑菌圈直径/mm | 处理 | 抑菌圈直径/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空白对照 | 0.00±0.00 d | 丙酸 | 38.34±3.42 b |
| 纸片对照 | 0.00±0.00 d | 乳酸 | 30.19±1.34 c |
| 甲酸 | 45.43±0.66 a | 柠檬酸 | 39.93±0.88 b |
| 乙酸 | 40.50±0.74 b | 酒石酸 | 40.30±1.64 b |
| 处理 | 抑菌圈直径/mm | 处理 | 抑菌圈直径/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空白对照 | 0.00±0.00 d | 丙酸 | 38.34±3.42 b |
| 纸片对照 | 0.00±0.00 d | 乳酸 | 30.19±1.34 c |
| 甲酸 | 45.43±0.66 a | 柠檬酸 | 39.93±0.88 b |
| 乙酸 | 40.50±0.74 b | 酒石酸 | 40.30±1.64 b |
| 有机酸种类 | 抑菌圈直径/mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 1% | 2.5% | 5% | 10% | 20% | |
| 甲酸 | 0.00±0.00 f | 29.22±0.30 e | 34.92±0.64 d | 45.43±0.66 c | 60.42±1.34 b | 71.44±0.78 a |
| 乙酸 | 0.00±0.00 f | 23.21±0.38 e | 31.09±0.73 d | 43.22±0.79 c | 52.43±1.12 b | 62.04±0.79 a |
| 有机酸种类 | 抑菌圈直径/mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 1% | 2.5% | 5% | 10% | 20% | |
| 甲酸 | 0.00±0.00 f | 29.22±0.30 e | 34.92±0.64 d | 45.43±0.66 c | 60.42±1.34 b | 71.44±0.78 a |
| 乙酸 | 0.00±0.00 f | 23.21±0.38 e | 31.09±0.73 d | 43.22±0.79 c | 52.43±1.12 b | 62.04±0.79 a |
| 处理 | 电导率/(ms/cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | |
| 水 | 0.296±0.006 a | 0.289±0.003 a | 0.287±0.002 a | 0.286±0.004 a |
| CK | 3.609±0.025 a | 3.621±0.037 a | 3.591±0.034 a | 3.625±0.031 a |
| 5%甲酸 | 5.068±0.470 b | 6.506±0.732 a | 7.102±0.341 a | 7.423±0.176 a |
| 水 | 0.286±0.003 a | 0.284±0.004 a | 0.283±0.003 a | 0.286±0.001 a |
| CK | 3.693±0.020 a | 3.696±0.064 a | 3.675±0.008 a | 3.669±0.082 a |
| 5%乙酸 | 3.906±0.074 b | 4.099±0.027 a | 4.075±0.039 a | 4.065±0.034 a |
| 处理 | 电导率/(ms/cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | |
| 水 | 0.296±0.006 a | 0.289±0.003 a | 0.287±0.002 a | 0.286±0.004 a |
| CK | 3.609±0.025 a | 3.621±0.037 a | 3.591±0.034 a | 3.625±0.031 a |
| 5%甲酸 | 5.068±0.470 b | 6.506±0.732 a | 7.102±0.341 a | 7.423±0.176 a |
| 水 | 0.286±0.003 a | 0.284±0.004 a | 0.283±0.003 a | 0.286±0.001 a |
| CK | 3.693±0.020 a | 3.696±0.064 a | 3.675±0.008 a | 3.669±0.082 a |
| 5%乙酸 | 3.906±0.074 b | 4.099±0.027 a | 4.075±0.039 a | 4.065±0.034 a |
| [1] |
杨艳丽, 刘霞. 马铃薯病害[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2019:54-59.
|
| [2] |
邱雪迎, 马丹丹, 赵伟全, 等. 微型薯蛭石基质中疮痂病原鉴定及菌药协同防治探索[J]. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(3):83-89.
|
| [3] |
贾云, 何江, 张静, 等. 不同药剂温室消毒对马铃薯微型薯疮痂病的防效试验[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25(17):73-75.
|
| [4] |
张建平, 尹玉和, 闫任沛, 等. 内蒙古马铃薯疮痂病发生与防治途径[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2013, 27(1):56-59.
|
| [5] |
张军, 田子罡, 王建华, 等. 有机酸抑菌分子机理研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2011, 42(3):323-328.
|
| [6] |
田家顺, 温弟如, 刘倩, 等. 苯甲酸对植物病原菌的离体抗菌活性研究[J]. 农药科学与管理, 2011, 32(5):26-31.
|
| [7] |
郭培钧, 何衍彪, 詹儒林, 等. 肉桂活性成分对芒果炭疽菌及香蕉枯萎病菌的抑制作用[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2009, 30(4):36-39.
|
| [8] |
王勇, 孙扬, 周明霞, 等. 14种小分子有机酸的抑菌活性筛选[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2018, 41(4):22-28.
doi: 10.13320/j. Cnki. Jauh. 2018.0073 |
| [9] |
孟秀梅, 吴杰, 李明华. 苯乳酸对黄曲霉抑菌活性及其作用机制初步研究[J]. 食品科技, 2022, 47(5):317-322.
|
| [10] |
王志新, 韩烁培, 王雨, 等. 植物乳杆菌的筛选、鉴定及其抑菌物质研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(9):133-139,146.
|
| [11] |
张晓旭, 刘欢, 肖苗, 等. 益生菌代谢产物对病原菌的抑菌作用研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2023, 49(8):297-302.
doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.032474 |
| [12] |
张丹丹, 姜修婷. 乌梅有机酸的提取工艺及其抑菌活性[J]. 生物加工过程, 2018, 16(3):47-52.
|
| [13] |
隆林芳, 张富龙, 唐冉, 等. 五味子有机酸对植物病原真菌的抑菌作用[J]. 农药, 2023, 62(5):369-373.
|
| [14] |
张海颖, 郭凤柳, 许华民, 等. 河北省张北地区马铃薯疮痂病的病菌鉴定[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(10):131-134.
|
| [15] |
康蓉, 王生荣. 甘肃马铃薯疮痂病病原初步鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2013, 39(3):78-82.
|
| [16] |
邢莹莹, 吕典秋, 魏琪, 等. 黑龙江省部分地区马铃薯疮痂病菌种类及致病性鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42(1):26-32,50.
|
| [17] |
关统伟, 张小平. 放线菌系统分类技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2016.
|
| [18] |
单文荣, 李俊霞, 刘花粉. 滤纸片法筛选不同活性物对棉花黄萎病菌抑制效果研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(19):285-289.
|
| [19] |
赵伟靖. 内蒙古地区马铃薯疮痂病病原菌的多样性及主要致病类型研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018.
|
| [20] |
赵伟全, 杨文香, 李亚宁, 等. 中国马铃薯疮痂病菌的鉴定[J]. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(2):313-318.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
张萌, 刘伯, 于秀梅, 等. 中国马铃薯疮痂病菌生物学特性分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(12):2603-2610.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.12.028 |
| [23] |
张铉哲, 赵雪, 陈苏慧, 等. 黑龙江省马铃薯疮痂病菌种群结构及PAI致病基因分析[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2022(5):53-59.
|
| [24] |
杨梦平, 王瑞仙, 杜魏甫, 等. 云南省马铃薯疮痂病致病链霉菌种类组成研究[J]. 植物病理学报, 2018, 48(4):445-454.
|
| [25] |
杜娟, 任娟, 赵思峰, 等. 新疆马铃薯疮痂病病原的鉴定[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 28(4):414-417.
|
| [26] |
黄勋, 杨艳丽, 刘霞, 等. 一种用于链霉菌扩繁试验的培养皿[P]. 中国专利,202120523410.X.2021-11-16.
|
| [27] |
李成良, 周安国, 王之盛. 有机酸的抗菌效应及其机制的研究进展[J]. 饲料工业, 2006, 27(11):35-41.
|
| [1] | 薛彤彤, 谢萌蒙, 孙辉, 李冲伟. 外源添加苯甲酸对紫苏种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(7): 72-77. |
| [2] | 姚泽, 姜生秀, 严子柱, 王祺, 马新兵. 干旱半干旱区不同中华钙果品种的生理及营养特性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(7): 44-48. |
| [3] | 张新新, 黄雍, 陈景益, 邹宏达, 罗忠霞, 王章英, 黄立飞. 甘薯疮痂病菌的生物学特性和产孢方法研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(3): 112-119. |
| [4] | 罗燕春, 赵鑫鑫, 盘欢, 廖琦, 俞奔驰, 劳赏业, 范锡恩, 刘翠娟, 李荣云, 曾新华, 付海天. 9个不同使用类型木薯品系在合浦县的适应性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 31-37. |
| [5] | 施贵芝, 丰加文, 徐亚锦, 林知许, 刘霞. 云南马铃薯不同品种(系)对马铃薯疮痂病的抗性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(15): 137-142. |
| [6] | 梁静, 伍兴隆, 杨晓东, 孙雨, 赵宇, 杨清川, 任洁, 肖海兵, 杨明禄. 槐豆木虱形态特征及生物学特性的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(14): 112-118. |
| [7] | 王梦园, 杜延全, 闫加力, 汪丹, 张阳阳, 朱建强. 一株草莓根腐病病原菌的鉴定及生物学特性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(13): 113-120. |
| [8] | 孙妍, 赵红盈, 石春玲, 李玉泉, 梁新宇, 黄颖, 韩爽. 农药增效剂对5种杀虫剂物理性质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(11): 121-126. |
| [9] | 郑童童, 王宁, 李进, 荣华, 雷斌, 郭庆元. 小麦镰刀菌叶枯病病原鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(8): 90-98. |
| [10] | 吕怡颖, 蔡永占, 白涛, 韩小女, 刘冬梅, 李祝安, 王瑞宝, 陈小龙, 王启宇, 林登智, 余磊, 黄飞燕. 曲靖市烟草黑胫病菌生物学特性及室内毒力测定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(7): 102-110. |
| [11] | 尹明华, 江玲, 姚慧婷, 宋粤涛, 王梦晴, 王沛棋, 张艺欣. 江西铅山红芽芋芋病毒种类lncRNA测序鉴定及其序列分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(30): 114-122. |
| [12] | 吕伯龙, 李国柱. 基于HPLC结合多元统计方法分析不同产地覆盆子药材中有机酸的差异[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(29): 129-136. |
| [13] | 邝瑞彬, 杨敏, 周陈平, 吴夏明, 魏岳荣. 番荔枝根腐病菌分离鉴定、生物学特性分析及药剂筛选[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(28): 99-106. |
| [14] | 陈文乐. 福建省三明地区非洲菊根腐病病原菌生物学特性与杀菌剂田间筛选[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(28): 107-111. |
| [15] | 伍晓露, 王帆帆, 唐涛, 段媛媛, 郭晓亮, 游景茂. 半夏菌核病病原菌鉴定、生物学特性及防治药剂筛选[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(24): 114-119. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||