
中国农学通报 ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 7-17.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0430
郑本川1( ), 张锦芳1, 蒋俊1, 崔成1, 柴靓1, 黄友涛2, 周正鉴2, 李浩杰1(
), 张锦芳1, 蒋俊1, 崔成1, 柴靓1, 黄友涛2, 周正鉴2, 李浩杰1( ), 蒋梁材1(
), 蒋梁材1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-22
修回日期:2021-10-14
出版日期:2022-03-05
发布日期:2022-04-13
通讯作者:
李浩杰,蒋梁材
作者简介:郑本川,男,1987年出生,助理研究员,硕士,研究方向为油菜育种/栽培。通信地址:610066 四川省成都市锦江区狮子山路4号 四川省农业科学院作物研究所,Tel:028-84504350,E-mail: 基金资助:
ZHENG Benchuan1( ), ZHANG Jinfang1, JIANG Jun1, CUI Cheng1, CHAI Liang1, HUANG Youtao2, ZHOU Zhengjian2, LI Haojie1(
), ZHANG Jinfang1, JIANG Jun1, CUI Cheng1, CHAI Liang1, HUANG Youtao2, ZHOU Zhengjian2, LI Haojie1( ), JIANG Liangcai1(
), JIANG Liangcai1( )
)
Received:2021-04-22
Revised:2021-10-14
Online:2022-03-05
Published:2022-04-13
Contact:
LI Haojie,JIANG Liangcai
摘要:
探讨在成都地区气候条件下不同熟期甘蓝型油菜产量的主要影响因素,以期为油菜抗性育种提供理论基础。采用相关分析、通径分析和主成分分析等方法,分析不同熟期甘蓝型油菜主要农艺性状、茎秆抗折力和菌核病发病率等与产量的关系。相关分析结果表明,早熟品种产量与单株有效角果数、每果粒数和茎秆中上部抗折力均呈显著或极显著正相关,中熟品种产量与株高、一次分枝高度、单株有效角果数、茎秆下部和茎秆中下部抗折力均呈极显著正相关。通径分析结果表明,早熟和中熟品种主要性状中,单株有效角果数对产量的直接作用最大。主要性状中,每果粒数对早熟品种产量的间接综合效应最大,中熟品种间接综合效应最大的是茎秆下部抗折力。主成分分析结果表明,早熟品种主要性状分为抗倒性状、株型性状、产量构成性状和抗病性状等4类性状。中熟品种为产量构成性状、株型性状和抗倒性性状等3类性状。研究表明,在四川省自然气候条件下,无论是早熟品种还是中熟品种选育,应在保证产量性状的同时,加强植株株型、抗倒性和抗病性的选择。
中图分类号:
郑本川, 张锦芳, 蒋俊, 崔成, 柴靓, 黄友涛, 周正鉴, 李浩杰, 蒋梁材. 不同熟期“川油”系列甘蓝型油菜品种主要性状与产量的相关分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 7-17.
ZHENG Benchuan, ZHANG Jinfang, JIANG Jun, CUI Cheng, CHAI Liang, HUANG Youtao, ZHOU Zhengjian, LI Haojie, JIANG Liangcai. Correlation Analysis of Main Traits and Yield of Brassica napus ‘Chuanyou’ Varieties with Different Maturity Stages[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(7): 7-17.
| 材料 | 父本来源 | 母本来源 | 全生育期/d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早熟组合 | PE1(川早油3号) | JR9 | JA10 | 204 |
| PE2 | JR11 | 21536/N9-6 | 206 | |
| PE3 | JR-NEA99-6678 | 04-21657/YY9 | 206 | |
| PE4 | R×川油18.F5 | (F9(F1[51/1005//H88-117/3/YY2])-另 | 207 | |
| PE5 | R×川油18.F5 | 768-5/571-577 | 207 | |
| PE6 | R×川油18.F5 | F3:转保父本/YY-9//ZS-11 | 207 | |
| PE7 | 川油18.BC2F6 | SL-7 | 207 | |
| PE8 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 95-41-45 | 207 | |
| PE9 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 99-16 | 207 | |
| PE10 | NR9.BC3F7 | 4A-3 | 205 | |
| PE11 | R川油18.F5 | (F5德-6/ZS9)//ZS11 | 207 | |
| PE12 | R川油18.F5 | 03-14490 | 205 | |
| PE13 | R川油18.F5 | 03-4031-4033 | 205 | |
| PE14 | R川油18.F5 | 207,地方种 | 205 | |
| PE15 | R川油18.F5 | 4A-3 | 205 | |
| PE16 | R川油18.F5 | 品系8908//97-转9B/97保-13 | 207 | |
| PE17 | NR9 BC3F7 | (S21D/97保-5H)//ZS11 | 207 | |
| PE18 | NR9 BC3F7 | 04-2371-5/GZHZ | 207 | |
| PE19 | NR9 BC3F7 | JJM-MRK | 207 | |
| PE20 | NR9 BC3F7 | YY-10 | 204 | |
| PE21 | NR9 BC3F7 | (F4、S21D/97B-5H)//ZS11 | 207 | |
| PE22 | NR9 BC3F7 | 省区试Y717 | 207 | |
| PE23 | NR9 BC3F7 | 97B-11/YY9号//H1707 | 205 | |
| PE24 | NR9 BC3F7 | MY129 | 207 | |
| PE25 | JR 99-6678 | 99-16 | 204 | |
| PE26 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 95-41-45 | 207 | |
| PE27 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 99-16 | 207 | |
| PE28 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 04-21030/ZYZ-1 | 205 | |
| PE29 | JR10977 BC3F6 | 04-21030/ZYZ-2 | 205 | |
| PE30 | JR10977 BC3F6 | 04-21657/YY9-2 | 205 | |
| PE31 | JR10977 BC3F6 | 99-16 | 205 | |
| 中熟组合 | PM1 | JR11 | ZS72 | 213 |
| PM2 | JR11 | Y459 | 213 | |
| PM3 | JR11 | 04-21030/ZYYZ-1 | 213 | |
| PM4 | JR11 | 省区试YY717 | 213 | |
| PM5(德喜油100) | JR1314 | JA1314 | 213 | |
| PM6 | JR11 | 03-4031-4033 | 213 | |
| PM7 | JR11 | 04-21030/ZY-1 | 210 | |
| PM8 | JR11 | F3:什-111/ZS72 | 212 | |
| PM9 | JR11 | F4:什-085/F4:Y9 | 213 | |
| PM10 | JR11 | 川油20 | 213 | |
| PM11 | JR11 | 德-23/ZY-2 | 212 | |
| PM12 | JR11 | S21D122-5 | 208 | |
| PM13 | JR11 | F3:川油21F2/YY10//ZS-11 | 213 | |
| PM14 | NR9 BC3F7 | D-23/Z-2 | 213 | |
| PM15 | NR9 BC3F7 | T8 | 213 | |
| PM16 | NR9 BC3F7 | 川油20 | 208 | |
| PM17 | NR9 BC3F7 | ZY-99 | 213 | |
| PM18 | NR9 BC3F7 | 04-21030/SHS | 213 | |
| PM19 | NR×YY-10.F3 | 03-14490 | 208 | |
| PM20 | NR×YY-10.F3 | 4A-3 | 213 | |
| PM21 | NR×YY-10.F3 | 768-5/571-577 | 208 | |
| PM22 | 川油18.BC2F6 | (F5德-6/ZS9)//ZS-11 | 214 | |
| PM23 | 川油18.BC2F6 | SQS-77 | 212 | |
| PM24 | 川油18.BC2F6 | R11 | 214 | |
| PM25 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 97-保-11/YZS-9 | 212 | |
| PM26 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM27(川油47) | JR18 | JA4-3 | 212 | |
| PM28 | .NR9 BC3F7 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM29 | (NR-S9RBC5F3×ZS11)F3 | YZ9号/德国油菜 F4/川油21 | 214 | |
| PM30 | (NR-S9RBC5F3×ZS11)F3 | zs-11 | 216 | |
| PM31 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM32 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | JJM-MEK | 212 | |
| PM33 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | 什-090 | 213 | |
| PM34 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | ZS-11 | 217 | |
| PM35 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM36 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | B1 | 212 | |
| PM37 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | ZS-11 | 216 | |
| 材料 | 父本来源 | 母本来源 | 全生育期/d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早熟组合 | PE1(川早油3号) | JR9 | JA10 | 204 |
| PE2 | JR11 | 21536/N9-6 | 206 | |
| PE3 | JR-NEA99-6678 | 04-21657/YY9 | 206 | |
| PE4 | R×川油18.F5 | (F9(F1[51/1005//H88-117/3/YY2])-另 | 207 | |
| PE5 | R×川油18.F5 | 768-5/571-577 | 207 | |
| PE6 | R×川油18.F5 | F3:转保父本/YY-9//ZS-11 | 207 | |
| PE7 | 川油18.BC2F6 | SL-7 | 207 | |
| PE8 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 95-41-45 | 207 | |
| PE9 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 99-16 | 207 | |
| PE10 | NR9.BC3F7 | 4A-3 | 205 | |
| PE11 | R川油18.F5 | (F5德-6/ZS9)//ZS11 | 207 | |
| PE12 | R川油18.F5 | 03-14490 | 205 | |
| PE13 | R川油18.F5 | 03-4031-4033 | 205 | |
| PE14 | R川油18.F5 | 207,地方种 | 205 | |
| PE15 | R川油18.F5 | 4A-3 | 205 | |
| PE16 | R川油18.F5 | 品系8908//97-转9B/97保-13 | 207 | |
| PE17 | NR9 BC3F7 | (S21D/97保-5H)//ZS11 | 207 | |
| PE18 | NR9 BC3F7 | 04-2371-5/GZHZ | 207 | |
| PE19 | NR9 BC3F7 | JJM-MRK | 207 | |
| PE20 | NR9 BC3F7 | YY-10 | 204 | |
| PE21 | NR9 BC3F7 | (F4、S21D/97B-5H)//ZS11 | 207 | |
| PE22 | NR9 BC3F7 | 省区试Y717 | 207 | |
| PE23 | NR9 BC3F7 | 97B-11/YY9号//H1707 | 205 | |
| PE24 | NR9 BC3F7 | MY129 | 207 | |
| PE25 | JR 99-6678 | 99-16 | 204 | |
| PE26 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 95-41-45 | 207 | |
| PE27 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 99-16 | 207 | |
| PE28 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 04-21030/ZYZ-1 | 205 | |
| PE29 | JR10977 BC3F6 | 04-21030/ZYZ-2 | 205 | |
| PE30 | JR10977 BC3F6 | 04-21657/YY9-2 | 205 | |
| PE31 | JR10977 BC3F6 | 99-16 | 205 | |
| 中熟组合 | PM1 | JR11 | ZS72 | 213 |
| PM2 | JR11 | Y459 | 213 | |
| PM3 | JR11 | 04-21030/ZYYZ-1 | 213 | |
| PM4 | JR11 | 省区试YY717 | 213 | |
| PM5(德喜油100) | JR1314 | JA1314 | 213 | |
| PM6 | JR11 | 03-4031-4033 | 213 | |
| PM7 | JR11 | 04-21030/ZY-1 | 210 | |
| PM8 | JR11 | F3:什-111/ZS72 | 212 | |
| PM9 | JR11 | F4:什-085/F4:Y9 | 213 | |
| PM10 | JR11 | 川油20 | 213 | |
| PM11 | JR11 | 德-23/ZY-2 | 212 | |
| PM12 | JR11 | S21D122-5 | 208 | |
| PM13 | JR11 | F3:川油21F2/YY10//ZS-11 | 213 | |
| PM14 | NR9 BC3F7 | D-23/Z-2 | 213 | |
| PM15 | NR9 BC3F7 | T8 | 213 | |
| PM16 | NR9 BC3F7 | 川油20 | 208 | |
| PM17 | NR9 BC3F7 | ZY-99 | 213 | |
| PM18 | NR9 BC3F7 | 04-21030/SHS | 213 | |
| PM19 | NR×YY-10.F3 | 03-14490 | 208 | |
| PM20 | NR×YY-10.F3 | 4A-3 | 213 | |
| PM21 | NR×YY-10.F3 | 768-5/571-577 | 208 | |
| PM22 | 川油18.BC2F6 | (F5德-6/ZS9)//ZS-11 | 214 | |
| PM23 | 川油18.BC2F6 | SQS-77 | 212 | |
| PM24 | 川油18.BC2F6 | R11 | 214 | |
| PM25 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 97-保-11/YZS-9 | 212 | |
| PM26 | 川油18.BC2F6 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM27(川油47) | JR18 | JA4-3 | 212 | |
| PM28 | .NR9 BC3F7 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM29 | (NR-S9RBC5F3×ZS11)F3 | YZ9号/德国油菜 F4/川油21 | 214 | |
| PM30 | (NR-S9RBC5F3×ZS11)F3 | zs-11 | 216 | |
| PM31 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM32 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | JJM-MEK | 212 | |
| PM33 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | 什-090 | 213 | |
| PM34 | 06C10977 BC3F3 | ZS-11 | 217 | |
| PM35 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | 03-4031-4033 | 212 | |
| PM36 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | B1 | 212 | |
| PM37 | JR07NH02 BC3F3 | ZS-11 | 216 | |
| 性状 | 早熟品种 | 中熟品种 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | ||
| 株高/cm | 201.2 | 236.2 | 223.0 | 9.2 | 4.1 | 186.5 | 244.3 | 221.7 | 15.2 | 6.9 | |
| 一次分枝高度/cm | 82.5 | 127.9 | 104.1 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 74.0 | 145.5 | 115.4 | 15.7 | 13.6 | |
| 主序长/cm | 57.8 | 79.5 | 69.2 | 5.3 | 7.6 | 55.5 | 78.6 | 66.6 | 5.0 | 7.5 | |
| 一次有效分枝数/个 | 5.8 | 8.5 | 7.2 | 0.7 | 9.6 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 6.7 | 0.7 | 11.1 | |
| 角果层厚度/cm | 66.8 | 83.3 | 73.8 | 5.0 | 6.7 | 55.5 | 113.9 | 72.7 | 9.3 | 12.7 | |
| 单株有效角果数/个 | 210.5 | 420.8 | 320.2 | 61.4 | 19.2 | 200.6 | 421.2 | 286.2 | 53.2 | 18.6 | |
| 每果粒数/粒 | 14.3 | 20.9 | 17.3 | 1.9 | 10.8 | 15.1 | 21.1 | 17.5 | 1.6 | 9.0 | |
| 千粒重/g | 3.3 | 5.2 | 4.2 | 0.5 | 11.0 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 0.4 | 8.9 | |
| 单株产量/g | 15.3 | 26.6 | 20.1 | 2.9 | 14.3 | 10.9 | 27.1 | 20.6 | 3.5 | 17.1 | |
| 菌核病发病率/% | 0.0 | 53.3 | 24.6 | 12.5 | 50.7 | 8.7 | 50.0 | 22.3 | 9.9 | 44.4 | |
| 根茎粗/cm | 16.1 | 20.9 | 18.0 | 1.2 | 6.4 | 13.1 | 21.3 | 18.0 | 1.8 | 10.2 | |
| 地上部分鲜重/g | 341.7 | 541.7 | 422.6 | 53.2 | 12.6 | 241.7 | 558.3 | 422.9 | 64.3 | 15.2 | |
| 茎秆下部抗折力/N | 89.2 | 191.7 | 139.4 | 27.5 | 19.7 | 83.2 | 190.2 | 129.1 | 28.2 | 21.9 | |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力/N | 78.7 | 156.0 | 109.7 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 63.6 | 145.9 | 106.5 | 20.9 | 19.6 | |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力/N | 43.6 | 105.5 | 76.7 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 54.8 | 153.7 | 87.7 | 20.3 | 23.2 | |
| 茎秆上部抗折力/N | 39.4 | 93.8 | 63.9 | 13.3 | 20.9 | 50.0 | 120.1 | 73.7 | 16.0 | 21.7 | |
| 性状 | 早熟品种 | 中熟品种 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | ||
| 株高/cm | 201.2 | 236.2 | 223.0 | 9.2 | 4.1 | 186.5 | 244.3 | 221.7 | 15.2 | 6.9 | |
| 一次分枝高度/cm | 82.5 | 127.9 | 104.1 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 74.0 | 145.5 | 115.4 | 15.7 | 13.6 | |
| 主序长/cm | 57.8 | 79.5 | 69.2 | 5.3 | 7.6 | 55.5 | 78.6 | 66.6 | 5.0 | 7.5 | |
| 一次有效分枝数/个 | 5.8 | 8.5 | 7.2 | 0.7 | 9.6 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 6.7 | 0.7 | 11.1 | |
| 角果层厚度/cm | 66.8 | 83.3 | 73.8 | 5.0 | 6.7 | 55.5 | 113.9 | 72.7 | 9.3 | 12.7 | |
| 单株有效角果数/个 | 210.5 | 420.8 | 320.2 | 61.4 | 19.2 | 200.6 | 421.2 | 286.2 | 53.2 | 18.6 | |
| 每果粒数/粒 | 14.3 | 20.9 | 17.3 | 1.9 | 10.8 | 15.1 | 21.1 | 17.5 | 1.6 | 9.0 | |
| 千粒重/g | 3.3 | 5.2 | 4.2 | 0.5 | 11.0 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 0.4 | 8.9 | |
| 单株产量/g | 15.3 | 26.6 | 20.1 | 2.9 | 14.3 | 10.9 | 27.1 | 20.6 | 3.5 | 17.1 | |
| 菌核病发病率/% | 0.0 | 53.3 | 24.6 | 12.5 | 50.7 | 8.7 | 50.0 | 22.3 | 9.9 | 44.4 | |
| 根茎粗/cm | 16.1 | 20.9 | 18.0 | 1.2 | 6.4 | 13.1 | 21.3 | 18.0 | 1.8 | 10.2 | |
| 地上部分鲜重/g | 341.7 | 541.7 | 422.6 | 53.2 | 12.6 | 241.7 | 558.3 | 422.9 | 64.3 | 15.2 | |
| 茎秆下部抗折力/N | 89.2 | 191.7 | 139.4 | 27.5 | 19.7 | 83.2 | 190.2 | 129.1 | 28.2 | 21.9 | |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力/N | 78.7 | 156.0 | 109.7 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 63.6 | 145.9 | 106.5 | 20.9 | 19.6 | |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力/N | 43.6 | 105.5 | 76.7 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 54.8 | 153.7 | 87.7 | 20.3 | 23.2 | |
| 茎秆上部抗折力/N | 39.4 | 93.8 | 63.9 | 13.3 | 20.9 | 50.0 | 120.1 | 73.7 | 16.0 | 21.7 | |
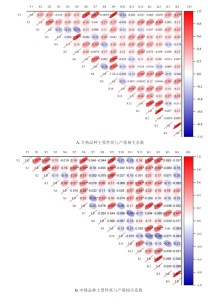
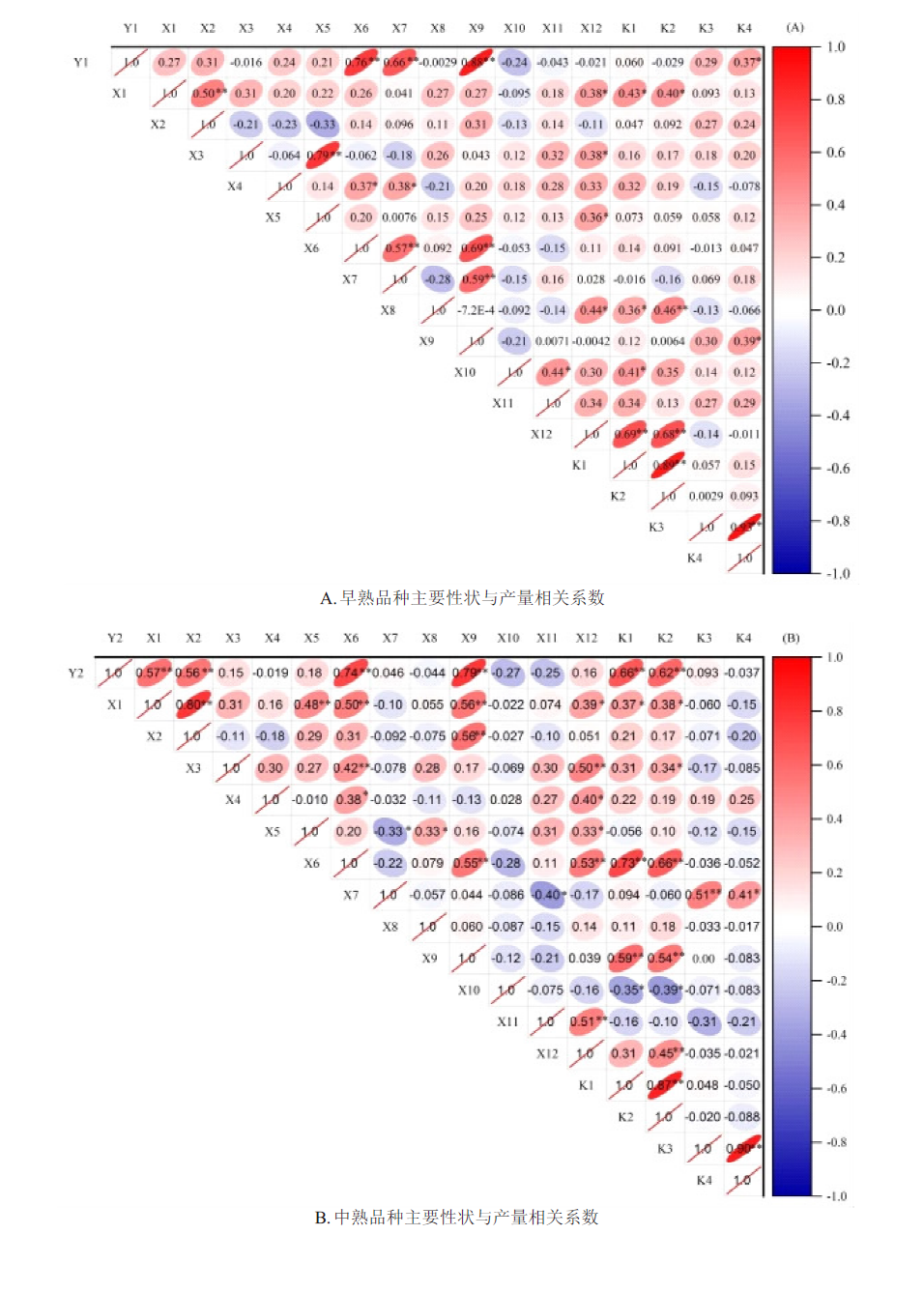
| 性状 | 早熟品种单位面积产量 | 中熟品种单位面积产量 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直接通径系数 | 间接综合效应 | 直接通径系数 | 间接综合效应 | ||
| 株高 | -0.034 | 0.309 | 0.131 | 0.380 | |
| 一次分枝高度 | 0.169 | 0.155 | 0.115 | 0.312 | |
| 主序长 | -0.169 | 0.164 | -0.009 | 0.160 | |
| 一次有效分枝数 | -0.104 | 0.264 | -0.220 | 0.156 | |
| 角果层厚度 | 0.351 | -0.133 | 0.076 | 0.019 | |
| 单株有效角果数 | 0.549** | 0.225 | 0.859** | -0.135 | |
| 每果粒数 | 0.226 | 0.405 | 0.198 | -0.137 | |
| 千粒重 | -0.045 | 0.051 | -0.158 | 0.123 | |
| 菌核病发病率 | -0.247 | 0.003 | -0.008 | -0.321 | |
| 根茎粗 | -0.014 | -0.023 | -0.111 | -0.139 | |
| 地上部分鲜重 | -0.087 | 0.079 | -0.279 | 0.406 | |
| 茎秆下部抗折力 | 0.267 | -0.193 | -0.330 | 0.982 | |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力 | -0.095 | 0.080 | 0.450 | 0.156 | |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力 | 0.0871 | 0.207 | 0.202 | -0.101 | |
| 茎秆上部抗折力 | 0.171 | 0.200 | -0.145 | 0.149 | |
| 性状 | 早熟品种单位面积产量 | 中熟品种单位面积产量 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直接通径系数 | 间接综合效应 | 直接通径系数 | 间接综合效应 | ||
| 株高 | -0.034 | 0.309 | 0.131 | 0.380 | |
| 一次分枝高度 | 0.169 | 0.155 | 0.115 | 0.312 | |
| 主序长 | -0.169 | 0.164 | -0.009 | 0.160 | |
| 一次有效分枝数 | -0.104 | 0.264 | -0.220 | 0.156 | |
| 角果层厚度 | 0.351 | -0.133 | 0.076 | 0.019 | |
| 单株有效角果数 | 0.549** | 0.225 | 0.859** | -0.135 | |
| 每果粒数 | 0.226 | 0.405 | 0.198 | -0.137 | |
| 千粒重 | -0.045 | 0.051 | -0.158 | 0.123 | |
| 菌核病发病率 | -0.247 | 0.003 | -0.008 | -0.321 | |
| 根茎粗 | -0.014 | -0.023 | -0.111 | -0.139 | |
| 地上部分鲜重 | -0.087 | 0.079 | -0.279 | 0.406 | |
| 茎秆下部抗折力 | 0.267 | -0.193 | -0.330 | 0.982 | |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力 | -0.095 | 0.080 | 0.450 | 0.156 | |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力 | 0.0871 | 0.207 | 0.202 | -0.101 | |
| 茎秆上部抗折力 | 0.171 | 0.200 | -0.145 | 0.149 | |
| 性状 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 | 0.587 | 0.120 | 0.402 | 0.122 | 0.372 |
| 一次分枝高度 | 0.031 | 0.478 | 0.719 | -0.095 | 0.174 |
| 主序长 | 0.549 | 0.052 | -0.564 | -0.144 | 0.509 |
| 一次有效分枝数 | 0.434 | -0.196 | -0.173 | 0.596 | -0.270 |
| 角果层厚度 | 0.473 | -0.059 | -0.629 | 0.200 | 0.487 |
| 单株有效角果数 | 0.218 | 0.028 | 0.263 | 0.770 | 0.159 |
| 每果粒数 | -0.003 | 0.285 | 0.076 | 0.791 | -0.098 |
| 千粒重 | 0.437 | -0.326 | 0.319 | -0.297 | 0.449 |
| 菌核病发病率 | 0.426 | 0.086 | -0.274 | -0.211 | -0.601 |
| 根茎粗 | 0.459 | 0.408 | -0.240 | -0.052 | -0.350 |
| 地上部分鲜重 | 0.835 | -0.278 | 0.002 | 0.004 | -0.062 |
| 茎秆下部抗折力 | 0.841 | -0.083 | 0.264 | -0.086 | -0.304 |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力 | 0.797 | -0.185 | 0.334 | -0.199 | -0.189 |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力 | 0.153 | 0.896 | -0.094 | -0.145 | 0.059 |
| 茎秆上部抗折力 | 0.260 | 0.866 | -0.080 | -0.058 | 0.066 |
| 特征值 | 3.821 | 2.322 | 1.929 | 1.866 | 1.598 |
| 贡献率/% | 25.471 | 15.480 | 12.858 | 12.437 | 10.650 |
| 累计贡献率/% | 25.471 | 40.951 | 53.809 | 66.246 | 76.896 |
| 性状 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 | 0.587 | 0.120 | 0.402 | 0.122 | 0.372 |
| 一次分枝高度 | 0.031 | 0.478 | 0.719 | -0.095 | 0.174 |
| 主序长 | 0.549 | 0.052 | -0.564 | -0.144 | 0.509 |
| 一次有效分枝数 | 0.434 | -0.196 | -0.173 | 0.596 | -0.270 |
| 角果层厚度 | 0.473 | -0.059 | -0.629 | 0.200 | 0.487 |
| 单株有效角果数 | 0.218 | 0.028 | 0.263 | 0.770 | 0.159 |
| 每果粒数 | -0.003 | 0.285 | 0.076 | 0.791 | -0.098 |
| 千粒重 | 0.437 | -0.326 | 0.319 | -0.297 | 0.449 |
| 菌核病发病率 | 0.426 | 0.086 | -0.274 | -0.211 | -0.601 |
| 根茎粗 | 0.459 | 0.408 | -0.240 | -0.052 | -0.350 |
| 地上部分鲜重 | 0.835 | -0.278 | 0.002 | 0.004 | -0.062 |
| 茎秆下部抗折力 | 0.841 | -0.083 | 0.264 | -0.086 | -0.304 |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力 | 0.797 | -0.185 | 0.334 | -0.199 | -0.189 |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力 | 0.153 | 0.896 | -0.094 | -0.145 | 0.059 |
| 茎秆上部抗折力 | 0.260 | 0.866 | -0.080 | -0.058 | 0.066 |
| 特征值 | 3.821 | 2.322 | 1.929 | 1.866 | 1.598 |
| 贡献率/% | 25.471 | 15.480 | 12.858 | 12.437 | 10.650 |
| 累计贡献率/% | 25.471 | 40.951 | 53.809 | 66.246 | 76.896 |
| 性状 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 | 0.708 | -0.042 | -0.370 | 0.510 | -0.111 |
| 一次分枝高度 | 0.403 | -0.111 | -0.712 | 0.458 | -0.187 |
| 主序长 | 0.598 | -0.027 | 0.406 | -0.050 | 0.221 |
| 一次有效分枝数 | 0.217 | 0.325 | 0.570 | 0.152 | -0.356 |
| 角果层厚度 | 0.459 | -0.369 | 0.011 | 0.491 | 0.435 |
| 单株有效角果数 | 0.836 | 0.219 | -0.008 | -0.077 | -0.167 |
| 每果粒数 | -0.261 | 0.643 | -0.145 | 0.052 | 0.017 |
| 千粒重 | 0.235 | -0.019 | 0.025 | -0.083 | 0.867 |
| 菌核病发病率 | -0.331 | -0.283 | 0.007 | 0.294 | -0.136 |
| 根茎粗 | 0.285 | -0.487 | 0.602 | 0.166 | -0.222 |
| 地上部分鲜重 | 0.706 | 0.011 | 0.456 | 0.155 | -0.035 |
| 茎秆下部抗折力 | 0.704 | 0.456 | -0.224 | -0.385 | -0.099 |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力 | 0.763 | 0.337 | -0.144 | -0.364 | 0.012 |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力 | -0.215 | 0.815 | 0.085 | 0.421 | 0.117 |
| 茎秆上部抗折力 | -0.246 | 0.762 | 0.265 | 0.396 | 0.129 |
| 特征值 | 3.975 | 2.601 | 1.874 | 1.504 | 1.301 |
| 贡献率/% | 26.498 | 17.342 | 12.493 | 10.025 | 8.674 |
| 累计贡献率/% | 26.498 | 43.840 | 56.334 | 66.359 | 75.033 |
| 性状 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 | 0.708 | -0.042 | -0.370 | 0.510 | -0.111 |
| 一次分枝高度 | 0.403 | -0.111 | -0.712 | 0.458 | -0.187 |
| 主序长 | 0.598 | -0.027 | 0.406 | -0.050 | 0.221 |
| 一次有效分枝数 | 0.217 | 0.325 | 0.570 | 0.152 | -0.356 |
| 角果层厚度 | 0.459 | -0.369 | 0.011 | 0.491 | 0.435 |
| 单株有效角果数 | 0.836 | 0.219 | -0.008 | -0.077 | -0.167 |
| 每果粒数 | -0.261 | 0.643 | -0.145 | 0.052 | 0.017 |
| 千粒重 | 0.235 | -0.019 | 0.025 | -0.083 | 0.867 |
| 菌核病发病率 | -0.331 | -0.283 | 0.007 | 0.294 | -0.136 |
| 根茎粗 | 0.285 | -0.487 | 0.602 | 0.166 | -0.222 |
| 地上部分鲜重 | 0.706 | 0.011 | 0.456 | 0.155 | -0.035 |
| 茎秆下部抗折力 | 0.704 | 0.456 | -0.224 | -0.385 | -0.099 |
| 茎秆中下部抗折力 | 0.763 | 0.337 | -0.144 | -0.364 | 0.012 |
| 茎秆中上部抗折力 | -0.215 | 0.815 | 0.085 | 0.421 | 0.117 |
| 茎秆上部抗折力 | -0.246 | 0.762 | 0.265 | 0.396 | 0.129 |
| 特征值 | 3.975 | 2.601 | 1.874 | 1.504 | 1.301 |
| 贡献率/% | 26.498 | 17.342 | 12.493 | 10.025 | 8.674 |
| 累计贡献率/% | 26.498 | 43.840 | 56.334 | 66.359 | 75.033 |
| 早熟品种 | 产量/(kg/hm2) | 菌核病发病率/% | 茎秆平均抗折力 | 中熟品种 | 产量/(kg/hm2) | 菌核病发病率/% | 茎秆平均抗折力 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE1(川早油3号) | 3543.0 | 20.0 | 119.5 | PM1 | 2986.5 | 13.3 | 128.1 |
| PE2 | 3199.5 | 10.0 | 105.4 | PM2 | 2562.0 | 24.3 | 75.0 |
| PE3 | 2908.5 | 0.0 | 83.9 | PM3 | 2782.5 | 14.7 | 120.6 |
| PE4 | 2415.0 | 15.0 | 91.1 | PM4 | 2563.5 | 29.3 | 75.3 |
| PE5 | 2148.0 | 30.0 | 108.4 | PM5(德喜油100) | 3178.5 | 20.0 | 124.3 |
| PE6 | 2748.0 | 13.3 | 100.7 | PM6 | 3133.5 | 10.0 | 102.7 |
| PE7 | 2662.5 | 26.7 | 104.7 | PM7 | 2577.0 | 31.7 | 80.5 |
| PE8 | 2743.5 | 36.7 | 100.5 | PM8 | 2857.5 | 32.7 | 100.6 |
| PE9 | 2983.5 | 53.3 | 116.6 | PM9 | 2767.5 | 27.3 | 107.4 |
| PE10 | 3180.0 | 27.3 | 88.4 | PM10 | 3043.5 | 15.0 | 109.4 |
| PE11 | 2875.5 | 33.3 | 117.3 | PM11 | 2661.0 | 19.7 | 94.9 |
| PE12 | 2710.5 | 36.7 | 102.2 | PM12 | 2776.5 | 17.3 | 95.4 |
| PE13 | 2562.0 | 10.0 | 75.1 | PM13 | 3064.5 | 13.3 | 92.2 |
| PE14 | 2796.0 | 26.7 | 93.1 | PM14 | 2488.5 | 20.0 | 82.7 |
| PE15 | 2808.0 | 40.0 | 98.4 | PM15 | 3070.5 | 20.0 | 118.4 |
| PE16 | 2598.0 | 33.3 | 110.1 | PM16 | 2695.5 | 33.3 | 90.4 |
| PE17 | 3015.0 | 33.3 | 88.5 | PM17 | 2616.0 | 50.0 | 92.2 |
| PE18 | 2968.5 | 20.0 | 85.5 | PM18 | 3001.5 | 20.0 | 106.7 |
| PE19 | 2877.0 | 26.7 | 102.1 | PM19 | 2404.5 | 26.7 | 84.1 |
| PE20 | 2820.0 | 23.3 | 96.6 | PM20 | 2905.5 | 26.7 | 89.3 |
| PE21 | 2836.5 | 10.0 | 93.3 | PM21 | 2785.5 | 33.3 | 94.0 |
| PE22 | 2556.0 | 33.3 | 123.0 | PM22 | 2596.5 | 10.0 | 109.7 |
| PE23 | 2659.5 | 16.7 | 70.2 | PM23 | 2746.5 | 26.7 | 101.8 |
| PE24 | 2925.0 | 20.0 | 121.5 | PM24 | 2473.5 | 26.7 | 98.6 |
| PE25 | 2362.5 | 36.7 | 77.6 | PM25 | 2581.5 | 10.0 | 99.0 |
| PE26 | 2821.5 | 10.0 | 87.0 | PM26 | 3033.0 | 11.7 | 110.1 |
| PE27 | 2640.0 | 13.3 | 101.4 | PM27(川油47) | 2728.5 | 10.0 | 142.2 |
| PE28 | 2484.0 | 30.0 | 94.3 | PM28 | 2961.0 | 33.3 | 109.2 |
| PE29 | 2122.5 | 50.0 | 98.6 | PM29 | 2592.0 | 10.0 | 88.6 |
| PE30 | 2539.5 | 16.7 | 88.5 | PM30 | 2565.0 | 8.7 | 92.4 |
| PE31 | 2845.5 | 11.7 | 76.7 | PM31 | 2484.0 | 33.3 | 90.7 |
| PM32 | 2497.5 | 33.3 | 96.9 | ||||
| PM33 | 2403.0 | 20.0 | 99.7 | ||||
| PM34 | 2355.0 | 16.7 | 79.9 | ||||
| PM35 | 2520.0 | 33.3 | 90.4 | ||||
| PM36 | 2448.0 | 33.3 | 99.1 | ||||
| PM37 | 2737.5 | 10.0 | 99.6 |
| 早熟品种 | 产量/(kg/hm2) | 菌核病发病率/% | 茎秆平均抗折力 | 中熟品种 | 产量/(kg/hm2) | 菌核病发病率/% | 茎秆平均抗折力 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE1(川早油3号) | 3543.0 | 20.0 | 119.5 | PM1 | 2986.5 | 13.3 | 128.1 |
| PE2 | 3199.5 | 10.0 | 105.4 | PM2 | 2562.0 | 24.3 | 75.0 |
| PE3 | 2908.5 | 0.0 | 83.9 | PM3 | 2782.5 | 14.7 | 120.6 |
| PE4 | 2415.0 | 15.0 | 91.1 | PM4 | 2563.5 | 29.3 | 75.3 |
| PE5 | 2148.0 | 30.0 | 108.4 | PM5(德喜油100) | 3178.5 | 20.0 | 124.3 |
| PE6 | 2748.0 | 13.3 | 100.7 | PM6 | 3133.5 | 10.0 | 102.7 |
| PE7 | 2662.5 | 26.7 | 104.7 | PM7 | 2577.0 | 31.7 | 80.5 |
| PE8 | 2743.5 | 36.7 | 100.5 | PM8 | 2857.5 | 32.7 | 100.6 |
| PE9 | 2983.5 | 53.3 | 116.6 | PM9 | 2767.5 | 27.3 | 107.4 |
| PE10 | 3180.0 | 27.3 | 88.4 | PM10 | 3043.5 | 15.0 | 109.4 |
| PE11 | 2875.5 | 33.3 | 117.3 | PM11 | 2661.0 | 19.7 | 94.9 |
| PE12 | 2710.5 | 36.7 | 102.2 | PM12 | 2776.5 | 17.3 | 95.4 |
| PE13 | 2562.0 | 10.0 | 75.1 | PM13 | 3064.5 | 13.3 | 92.2 |
| PE14 | 2796.0 | 26.7 | 93.1 | PM14 | 2488.5 | 20.0 | 82.7 |
| PE15 | 2808.0 | 40.0 | 98.4 | PM15 | 3070.5 | 20.0 | 118.4 |
| PE16 | 2598.0 | 33.3 | 110.1 | PM16 | 2695.5 | 33.3 | 90.4 |
| PE17 | 3015.0 | 33.3 | 88.5 | PM17 | 2616.0 | 50.0 | 92.2 |
| PE18 | 2968.5 | 20.0 | 85.5 | PM18 | 3001.5 | 20.0 | 106.7 |
| PE19 | 2877.0 | 26.7 | 102.1 | PM19 | 2404.5 | 26.7 | 84.1 |
| PE20 | 2820.0 | 23.3 | 96.6 | PM20 | 2905.5 | 26.7 | 89.3 |
| PE21 | 2836.5 | 10.0 | 93.3 | PM21 | 2785.5 | 33.3 | 94.0 |
| PE22 | 2556.0 | 33.3 | 123.0 | PM22 | 2596.5 | 10.0 | 109.7 |
| PE23 | 2659.5 | 16.7 | 70.2 | PM23 | 2746.5 | 26.7 | 101.8 |
| PE24 | 2925.0 | 20.0 | 121.5 | PM24 | 2473.5 | 26.7 | 98.6 |
| PE25 | 2362.5 | 36.7 | 77.6 | PM25 | 2581.5 | 10.0 | 99.0 |
| PE26 | 2821.5 | 10.0 | 87.0 | PM26 | 3033.0 | 11.7 | 110.1 |
| PE27 | 2640.0 | 13.3 | 101.4 | PM27(川油47) | 2728.5 | 10.0 | 142.2 |
| PE28 | 2484.0 | 30.0 | 94.3 | PM28 | 2961.0 | 33.3 | 109.2 |
| PE29 | 2122.5 | 50.0 | 98.6 | PM29 | 2592.0 | 10.0 | 88.6 |
| PE30 | 2539.5 | 16.7 | 88.5 | PM30 | 2565.0 | 8.7 | 92.4 |
| PE31 | 2845.5 | 11.7 | 76.7 | PM31 | 2484.0 | 33.3 | 90.7 |
| PM32 | 2497.5 | 33.3 | 96.9 | ||||
| PM33 | 2403.0 | 20.0 | 99.7 | ||||
| PM34 | 2355.0 | 16.7 | 79.9 | ||||
| PM35 | 2520.0 | 33.3 | 90.4 | ||||
| PM36 | 2448.0 | 33.3 | 99.1 | ||||
| PM37 | 2737.5 | 10.0 | 99.6 |
| [1] | 易斌, 陈伟, 马朝芝, 等. 甘蓝型油菜产量及相关性状的QTL分析[J]. 作物学报, 2006,5:676-682. |
| [2] | 胡虹文. 甘蓝型油菜12种主要性状与产量的关系[J]. 中国油料, 1997,19(3):10-11 |
| [3] | 胡俊鹏. 油菜三系组合性状与产量相关分析[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2002(5):4-6. |
| [4] | 杨安中, 彭春华. 油菜单株产量与若干农艺性状的相关分析[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2006,12(2):33-34. |
| [5] | 郑本川, 张锦芳, 李浩杰, 等. 甘蓝型油菜生育期天数与产量构成性状的相关分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2013,36(3):240-245. |
| [6] | 王学芳, 郑磊, 张智, 等. 甘蓝型油菜抗倒性及其与株型结构的关系研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016,28(9):9-13. |
| [7] | 官邑. 油菜抗倒伏性及其影响因素[J]. 作物研究, 2014,28(2):216-225. |
| [8] | 陈新军, 戚存扣, 浦惠明, 等. 甘蓝型油菜抗倒性评价及抗倒性与株型结构的关系[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2007,29(1):54-57. |
| [9] | 许凤英, 毛群帮, 邢丹英, 等. 油菜抗倒伏性的评价方法研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 2009,11(15):41-43. |
| [10] | 孙祥良, 王华弟, 曹奎荣, 等. 油菜菌核病对油菜千粒重及产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2014(11):1732-1733. |
| [11] | 王健胜, 梁亚红, 侯桂玲, 等. 油菜育种亲本主要性状相关性及主成分分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015,31(27):147-152. |
| [12] | 张文英, 王凯华. 甘蓝型油菜农艺性状相关性及主成分分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2012,51(11):2183-2185. |
| [13] | 郑本川, 崔成, 张锦芳, 等. 甘蓝型油菜育种亲本单株产量与农艺性状相关性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019,20(1):113-121. |
| [14] | 郑本川, 崔成, 李浩杰, 等. 长江流域甘蓝型油菜育种亲本农艺性状的遗传变异,相关及主成分分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2019,50(10):2196-2204. |
| [15] | 刘唐兴, 雷冬阳, 傅爱斌, 等. 高氮条件下前后期不同施氮比例对油菜倒伏和品质的影响[J]. 江西农业学报, 2009(9):104-104. |
| [16] | 薛艳, 李英, 陈乔, 等. 施氮量和栽培密度对直播油菜产量与抗病性的影响[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2018(10):36-38. |
| [17] | 张芳, 赵永国, 谷铁城, 等. 2001—2010年国家审定冬油菜品种的产量与主要性状分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2012,34(3):239-244. |
| [18] | 宋稀, 刘凤兰, 郑普英, 等. 高密度种植专用油菜重要农艺性状与产量的关系分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010,43(9):1800-1806. |
| [19] | 宋丰萍, 蒙祖庆, 窦胜玮, 等. 春播半冬性甘蓝型油菜光温因子与产量及农艺性状的典型相关分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015,23(8):987-993. |
| [20] | 张锦芳, 蒲晓斌, 李浩杰, 等. 不同来源甘蓝型油菜主要农艺性状与产量的相关分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2007,20(4):587-590. |
| [21] | 黄益国, 张学昆, 张毅, 等. 不同熟期油菜品种农艺性状与产量的相关分析[J]. 作物研究, 2017,31(3):260-264. |
| [22] | 关周博, 田建华, 郑磊, 等. 适宜机械化栽培的甘蓝型油菜农艺性状与单株产量的相关性分析及耐密油菜育种探讨[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013,29(18):79-83. |
| [23] | 李宏军, 杨鸿, 朱传霞, 等. 湖南省油菜品种农艺性状分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2015(3):41-44. |
| [24] | 陈新军, 戚存扣, 浦惠明, 等. 甘蓝型油菜抗倒性评价及抗倒性与株型结构的关系[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2007,29(1):54-57. |
| [25] | 袁志华, 冯宝萍, 赵安庆, 等. 作物茎秆抗倒伏的力学分析及综合评价探讨[J]. 农业工程学报, 2002(6):48-49. |
| [26] | 施贤波, 金林灿. 早籼稻甬籼69茎秆抗折力及稻谷容重性状探讨[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2015,56(1):46-47. |
| [1] | 金梅娟, 佘旭东, 沈明星, 陆长婴, 陶玥玥, 王海候. 稻田构建垄型土槽耦合基质栽培草莓的生产效应研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 71-76. |
| [2] | 周冬冬, 张军, 葛梦婕, 刘忠红, 朱晓欢, 李春燕. 不同氮肥处理对稻茬晚播小麦‘淮麦36’产量、氮素利用率和品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 1-7. |
| [3] | 王福玉, 陈贵菊, 孙雷明, 黄玲, 邵敏敏, 赵凯, 杨本洲, 张玉丹, 闫璐, 王霖. 耕作方式与施氮量互作对小麦生长、产量与品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 20-26. |
| [4] | 陈英花, 白如霄, 王娟, 张新疆, 刘玲慧, 刘小龙, 冯国瑞, 危常州. 叶面喷施烯效唑和硼对塔额盆地甜菜产量和含糖率的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 41-48. |
| [5] | 李兴华, 王欢, 张盛, 蔡星星, 周强, 周楠. 氮肥用量与运筹方式对晚籼稻产量及花后干物质积累与转运的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 6-13. |
| [6] | 王强强, 杨自辉, 郭树江, 张剑挥, 王多泽. 灌水量对民勤干旱沙区骏枣生长和产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 71-74. |
| [7] | 周小红. 基于多元回归分析的农作物产量估测模型研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 152-156. |
| [8] | 秦乃群, 马巧云, 高敬伟, 杨璞, 蔡金兰, 郝迎春, 李艳梅, 冀洪策, 廖祥政. 沼渣施用对花生小麦轮作作物产量及土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 58-63. |
| [9] | 武志斌, 黄超, 雷媛, 敬峰, 刘战东. 不同产量水平下冬小麦水肥利用特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 64-71. |
| [10] | 沈吉成, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 李亚鑫, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 沈裕虎, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 基于农艺性状解析乐都长辣椒种质分化情况[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 29-34. |
| [11] | 付焱焱, 李云峰, 韩冬, 马树庆. 吉林省粮食主产区玉米生长季水分盈亏及其对产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 99-105. |
| [12] | 钮力亚, 王伟伟, 张玉洁, 邹景伟, 王志, 陆莉, 王奉芝, 王伟, 于亮. 小麦品质性状及产量性状对馒头面条评分的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 129-133. |
| [13] | 姚金保, 杨学明, 周淼平, 张鹏. 江苏省小麦参试品种(系)产量与产量构成因素分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 15-19. |
| [14] | 田艺心, 高凤菊, 曹鹏鹏, 高祺. 黄淮海夏大豆干物质积累、转运及产量对播期的响应特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 20-25. |
| [15] | 董红业, 徐婷, 刘文豪, 李强, 柳延涛. 新疆塔里木盆地东南缘花生主要农艺性状的分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 26-30. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||