
中国农学通报 ›› 2023, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 107-116.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0076
所属专题: 水产渔业
李谣1( ), 杨智茹1, 程景颢1, 李杰1, 王涛1, 张凯1, 张国松2(
), 杨智茹1, 程景颢1, 李杰1, 王涛1, 张凯1, 张国松2( ), 尹绍武1(
), 尹绍武1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-15
修回日期:2022-09-22
出版日期:2023-01-15
发布日期:2023-01-17
作者简介:李谣,女,1997年出生,四川遂宁人,硕士研究生,主要从事鱼类种质资源与遗传育种研究。通信地址:210023 江苏省南京市学林路2号 南京师范大学海洋科学与工程学院,E-mail:2409509422@qq.com。
基金资助:
LI Yao1( ), YANG Zhiru1, CHENG Jinghao1, LI Jie1, WANG Tao1, ZHANG Kai1, ZHANG Guosong2(
), YANG Zhiru1, CHENG Jinghao1, LI Jie1, WANG Tao1, ZHANG Kai1, ZHANG Guosong2( ), YIN Shaowu1(
), YIN Shaowu1( )
)
Received:2022-02-15
Revised:2022-09-22
Online:2023-01-15
Published:2023-01-17
摘要:
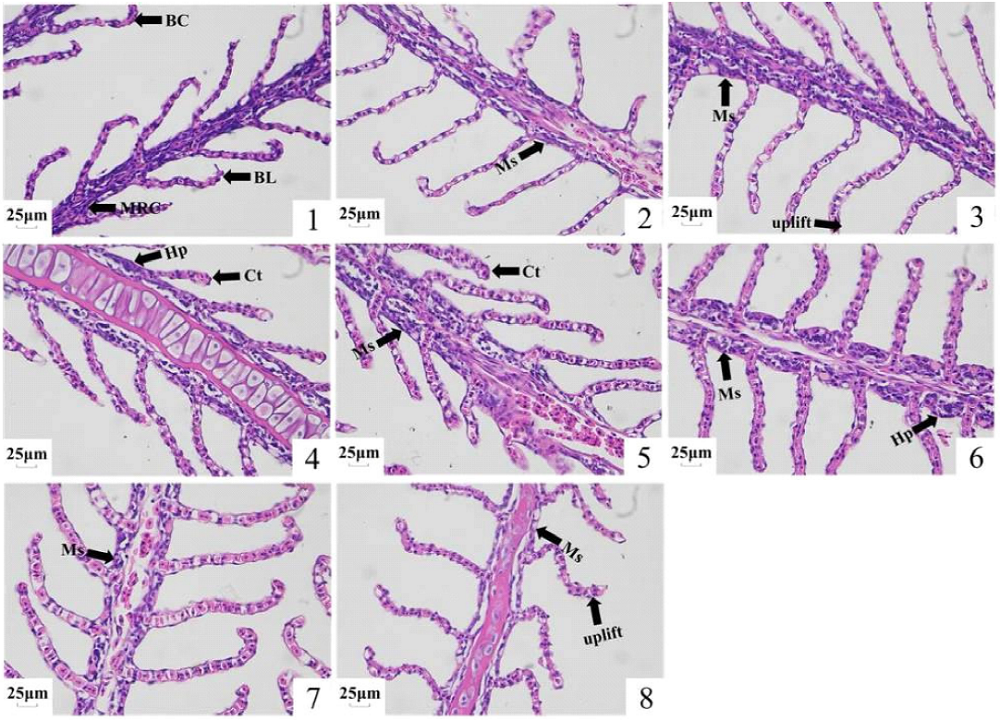
为了研究低氧胁迫(0.8±0.1) mg/L和复氧(7.3±0.5) mg/L对长吻鮠(Leiocassis longirostris)鳃组织氧传感蛋白、呼吸代谢、氧化应激、组织结构和细胞凋亡的影响。本研究对长吻鮠进行了低氧胁迫(0、2、4、6 h)和复氧(2、4、6 h)试验,采用qRT-PCR、酶活性测定、H&E染色和TUNEL切片检测等方法,比较和分析了该鱼鳃组织低氧应答基因、生理生化指标的变化。结果表明:在低氧胁迫下,长吻鮠鳃组织氧传感蛋白相关基因(HIF-1α、HIF-2α、PHDs和Vhl)表达量显著升高,复氧后较对照组仍有显著差异(P<0.05);糖酵解相关酶(PFK、HK和PK)、无氧呼吸酶(LDH)、抗氧化酶(GSH-Px、CAT和SOD)和氧化应激指标(MDA和LPO)活性和含量显著升高,TCA循环相关酶(SDH和MDH)活性显著降低,复氧后多数生理指标均逐渐恢复至对照水平。H&E染色显示低氧胁迫下长吻鮠鳃组织上皮出现了抬升,部分血细胞大量聚集使鳃小片顶端呈棒状,发生线粒体丰富细胞肿胀和增生等变化,在恢复溶氧后低氧引起的这些组织形态变化并未得到改善;TUNEL切片结果显示长吻鮠鳃组织凋亡细胞数量随低氧时间延长不断增加,凋亡相关基因(Bax、Caspase 3、p53和Apaf-1)表达量显著升高,Bcl-2表达量显著降低,恢复溶氧后细胞凋亡现象仍然存在。低氧胁迫和复氧对长吻鮠鳃组织氧传感蛋白、呼吸代谢、氧化应激、组织结构、细胞凋亡等具有明显的影响,该结果为探究鱼类低氧胁迫下分子调控机制奠定一定的理论基础,为今后开展长吻鮠耐低氧新品种选育提供基础资料。
李谣, 杨智茹, 程景颢, 李杰, 王涛, 张凯, 张国松, 尹绍武. 低氧胁迫和复氧对长吻鮠鳃组织低氧应答基因和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(2): 107-116.
LI Yao, YANG Zhiru, CHENG Jinghao, LI Jie, WANG Tao, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Guosong, YIN Shaowu. Effects of Hypoxic Stress and Reoxygenation on Hypoxic Response Genes and Physiological and Biochemical Indexes in the Gill Tissue of Leiocassis longirostris[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(2): 107-116.
| 基因 | 引物 | 引物序列(5’-3’) | 长度/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| IF-1α | HIF-1α-F | CTGGAAAGAGGGCTAAGGTG | 20 |
| HIF-1α-R | AGTGACGGTCCTGAATAGGG | 20 | |
| HIF-2α | HIF-2α-F | AAAAGCCCAGTGGATGAC | 18 |
| HIF-2α-R | TGGCGATGTTGCTGAAGT | 18 | |
| PHD1 | PHD1-F | AGCAATGGTGGCTTGTTAC | 19 |
| PHD1-R | TCAAATAAGGGCTCAATGTC | 20 | |
| PHD2 | PHD2-F | AGCCTGGATGTGAGAAGATAGC | 22 |
| PHD2-R | CCGTCTCCGTTAGGGTTGT | 19 | |
| PHD3 | PHD3-F | CTGTTTGATCGACTCCTGCTT | 21 |
| PHD3-R | TGTGGTGCTGCTTTGTGAA | 19 | |
| Vhl | Vhl-F | AGACGGATGACCCGATGTTG | 20 |
| Vhl-R | GCACACTAGCTTCCTCACCA | 20 | |
| Bax | Bax-F | TGACCGTGGCAAAGAGCA | 18 |
| Bax-R | GATCCAGGCGGAAATGTG | 18 | |
| Caspase 3 | Caspase 3-F | GGGAAACTGGGCTACAAA | 18 |
| Caspase 3-R | CTCAGCAACACGCAAACA | 18 | |
| Bcl-2 | Bcl-2-F | CGTAGCCTCGCTTCAAAA | 18 |
| Bcl-2-R | CGCGTCAGATCAATTCACA | 19 | |
| p53 | p53-F | CGTCGTAGCAGTGTCTAAAGT | 21 |
| p53-R | GACCCTCTTGTCCATTGTG | 19 | |
| Apaf-1 | Apaf-1-F Apaf-1-R | TCGCCTCTGAACCCTGCTC CTGATGGAGTCCACTGGCTGTC | 19 22 |
| β-actin | β-actin-F | TGCTGCCTCTTCCTCCTCTC | 20 |
| β-actin-R | GGACACCTGAACCTCTCATTGC | 22 |
| 基因 | 引物 | 引物序列(5’-3’) | 长度/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| IF-1α | HIF-1α-F | CTGGAAAGAGGGCTAAGGTG | 20 |
| HIF-1α-R | AGTGACGGTCCTGAATAGGG | 20 | |
| HIF-2α | HIF-2α-F | AAAAGCCCAGTGGATGAC | 18 |
| HIF-2α-R | TGGCGATGTTGCTGAAGT | 18 | |
| PHD1 | PHD1-F | AGCAATGGTGGCTTGTTAC | 19 |
| PHD1-R | TCAAATAAGGGCTCAATGTC | 20 | |
| PHD2 | PHD2-F | AGCCTGGATGTGAGAAGATAGC | 22 |
| PHD2-R | CCGTCTCCGTTAGGGTTGT | 19 | |
| PHD3 | PHD3-F | CTGTTTGATCGACTCCTGCTT | 21 |
| PHD3-R | TGTGGTGCTGCTTTGTGAA | 19 | |
| Vhl | Vhl-F | AGACGGATGACCCGATGTTG | 20 |
| Vhl-R | GCACACTAGCTTCCTCACCA | 20 | |
| Bax | Bax-F | TGACCGTGGCAAAGAGCA | 18 |
| Bax-R | GATCCAGGCGGAAATGTG | 18 | |
| Caspase 3 | Caspase 3-F | GGGAAACTGGGCTACAAA | 18 |
| Caspase 3-R | CTCAGCAACACGCAAACA | 18 | |
| Bcl-2 | Bcl-2-F | CGTAGCCTCGCTTCAAAA | 18 |
| Bcl-2-R | CGCGTCAGATCAATTCACA | 19 | |
| p53 | p53-F | CGTCGTAGCAGTGTCTAAAGT | 21 |
| p53-R | GACCCTCTTGTCCATTGTG | 19 | |
| Apaf-1 | Apaf-1-F Apaf-1-R | TCGCCTCTGAACCCTGCTC CTGATGGAGTCCACTGGCTGTC | 19 22 |
| β-actin | β-actin-F | TGCTGCCTCTTCCTCCTCTC | 20 |
| β-actin-R | GGACACCTGAACCTCTCATTGC | 22 |
| [1] |
MOHSEN, ABDEL-TAWWAB,
doi: 10.1007/s10695-019-00614-9 URL |
| [2] |
徐畅, 丁炜东, 曹哲明, 等. 急性低氧胁迫对翘嘴鳜抗氧化酶,呼吸相关酶活性及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(3):686-694.
|
| [3] |
吴志强. 鱼鳃的构造及其生理机能[J]. 生物学通报, 1993, 28(11):6-7.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1002/cne.23392 URL |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.06.020 URL |
| [8] |
肖武汉. 低氧信号传导途径与鱼类低氧适应[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2014, 44(12):1227-1235.
|
| [9] |
任倩妍, 张木子, 黎明, 等. 急性缺氧对大弹涂鱼(Boleophthalmus pectinirostris)肝脏中缺氧应答相关基因表达、蛋白含量及酶活性的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(4):889-896.
|
| [10] |
林星桦, 叶明慧,
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2013.12.007 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s00360-017-1083-8 URL |
| [13] |
徐湛宁. 草鱼在低氧胁迫下鳃的差异蛋白质组学及热休克诱导草鱼四倍体育种研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018.
|
| [14] |
区又君, 陈世喜, 王鹏飞, 等. 低氧环境下卵形鲳鲹的氧化应激响应与生理代谢相关指标的研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2017, 13(3):120-124.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
张倩, 黄进强, 权金强, 等. 急性低氧胁迫和复氧对鲫鱼氧化应激的影响[J]. 水产科学, 2020, 39(5):649-656.
|
| [17] |
凌晨, 张美东, 沙航, 等. 低氧胁迫对鲢抗氧化酶活性及SODs基因表达的影响[J]. 淡水渔业, 2021, 51(3):53-59.
|
| [18] |
常志成, 温海深, 张美昭, 等. 溶解氧水平对花鲈幼鱼氧化应激与能量利用的影响及生理机制[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(7):20-28.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1242/jeb.00594 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1252-x URL |
| [22] |
刘康, 何金钊. 投喂频率和投喂水平对长吻鮠幼鱼生长和免疫的影响[J]. 渔业现代化, 2019, 46(1):1-5.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
孙玲玲. 麦穗鱼缺氧诱导因子-1α的鉴定与功能分析[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2012.
|
| [25] |
林星桦, 潘炎杨, 陈芳圆, 等. 多鳞鱚vhl基因克隆及其低氧胁迫下的表达变化[J]. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(5):1201-1208.
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s00360-005-0059-2 URL |
| [27] |
王资生. 半滑舌鳎HIF-1α,Hb-α1和Tf基因克隆及在低氧胁迫下的表达分析[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2012.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
钱辰颖, 郑国栋, 陈杰, 等. 溶解氧对团头鲂耐低氧新品系F5代的鳃组织形态及各组织酶活性的影响[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(4):73-81.
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.002 URL |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2000.tb00478.x URL |
| [33] |
贾秀琪, 张宏叶, 王丽, 等. 低氧胁迫对河川沙塘鳢抗氧化酶及ATP酶活性的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 2017(3):306-313.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.09.024 URL |
| [37] |
丁晨雨, 胡利双, 李云, 等. 低氧胁迫对鲢心肌细胞凋亡及其调控基因Bax、Bcl-2表达的影响[J]. 淡水渔业, 2018, 48(2):10-15.
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.08.029 URL |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1007/s10695-021-00989-8 pmid: 34313912 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00267.2005 URL |
| [43] |
陈世喜, 王鹏飞, 区又君, 等. 急性和慢性低氧胁迫对卵形鲳鲹鳃器官的影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 2017, 13(1):124-130.
|
| [1] | 卢倩倩, 冯琳骄, 王爽, 古力扎提·包尔汗, 褚韧, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫对鲜食葡萄生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 62-70. |
| [2] | 罗志明, 覃伟, 尹炯, 李银煳, 张荣跃, 李俊. 甘蔗种质对甘蔗蓟马的耐害性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(34): 107-112. |
| [3] | 王硕, 贾潇倩, 何璐, 李浩然, 王红光, 何建宁, 李东晓, 房琴, 李瑞奇. 作物对干旱胁迫的响应机制及提高作物抗旱能力的调控措施研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(29): 31-44. |
| [4] | 杨瑞卿, 梁晶, 施凯峰, 沈青云, 赵昀, 石杨, 严巍. 化学药剂对行道树悬铃木球果的形态和生理影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(2): 26-30. |
| [5] | 张瑞玖, 马恢, 籍立杰, 任德志, 李双东, 张耀辉, 王莉红. 干旱胁迫对马铃薯品种生长及生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(15): 34-39. |
| [6] | 郑植尹, 王芳. 干旱胁迫对马铃薯生理特性及解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(8): 14-24. |
| [7] | 孙璐, 冯国军, 刘大军, 杨晓旭, 刘畅, 闫志山. 超干处理延长菜豆种子寿命的生理生化机制研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(34): 64-70. |
| [8] | 柴芃沛, 韩锁义, 崔梦杰, 郭俊佳, 黄冰艳, 董文召, 张新友. 花生籽仁抗黄曲霉菌生理生化机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(30): 89-97. |
| [9] | 姜露露, 于坤, 刘冬冬, 王军武, 包兴成, 郑重. 干旱胁迫对无花果叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(28): 62-67. |
| [10] | 张妞, 王东, 赵远征, 项鹏, 邱廷艳, 赵鑫, 高腾达, 高志超, 周洪友. 马铃薯腐烂茎线虫生防细菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(18): 138-146. |
| [11] | 张金凤, 陈佩珍, 孙晓波, 胡兴峰, 季孔庶. 干旱对马尾松幼苗光合作用及相关生理的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(1): 32-38. |
| [12] | 杜卓, 路运才. 玉米抗旱化学调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(33): 7-11. |
| [13] | 文章, 耿贵, 王宇光, 孙菲, 王皙玮, 於丽华. 盐胁迫下耐盐甜菜生理及其蛋白差异表达分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(32): 8-16. |
| [14] | 刘忠奇, 贺记外, 张海清, 刘爱民. 植物种子脱水耐性的研究现状分析与展望[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(2): 36-41. |
| [15] | 乔志文, 王积琛, 李彦丽. 甘蓝夜蛾研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(18): 147-153. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||