
中国农学通报 ›› 2023, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (35): 94-102.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-1001
收稿日期:2022-11-28
修回日期:2023-01-23
出版日期:2023-12-11
发布日期:2023-12-11
通讯作者:
作者简介:盛妮,女,1998年出生,浙江金华人,硕士研究生,研究方向:土壤微生物学。通信地址:311300 浙江省杭州市临安区锦城街道武肃街666号 浙江农林大学东湖校区林业与生物技术学院,E-mail:shengni@stu.zafu.edu.cn。
基金资助:
SHENG Ni1( ), CHENG Jianhua1,2(
), CHENG Jianhua1,2( ), SUN Zhixiang2, TANG Xiangyu1,2
), SUN Zhixiang2, TANG Xiangyu1,2
Received:2022-11-28
Revised:2023-01-23
Published-:2023-12-11
Online:2023-12-11
摘要:
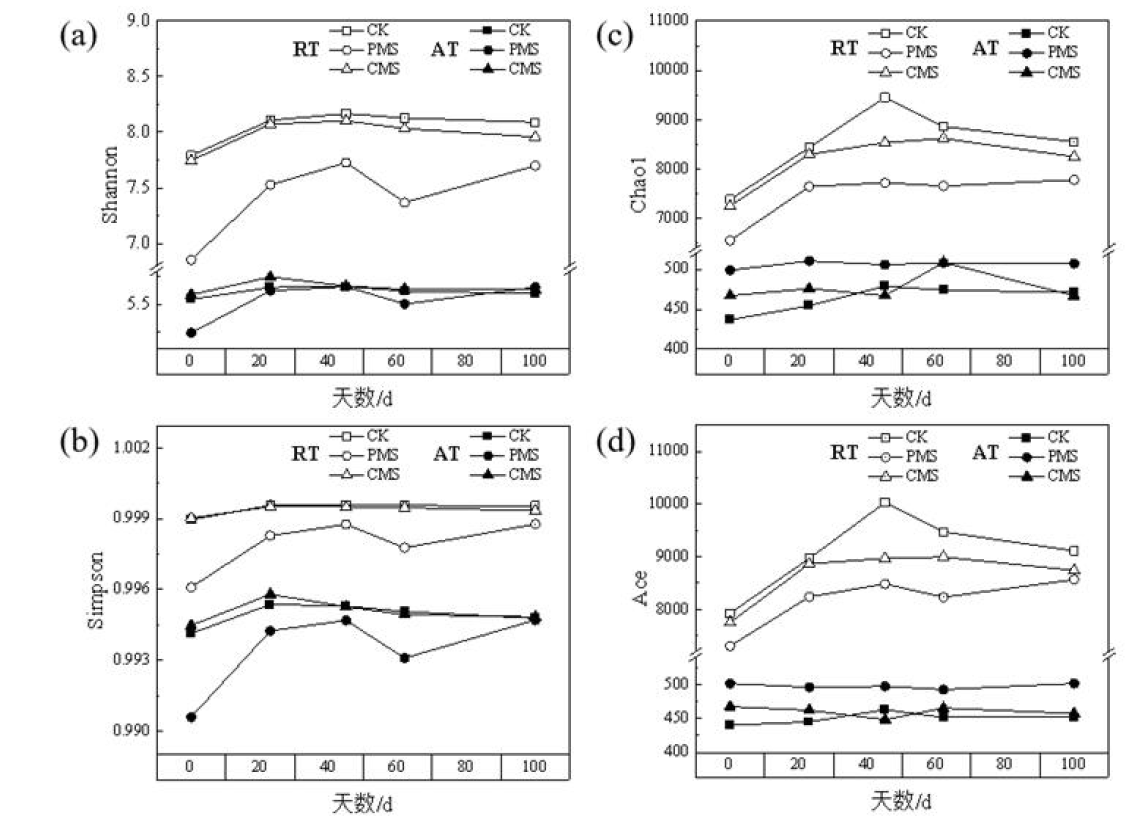
土壤微生物群落由少数丰富类群和多数稀有类群组成,揭示丰富和稀有细菌的分布特征和动态变化对于理解土壤生态系统至关重要。本研究以旱地紫色土为研究对象,以猪粪和鸡粪为有机肥的外源,进行为期100 d的培养试验,并设计5个采样时间点,采用高通量测序技术,对不施肥对照处理(CK),施加猪粪处理(PMS),施加鸡粪处理(CMS)紫色土中细菌群落进行分析。结果表明:稀有细菌的数量、分类群以及α多样性指数高于丰富细菌,说明两者的分布组成存在差异。丰富和稀有细菌群落结构具有相似的动态变化,施用猪粪对微生物群落结构的影响异于未施肥和施鸡粪处理。共现网络分析显示稀有细菌的拓扑特性显著高于其他类群,但少数丰富细菌占据了网络的中心节点。条件稀有或丰富细菌具有高度中介中心性,表明其在群落动态变化中存在一定贡献。研究结果有助于理解施用粪肥土壤中细菌群落的动态变化及其生态网络。
盛妮, 程建华, 孙志祥, 唐翔宇. 四川盆地紫色土中丰富及稀有细菌的分布特征与动态变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(35): 94-102.
SHENG Ni, CHENG Jianhua, SUN Zhixiang, TANG Xiangyu. Distribution Characteristics and Dynamics of Abundant and Rare Bacteria in Purple Soil of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(35): 94-102.
| [1] |
林先贵, 胡君利. 土壤微生物多样性的科学内涵及其生态服务功能[J]. 土壤学报, 2008(5):892-900.
|
| [2] |
doi: S0966-842X(18)30047-7 pmid: 29550356 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1146/marine.2012.4.issue-1 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13606 pmid: 27871146 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1111/mec.14218 pmid: 28665016 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.01.007 pmid: 25667105 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.11.017 pmid: 22154467 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01516 pmid: 28861048 |
| [10] |
李江涛, 罗甜甜, 杜满聪, 等. 畜禽粪肥添加及干湿交替强度对土壤微生物功能多样性的影响[J]. 广东农业科学, 2018, 45(6):68-77.
|
| [11] |
许来鹏, 万鲜花, 孙向丽, 等. 畜禽粪肥和秸秆还田对玉米根际微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(9):137-146.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-0913 |
| [12] |
朱菲莹, 张屹, 肖姬玲, 等. 生物有机肥对土壤微生物群落结构变化及西瓜枯萎病的调控[J]. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(12):2323-2333.
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.08.018 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.2136/sssaj2008.0259 URL |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1007/s11368-011-0449-x URL |
| [16] |
王齐齐, 徐虎, 马常宝, 等. 西部地区紫色土近30年来土壤肥力与生产力演变趋势分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(6)1492-1499.
|
| [17] |
程建华. 施用粪肥对紫色土抗生素抗性基因丰度和多样性的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019.
|
| [18] |
孙志祥, 邓建波, 吕玉娟, 等. 长江上游低山丘陵区土壤水分特征曲线传递函数研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2022, 41(6):97-104.
|
| [19] |
鲜青松, 唐翔宇, 朱波. 坡耕地薄层紫色土-岩石系统中氮磷的迁移特征[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(7):2843-2849.
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.29 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601602103 pmid: 16723398 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.104483 URL |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1139/cjm-2020-0143 URL |
| [26] |
郑丹, 李鹤鸣, 韩力. 土壤放线菌资源及其应用[J]. 绿色科技, 2021, 23(2):183-187,193.
|
| [27] |
doi: S0269-7491(16)32803-2 pmid: 28336094 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.54 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01458-9 pmid: 31836929 |
| [30] |
pmid: 16168637 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aap9516 URL |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.174 |
| [33] |
田飞飞, 纪鸿飞, 王乐云, 等. 施肥类型和水热变化对农田土壤氮素矿化及可溶性有机氮动态变化的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10):4717-4726.
|
| [34] |
于树, 汪景宽, 王鑫, 等. 不同施肥处理的土壤肥力指标及微生物碳、氮在玉米生育期内的动态变化[J]. 水土保持学报, 2007(4):137-140.
|
| [35] |
潘丹, 孔凡斌, 张雅燕, 等. 基于环境要素禀赋的畜禽养殖总量控制研究——以鄱阳湖生态经济区为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(29):1-7.
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102938108 pmid: 21436049 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109326109 pmid: 22232669 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-113 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108222 URL |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63462-1 URL |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.2013.58.1.0267 URL |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1038/nature04983 URL |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1007/s11756-021-00928-1 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1111/ele.12527 pmid: 26415689 |
| [46] |
|
| [1] | 沙刚, 阴红彬, 曹宏杰, 谢立红, 黄庆阳, 徐明怡. 不同地质年代火山森林土壤甲烷氧化通量及其影响因素[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(31): 83-92. |
| [2] | 邓利梅, 陈晓芬, 汪璇, 崔荣阳, 周涛, 刘刚才. 水肥耦合对紫色土中小麦肥料减施效应的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(24): 51-56. |
| [3] | 薛艳凌, 陈新平, 张伟. 振荡方式对土壤磷素分级的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(33): 80-86. |
| [4] | 乔志文. 甜菜褐斑病发生时间动态规律研究乔志文[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(6): 83-88. |
| [5] | 王利民,刘佳,季富华,姚保民,杨福刚. 中国小麦面积种植结构时空动态变化分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(18): 12-24. |
| [6] | 张红梅,余砚碧,计思贵,王 燕,杨海林,吴 迪,陈福寿,张立猛. 烤烟-油菜轮作田昆虫群落结构及时间动态[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(14): 122-128. |
| [7] | 陈奋林. 紫色土侵蚀区种植福建柏的技术措施研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(25): 32-36. |
| [8] | 黄石德,黄龙为,李建民,黄雍容,黄锦祥,朱洪如. 不同生态恢复措施对紫色土活性有机碳的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(18): 107-113. |
| [9] | 赵丽,贺玉晓,刘刚才,史亮涛,张明忠,戴怡. 干热河谷区紫色土玉米季协调农学、水体环境和经济效益的容许施肥量[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(33): 55-63. |
| [10] | 李淑英,朱加保,路献勇,崔金杰,马 艳,雒珺瑜,程福如. 皖西南春棉田主要害虫和天敌种群时序动态格局[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(14): 68-74. |
| [11] | 郝文静,陈晓燕,胡建新,莫 斌. 紫色土区林地土壤入渗性能试验研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(24): 204-209. |
| [12] | 姜俊红,汪 军,韦歆娜. 南雄紫色土特性及土壤水分特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(2): 215-218. |
| [13] | 颜衡祁. 衡阳紫色土丘陵坡地恢复过程中植物群落结构及多样性的变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(19): 180-184. |
| [14] | 刘作云,杨 宁. 紫色土丘陵坡地不同恢复阶段土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(18): 163-167. |
| [15] | 郑磊 江长胜 孙丽娟 刘聪 冉思丹 黄欢 邱昕恺. 地膜覆盖对菜园紫色土壤环境因子及N2O排放的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(30): 82-87. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||