
中国农学通报 ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (34): 97-101.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0587
徐翎清1,2( ), 李佳佳1,2, 常晓1,2, 张云龙1,2, 刘大丽1,2(
), 李佳佳1,2, 常晓1,2, 张云龙1,2, 刘大丽1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-10
修回日期:2022-09-27
出版日期:2022-12-05
发布日期:2022-11-25
通讯作者:
刘大丽
作者简介:徐翎清,男,1998年出生,贵州贵阳人,在读研究生,研究方向:作物分子生物学。通信地址:150080 黑龙江省哈尔滨市南岗区学府路74号 黑龙江大学现代农业与生态环境学院,Tel:0451-86609494,E-mail:基金资助:
XU Lingqing1,2( ), LI Jiajia1,2, CHANG Xiao1,2, ZHANG Yunlong1,2, LIU Dali1,2(
), LI Jiajia1,2, CHANG Xiao1,2, ZHANG Yunlong1,2, LIU Dali1,2( )
)
Received:2022-07-10
Revised:2022-09-27
Online:2022-12-05
Published:2022-11-25
Contact:
LIU Dali
摘要:
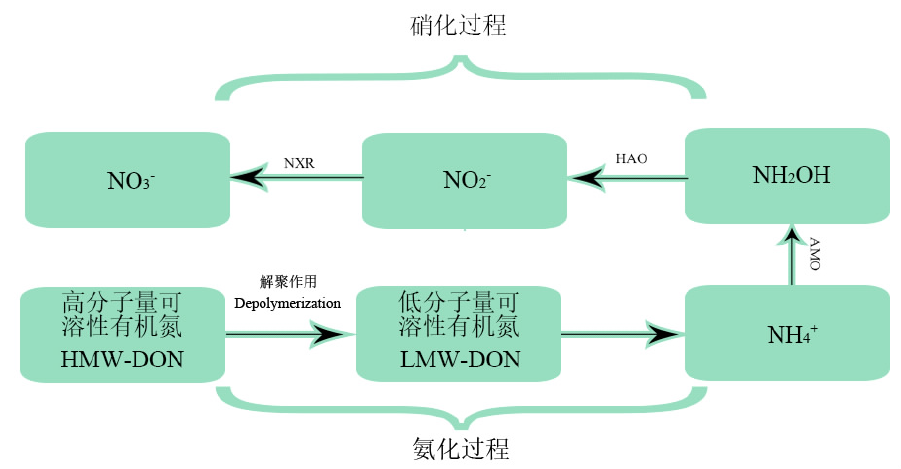
无机氮是作物吸收利用氮的重要来源,土壤有机氮矿化能力的强弱决定着土壤对作物的供氮能力。土壤有机氮矿化主要由土壤微生物驱动,是在微生物作用下将有机氮分解成氨态氮和硝态氮的过程。有机氮矿化速率的变化主要归因于环境因素变化后土壤微生物的变化,研究土壤氮矿化对土壤氮循环和土壤供氮能力有着重要意义。文章综述了土壤氮矿化过程中微生物的作用机理,探讨了在不同环境因素下微生物的变化对土壤氮矿化速率的影响,以及植物—土壤—微生物的互作机制。研究可为探索土壤氮矿化过程和改善土壤供氮能力提供理论参考。
中图分类号:
徐翎清, 李佳佳, 常晓, 张云龙, 刘大丽. 土壤氮矿化相关机理的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(34): 97-101.
XU Lingqing, LI Jiajia, CHANG Xiao, ZHANG Yunlong, LIU Dali. The Mechanism of Soil Nitrogen Mineralization: Research Progress[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(34): 97-101.
| [1] | 李佳佳, 魏多, 徐翎清, 等. 甜菜对低氮胁迫的形态学响应机制[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(36):41-46. |
| [2] |
VIDAL E A, ALVAREZ J M, ARAUS V, et al. Nitrate in 2020: Thirty years from transport to signaling networks[J]. Plant cell, 2020, 32(7):2094-2119.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00748 URL |
| [3] |
MOREAU D, BARDGETT R D, FINLAY R D, et al. A plant perspective on nitrogen cycling in the rhizosphere[J]. Functional ecology, 2019, 33(4):540-552.
doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13303 |
| [4] |
SCHULTEN H R, SCHNITZER M. The chemistry of soil organic nitrogen: a review[J]. Biology and fertility of soils, 1997, 26(1):1-15.
doi: 10.1007/s003740050335 URL |
| [5] |
KEUPER F, DORREPAAL E, VAN BODEGOM P M, et al. Experimentally increased nutrient availability at the permafrost thaw front selectively enhances biomass production of deep-rooting subarctic peatland species[J]. Global change biology, 2017, 23(10):4257-4266.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.13804 pmid: 28675586 |
| [6] |
GUNTINAS M E, LEIROS M C, TRASAR-CEPEDA C, et al. Effects of moisture and temperature on net soil nitrogen mineralization: A laboratory study[J]. European journal of soil biology, 2012, 48:73-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2011.07.015 URL |
| [7] | 杜薇, 孙楠, 周古月, 等. 温湿度对不同管理方式高寒草甸土壤氮矿化的影响[J]. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(4):1-11. |
| [8] |
CANFIELD D E, GLAZER A N, FALKOWSKI P G. The evolution and future of earth's nitrogen cycle[J]. Science, 2010, 330:192-196.
doi: 10.1126/science.1186120 pmid: 20929768 |
| [9] |
KUYPERS M M M, MARCHANT H K, KARTAL B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature reviews microbiology, 2018, 16(5):263-276.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2018.9 pmid: 29398704 |
| [10] | 孔得杨. 微生物氮转化途径综述[J]. 西部皮革, 2017, 39(4):42-47. |
| [11] | 王翰琨, 吴永波, 刘俊萍, 等. 生物炭对土壤氮循环及其功能微生物的影响研究进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2022, 38(6):689-701. |
| [12] |
JONES D L, SHANNON D, V. MURPHY D, et al. Role of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in soil N cycling in grassland soils[J]. Soil biology and biochemistry, 2004, 36(5):749-756.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.01.003 URL |
| [13] |
GE S, WANG S, YANG X, et al. Detection of nitrifiers and evaluation of partial nitrification for wastewater treatment: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 140:85-98.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.004 pmid: 25796420 |
| [14] |
SOLIMAN M, ELDYASTI A. Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB): Opportunities and applications—a review[J]. Reviews in environmental science and biotechnology, 2018, 17(2):285-321.
doi: 10.1007/s11157-018-9463-4 URL |
| [15] |
CáCERES R, MALIńSKA K, MARFà O. Nitrification within composting: A review[J]. Waste management, 2018, 72:119-137.
doi: S0956-053X(17)30795-X pmid: 29153903 |
| [16] |
LEININGER S, URICH T, SCHLOTER M, et al. Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils[J]. Nature, 2006, 442:806-809.
doi: 10.1038/nature04983 URL |
| [17] | 贺纪正, 张丽梅. 土壤氮素转化的关键微生物过程及机制[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(1):98-108. |
| [18] | 程宽, 李涵, 杜衍红, 等. 微生物介导铁还原耦合氨氧化过程的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2022, 62(6):2249-2264. |
| [19] | 陈阳军, 陈敏. 亚硝酸盐氮、氧同位素技术及其在海洋氮循环中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2021, 36(12):1224-1234. |
| [20] |
NENDEL C, MELZER D, THORBURN P J. The nitrogen nutrition potential of arable soils[J]. Scientific reports, 2019, 9(1):5851.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42274-y pmid: 30971710 |
| [21] |
MILLER K S, GEISSELER D. Temperature sensitivity of nitrogen mineralization in agricultural soils[J]. Biology and fertility of soils, 2018, 54(7):853-860.
doi: 10.1007/s00374-018-1309-2 URL |
| [22] | WANG Y, DIAO H-J, DONG K-H, et al. Effects of precipitation change and nitrogen addition on soil net N mineralization in a saline-alkaline grassland of Northern Shanxi Province, China[J]. The journal of applied ecology, 2021, 32(7):2389-2396. |
| [23] |
BRAOS L B, RUIZ J, LOPES I G, et al. Mineralization of nitrogen in soils with application of acid whey at different pH[J]. Journal of soil science and plant nutrition, 2020, 20(3):1102-1109.
doi: 10.1007/s42729-020-00196-z URL |
| [24] |
WATTS D B, TORBERT H A, FENG Y C, et al. Soil microbial community dynamics as influenced by composted dairy manure, soil properties, and landscape position[J]. Soil science, 2010, 175(10):474-486.
doi: 10.1097/SS.0b013e3181f7964f URL |
| [25] |
SRADNICK A, MURUGAN R, OLTMANNS M, et al. Changes in functional diversity of the soil microbial community in a heterogeneous sandy soil after long-term fertilization with cattle manure and mineral fertilizer[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2013, 63:23-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.09.011 URL |
| [26] | TIAN F F, JI H F, WANG L Y, et al. Effects of various combinations of fertilizer, soil moisture, and temperature on nitrogen mineralization and soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soil[J]. Environmental science, 2018, 39(10):4717-4726. |
| [27] | AKBARI F, FALLAH S, DAHMARDEH M, et al. Interaction effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on nitrogen mineralization of wheat residues in a calcareous soil[J]. Journal of plant nuturition, 2020, 43(1):1-12. |
| [28] | HAN B Y, ZHANG W, HU F Y, et al. Influence of artificial root exudates and actual root exudates on the microbial community in pyrene-contaminated soil[J]. Environmental science, 2022, 43(2):1077-1088. |
| [29] |
HAICHAR F E, MAROL C, BERGE O, et al. Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure[J]. ISME Journal, 2008, 2(12):1221-1230.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2008.80 pmid: 18754043 |
| [30] |
SCHLATTER D C, REARDON C L, JOHNSON-MAYNARD J, et al. Mining the drilosphere: Bacterial communities and denitrifier abundance in a no-till wheat cropping system[J]. Frontiers in microbiology, 2019, 10:1339.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01339 pmid: 31316473 |
| [31] |
NAVARRO-NOYA Y E, GOMEZ-ACATA S, MONTOYA-CIRIACO N, et al. Relative impacts of tillage, residue management and crop-rotation on soil bacterial communities in a semi-arid agroecosystem[J]. Soil Biology & biochemistry, 2013, 65:86-95.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.05.009 URL |
| [32] | JIANG Y Z, LIU Q L, ZHANG Y G, et al. Effect of crop rotation and continuous cropping on nitrogen mineralization characteristics in yellow cornfield[J]. International journal of agriculture and biology, 2018, 20(5):1175-1180. |
| [33] | 于树, 汪景宽, 李双异. 应用PLFA方法分析长期不同施肥处理对玉米地土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2008(9):4221-4227. |
| [34] | 邬子俊, 段晓清, 李文卿, 等. 混交对亚热带针叶树根际土壤氮矿化和微生物特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2022(20):1-11. |
| [35] |
CRUZ A F, HAMEL C, HANSON K, et al. Thirty-seven years of soil nitrogen and phosphorus fertility management shapes the structure and function of the soil microbial community in a brown chernozem[J]. Plant and soil, 2009, 315(1-2):173-184.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-008-9742-x URL |
| [36] |
李娟, 赵秉强, 李秀英, 等. 长期不同施肥制度下几种土壤微生物学特征变化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2008(4):891-899.
doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2008.04.018 |
| [37] |
HASSINK J, BOUWMAN L A, ZWART K B, et al. Relationships between habitable pore space, soil biota and mineralization rates in grassland soils[J]. Soil biology and biochemistry, 1993, 25(1):47-55.
doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(93)90240-C URL |
| [38] | 周煜杰, 贾夏, 赵永华, 等. 森林生态系统土壤真菌群落及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(8):1703-1712. |
| [39] |
MICHAEL H B. Microbial and faunal interactions and effects on litter nitrogen and decomposition in agroecosystems[J]. Ecological monographs, 1992, 62(4):569-591.
doi: 10.2307/2937317 URL |
| [40] | 高珊, 尹航, 傅民杰, 等. 冻融循环对温带3种林型下土壤微生物量碳、氮和氮矿化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(21):7859-7869. |
| [41] | 王常慧, 邢雪荣, 韩兴国. 草地生态系统中土壤氮素矿化影响因素的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2004(11):2184-2188. |
| [42] | 龚伟, 胡庭兴, 王景燕, 等. 川南天然常绿阔叶林人工更新后枯落物对土壤供氮潜力的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2006(S2):64-72. |
| [43] |
TAO K, KELLY S, RADUTOIU S. Microbial associations enabling nitrogen acquisition in plants[J]. Current opinion in microbiology, 2019, 49:83-89.
doi: S1369-5274(19)30059-1 pmid: 31733615 |
| [44] |
ZHALNINA K, LOUIE K B, HAO Z, et al. Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly[J]. Nature microbiology, 2018, 3(4):470-480.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0129-3 pmid: 29556109 |
| [45] | 刘王锁, 李海泉, 何毅, 等. 根际微生物对植物与土壤交互调控的研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(5):318-327. |
| [46] |
BAIS H P, WEIR T L, PERRY L G, et al. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms[J]. Annual review of plant biology, 2006, 57:233-266.
pmid: 16669762 |
| [47] |
HAICHAR F E Z, MAROL C, BERGE O, et al. Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure[J]. The ISME Journal, 2008, 2(12):1221-1230.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2008.80 URL |
| [48] |
WANG Q T, XIAO J, DING J X, et al. Differences in root exudate inputs and rhizosphere effects on soil N transformation between deciduous and evergreen trees[J]. Plant and soil, 2021, 458(1-2):277-289.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-019-04156-0 URL |
| [49] |
LIU Y, EVANS S E, FRIESEN M L, et al. Root exudates shift how N mineralization and N fixation contribute to the plant-available N supply in low fertility soils[J]. Soil biology and biochemistry, 2022, 165:108541.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108541 URL |
| [50] |
YUAN Y S, ZHAO W Q, ZHANG Z L, et al. Impacts of oxalic acid and glucose additions on N transformation in microcosms via artificial roots[J]. Soil biology & biochemistry, 2018, 121:16-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.03.002 URL |
| [51] |
DRAKE J E, DARBY B A, GIASSON M A, et al. Stoichiometry constrains microbial response to root exudation-insights from a model and a field experiment in a temperate forest[J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(2):821-838.
doi: 10.5194/bg-10-821-2013 URL |
| [1] | 赵双梅, 刘宪斌, 李红梅, 董文彩, 沈健萍, 包金美, 梁芳, 鲁美. 云南哀牢山湿性常绿阔叶林土壤碳分布特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 88-95. |
| [2] | 王丽霞, 殷晓敏, 刘永霞, 连子豪, 王必尊, 何应对. 间作韭菜模式下番木瓜根区微生物群落变化特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(31): 66-76. |
| [3] | 晁赢, 付钢锋, 阎祥慧, 杭中桥, 杨全刚, 王会, 潘红, 娄燕宏, 诸玉平. 有机肥对作物品质、土壤肥力及环境影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(29): 103-107. |
| [4] | 范雅琦, 王亚南, 霍瑞轩, 姚涛, 杨珍平, 乔月静, 郭来春. 轮作模式下土壤微生物与线虫群落的互作研究现状[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(25): 108-113. |
| [5] | 洪慈清, 孙语遥, 莫雯婧, 方云, 陈芳容, 桂芳泽, 关雄, 潘晓鸿. 茶叶浸取液制备的纳米银对土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(23): 56-63. |
| [6] | 杜倩, 李琳, 刘铁男, 梁素钰. 复合菌肥对盐渍土土壤微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(2): 38-43. |
| [7] | 魏加弟, 王永芬, 何翔, 杨佩文, 俞艳春, 郑泗军, 徐胜涛. 植物覆盖对蕉园土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(17): 90-97. |
| [8] | 于会丽, 徐变变, 徐国益, 邵微, 高登涛, 司鹏. 生物有机肥对苹果幼苗生长、生理特性以及土壤微生物功能多样性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(1): 32-38. |
| [9] | 林秀颜, 江赜伟, 陈曦, 张淑娜, 戴惠东, 杨士红. 稻田土壤微生物数量和酶活性对水碳调控的响应[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(7): 75-80. |
| [10] | 谢云, 郭芳芸, 曹兵. 大气CO2浓度倍增对宁夏枸杞根区土壤微生物与酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(3): 90-97. |
| [11] | 李林蓉, 冯建路, 刘苗苗, 梅昊, 康振烨, 蔡青年. 作物种植模式对土壤微生物和农田有害生物的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(29): 99-106. |
| [12] | 李静超, 佘容, 杨晓燕. 土壤微生物宏基因组研究现状——基于Citespace文献计量分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(28): 142-152. |
| [13] | 张仁军, 陈雅琼, 张洁梅, 姚正平, 吴金虎, 侯正学, 殷红慧, 徐天养, 欧阳进, 王亮, 陈穗云. 健康与根结线虫病烟田根际土壤微生物群落对比分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(26): 124-132. |
| [14] | 游萍, 肖群英, 王丹, 尚桃, 杨敬义, 李亚梅, 薛晓辉. 草海湿地黑色沼泽土不同利用方式可培养微生物的多样性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(26): 74-79. |
| [15] | 王秋红, 宋柏权, 王孝纯, 景若楠, 杨曦娅, 周建朝. 苗期甜菜根系分泌物的分布特征研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(17): 13-18. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||