
中国农学通报 ›› 2023, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (28): 151-157.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0812
张明1( ), 杨帅1, 曹艳飞1, 卢晓文1, 焦钰1,2(
), 杨帅1, 曹艳飞1, 卢晓文1, 焦钰1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-26
修回日期:2022-12-28
出版日期:2023-10-05
发布日期:2023-09-25
通讯作者:
焦钰,女,1981年出生,山东枣庄人,教授,博士,研究方向:海产无脊椎动物生物学及增养殖技术。通信地址:524088 广东省湛江市麻章区海大路1号 广东海洋大学水产学院,Tel:0759-2383346,E-mail:jiaoyu1981@hotmail.com。
作者简介:张明,女,1995年出生,山东菏泽人,硕士,研究方向:珍珠培育与加工。通信地址:524088 广东省湛江市麻章区海大路1号 广东海洋大学水产学院,Tel:0759-2383346,E-mail:919163113@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Ming1( ), YANG Shuai1, CAO Yanfei1, LU Xiaowen1, JIAO Yu1,2(
), YANG Shuai1, CAO Yanfei1, LU Xiaowen1, JIAO Yu1,2( )
)
Received:2022-09-26
Revised:2022-12-28
Published-:2023-10-05
Online:2023-09-25
摘要:
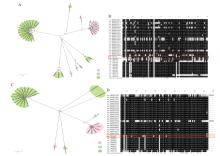
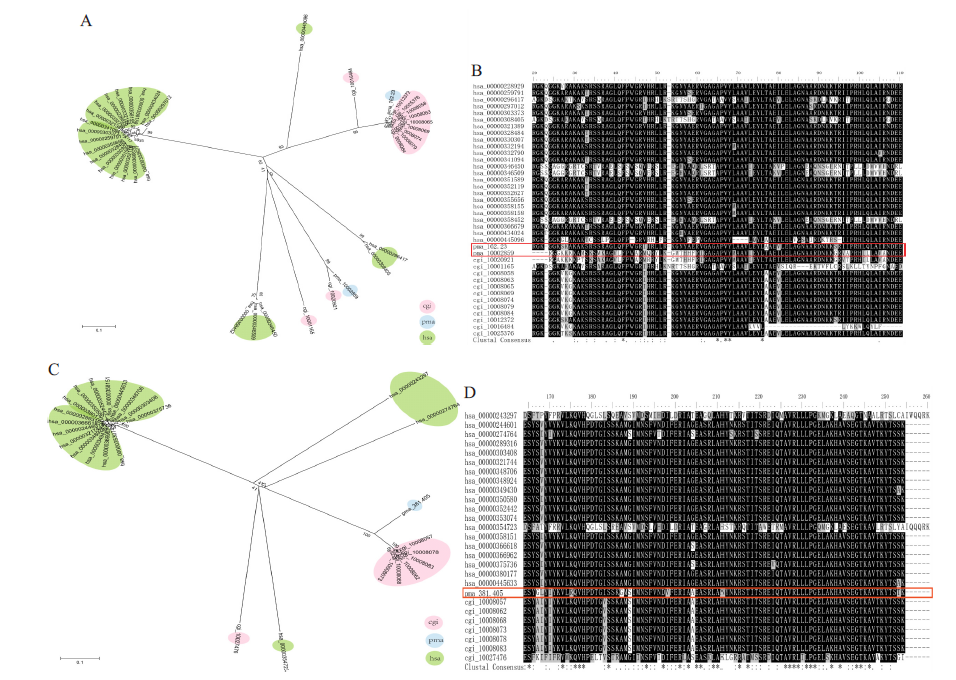
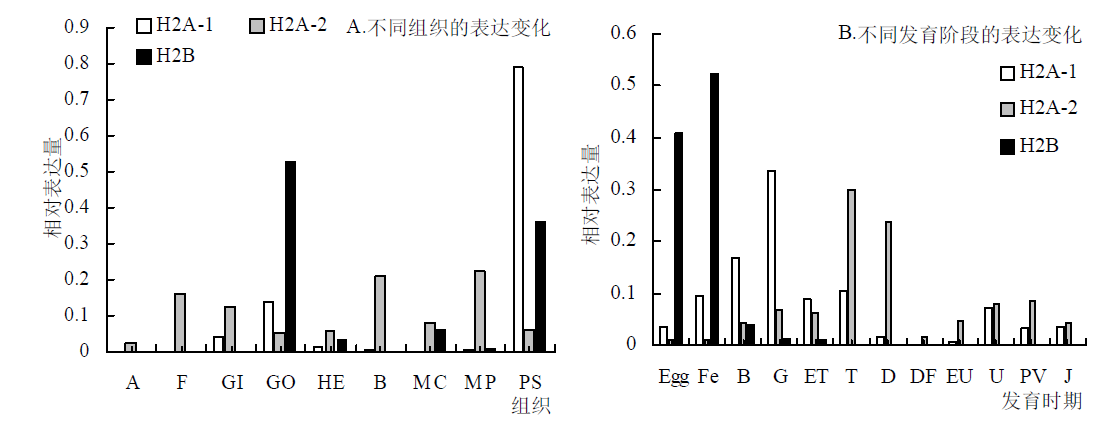
分析马氏珠母贝组蛋白H2的分子进化特征,及其在马氏珠母植核免疫调控中的作用,为进一步阐述组蛋白H2在马氏珠母贝中的生理功能提供理论基础。应用生物信息学分析方法对马氏珠母贝(Pinctada fucata martensi)、人(Homo sapiens)、长牡蛎(Crassostrea gigas)等9个物种中的组蛋白H2A和H2B进行全基因组鉴定,并分析了它们的分子进化历程;利用课题组已有数据,分析组蛋白H2A和H2B在马氏珠母贝发育、组织和植核免疫中的功能。通过比较基因组分析发现,人的基因组中含有27个组蛋白H2A、20个组蛋白H2B,长牡蛎基因组中含有12个组蛋白H2A、8个组蛋白H2B,马氏珠母贝基因组中仅含有2个H2A(H2A-1和H2A-2)、1个H2B,与其他物种相比呈现收缩现象。序列比对分析发现,人的基因组中有6个H2A变体和2个H2B变体,牡蛎有3个H2A变体和1个H2B变体,马氏珠母贝中有1个H2A变异体(H2A-2)。在马氏珠母贝中,植核后H2A-1和H2B的表达发生了不同程度的变化,说明它们参与植核免疫调控;基因H2A-1在原肠胚期表达量较高,H2A-2在担轮幼虫和D型幼虫中的表达量较高,H2B发育前期表达量较高。H2A-1在珍珠囊中表达量较高,H2A-2在血细胞、足和外套膜套膜区表达量相对较高,H2B在性腺和珍珠囊中表达量较高。马氏珠母贝基因组中仅含有2个组蛋白H2基因,它们参与调控植核免疫且在免疫调控过程中发挥的作用不同。
张明, 杨帅, 曹艳飞, 卢晓文, 焦钰. 马氏珠母贝组蛋白H2分子进化及功能分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(28): 151-157.
ZHANG Ming, YANG Shuai, CAO Yanfei, LU Xiaowen, JIAO Yu. Molecular Evolution and Functional Analysis of Histone H2 from Pinctada fucata martensii[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(28): 151-157.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-1-202 pmid: 18226187 |
| [2] |
pmid: 293727 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)89191-8 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.07.001 URL |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019364 pmid: 25561719 |
| [7] |
黄艳, 周政. H2A-H2B类型组蛋白及其伴侣蛋白的研究进展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2018, 45(9):971-980.
|
| [8] |
pmid: 14583738 |
| [9] |
pmid: 11993987 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.C900032200 pmid: 19351884 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02511-9 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/S0300-9084(98)80018-7 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.5.2356 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0071 URL |
| [15] |
武向敏, 赵燕静, 孔祥会, 等. 青鱼、草鱼、鲢鱼和鳙鱼组蛋白H2A N-端基因克隆及其衍生抗菌肽[J]. 水产科学, 2014, 33(5):311-316.
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1042/bj20020980 URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2009.08.007 URL |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2006.08.013 URL |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9534-2 URL |
| [20] |
王志成, 梁志辉, 杨家林, 等. 北海营盘近海区马氏珠母贝自然资源调查[J]. 广西科学, 2008, 15(2):205-208.
|
| [21] |
王梅芳, 余祥勇. 育珠贝细胞小片及处理技术研究进展[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2010, 30(4):86-91.
|
| [22] |
邓岳文, 邓陈茂, 杜晓东, 等. 细胞小片处理对马氏珠母贝育珠效果影响[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2011(3):46-50.
|
| [23] |
符韶, 黄邦双, 邓岳文, 等. 马氏珠母贝育珠效果影响因素分析[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2013, 33(1):28-32.
|
| [24] |
焦钰, 师尚丽, 杜晓东, 等. 马氏珠母贝珍珠囊发育的组织和组织化学研究[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2010, 30(4):7-10.
|
| [25] |
梁飞龙, 林伟财, 邓岳文, 等. 术前处理对马氏珠母贝育珠效果的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(8):36-41.
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1038/nature11413 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl097 pmid: 16543274 |
| [29] |
郑哲. 基于多组学分析的马氏珠母贝矿化相关基因研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2017.
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.04.061 URL |
| [31] |
周蔚. 组蛋白修饰与基因调控[J]. 国外医学(分子生物学分册), 2003, 25(2):71-73.
|
| [32] |
任庆虎, 童坦君. 组蛋白乙酰化在转录调节中的作用[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 1997, 24(4):309-312.
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1084/jem.108.6.925 URL |
| [34] |
pmid: 16936823 |
| [35] |
李微微, 郭东林. 组蛋白变体及组蛋白分子伴侣的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(1):56-61.
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2010.03.002 URL |
| [37] |
doi: 10.4238/2014.August.7.8 pmid: 25117351 |
| [38] |
武向敏. 淇河鲫H2A与Ca-L-hipposin克隆和特征分析及其对细菌感染的表达响应[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2015.
|
| [1] | 隋心意, 赵小刚, 毛欣, 李亚灵, 温祥珍. 生菜bHLH转录因子家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 104-110. |
| [2] | 李战彪, 莫翠萍, 陈锦清, 秦碧霞, 崔丽贤, 谢慧婷, 蒋雅琴, 汤亚飞, 蔡健和. 广西番茄花叶病毒和番茄褪绿病毒的分子鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(28): 92-98. |
| [3] | 孙博, 刘闰, 王占斌, 陈黄欣, 阎肃. 桃叶蓼白粉菌的显微观察及进化关系分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 130-136. |
| [4] | 陈道, 王新, 江山, 张洁, 吴祖建, 丁新伦. 福建地区草莓斑驳病毒全基因组测序和分子变异分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 94-101. |
| [5] | 张海燕, 陈光辉, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张秀英, 王玉涛. 基于mt DNA COI基因的新疆部分地区叶蝉的分子鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(36): 119-129. |
| [6] | 关思静, 高静, 徐蓉蓉, 葛甜甜, 王楠, 颜永刚, 张岗, 陈莹, 刘阿萍, 程萌格. 甘草生长素反应因子(ARF)基因家族的鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(29): 20-27. |
| [7] | 张敏莹, 徐东坡, 周彦锋, 方弟安, 刘凯, 潘泽钰. 秀丽白虾线粒体16S rRNA基因序列及长臂虾亚科系统进化初步分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(17): 157-164. |
| [8] | 高帆, 何中石, 宋韡, 徐璐, 赵佳. 植物miR398家族的分子特征与进化分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(11): 33-42. |
| [9] | 徐利剑,梁晶,李泽宇,刘博洋,孟威. 植物酰基辅酶A结合蛋白的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(30): 78-83. |
| [10] | 黄世全,王棚涛,郭思义,宋纯鹏. 植物木质部进化与发育的研究概述[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(21): 82-89. |
| [11] | 周 森. H5亚型高致病性禽流感病毒的全球传播与进化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(2): 104-110. |
| [12] | 兰冬雪,收件人:戚晓利,汤丽影,李佳,谢鹏远,吕玉光,戚晓利. 禾本科植物NBS-LRR类抗病基因结构、功能和进化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(15): 124-127. |
| [13] | 王哲,杨创业,李俊辉,邓岳文. 马氏珠母贝金黄壳色选育群体与养殖群体血清免疫酶活力比较[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(11): 160-164. |
| [14] | 邓远球,符韶,邓岳文,梁飞龙. 养殖笼具对马氏珠母贝育珠效果的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(10): 148-152. |
| [15] | 邹霖湘,何中声. 戴云山自然保护区种子植物传粉模式研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(4): 38-42. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||