
中国农学通报 ›› 2023, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (36): 102-111.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0035
收稿日期:2023-01-10
修回日期:2023-05-15
出版日期:2023-12-25
发布日期:2023-12-20
通讯作者:
作者简介:孙保娟,女,1976年出生,吉林磐石人,研究员,博士,研究方向:茄果类蔬菜遗传育种及分子生物学。通信地址:510640 广东省广州市天河区金颖路66号,Tel:020-38469456,E-mail:sunbaojuan@hotmail.com。
基金资助:
SUN Baojuan( ), LI Tao, YOU Qian, GONG Chao, LI Zhenxing, LI Zhiliang(
), LI Tao, YOU Qian, GONG Chao, LI Zhenxing, LI Zhiliang( )
)
Received:2023-01-10
Revised:2023-05-15
Published-:2023-12-25
Online:2023-12-20
摘要:
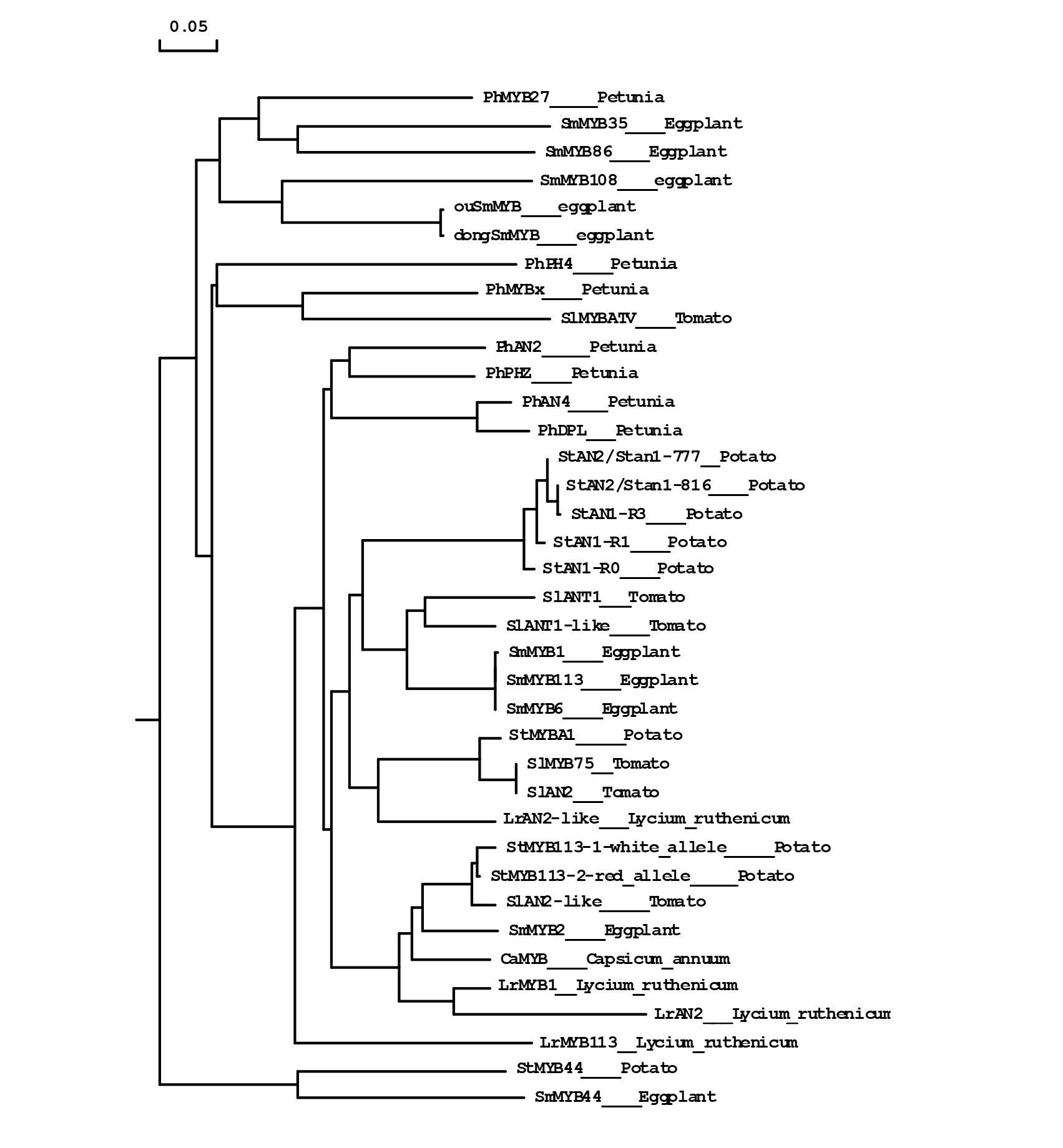
MYB转录因子是植物中最大的一类转录因子家族,其重要的功能之一是调控花青素的合成。为了全面了解MYB转录因子对茄科植物花青素合成的调控作用,本研究从基因分离克隆、时空表达、调控方式等方面归纳了矮牵牛、马铃薯、番茄、辣椒、茄子、烟草、枸杞等7种茄科植物与花青素合成相关的MYB转录因子的研究进展。通过对已报道的茄科植物花青素代谢途径相关的MYB转录因子基因进行系统发育分析,发现不同茄科植物上激活型和抑制型MYB转录因子按功能聚类;调控果实花青素合成的关键MYB转录因子基因SlANT1、SmMYB1、StAN1、StAN2优先聚为一类,再与StMYBA1、SlAN2和LrAN2-like聚为一类;SlAN2-like、SmMYB2、StMYB113、LrMYB1以及CaMYB聚为一类;番茄的SlAN2和SlMYB75为不同命名的相同基因;茄子的SmMYB1、SmMYB6和SmMYB113为不同命名的同一MYB转录因子基因。本文指出了有关花青素合成的MYB转录因子基因在茄科蔬菜上进一步的研究方向,为茄科蔬菜花青素合成组织特异性调控机制解析以及通过基因调控和基因工程改良果色等方面的研究提供参考。
孙保娟, 李涛, 游倩, 宫超, 黎振兴, 李植良. 茄科植物花青素合成相关的MYB转录因子研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(36): 102-111.
SUN Baojuan, LI Tao, YOU Qian, GONG Chao, LI Zhenxing, LI Zhiliang. Research Progress on MYB Transcription Factors Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis in Solanaceae[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(36): 102-111.

| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1071/FP03118 URL |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01070 URL |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2008.134.issue-2 URL |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s11816-015-0382-3 URL |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.04.072 pmid: 23707429 |
| [9] |
pmid: 16076105 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.012 pmid: 23769702 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.7.1071 pmid: 12242398 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.011 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.3109/07388551.2016.1141391 pmid: 26912350 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00199-0 URL |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1002/bies.v17:4 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005 URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90549-5 pmid: 7954830 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1071/FP12195 URL |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp030 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.122069 pmid: 24642943 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.8.1433 URL |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms22094838 URL |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00046.x URL |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.034041 URL |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1158-3 URL |
| [29] |
许芸梅, 李玉梅, 贾玉鑫, 等. 马铃薯红色薯肉调控基因的精细定位与候选基因分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(5):2678-2685.
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw014 pmid: 26884602 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1007/s12374-016-0199-9 URL |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1186/s12863-019-0728-x pmid: 30885125 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.07.018 URL |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz194 pmid: 31020330 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.012963 URL |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1705-6 URL |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.02.005 URL |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1038/s41438-018-0098-y pmid: 30729012 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1007/s10535-013-0376-3 URL |
| [41] |
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.133.2.262 URL |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1093/jhered/esm128 pmid: 18344529 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx382 pmid: 29186488 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.10.010 URL |
| [45] |
pmid: 12647064 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-004-1625-9 URL |
| [47] |
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.134.2.244 URL |
| [48] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00500 pmid: 26217354 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.5897/AJB URL |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
张彦杰. 紫白菜与紫茄花色苷生物合成及光调控的分子机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2015.
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsu027 URL |
| [54] |
王世界. 茄子花青素生物合成关键MYB转录因子的筛选及克隆[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2016.
|
| [55] |
李鲁俊. 茄皮花青素含量分析及其受SmMYB6调控的分子机制[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018.
|
| [56] |
doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac268 URL |
| [57] |
邵文婷, 刘杨, 韩洪强, 等. 茄子花青素合成相关基因SmMYB的克隆与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2013, 40(3):467-478.
|
| [58] |
周婷婷. 茄子萼片花青素合成相关基因DFR和MYB的克隆及表达分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2016.
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.843996 URL |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03698-x |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110696 URL |
| [63] |
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6023-4 pmid: 31455222 |
| [64] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1108-y pmid: 20157728 |
| [65] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.12131 URL |
| [66] |
王翠平, 陈建伟, 严莉, 等. 黑果枸杞R1-MYB转录因子基因的克隆及表达分析[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(1):203-210.
|
| [67] |
严莉. 黑果枸杞MYB转录因子的识别及LrMYB1的功能研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2018.
|
| [68] |
doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6663-4 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1752-8 |
| [70] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01256 URL |
| [71] |
doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(96)10049-4 URL |
| [72] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00898-x pmid: 33846596 |
| [73] |
刘彻, 姚盼盼, 宋皓, 等. 烟草1R MYB转录因子亚家族鉴定与分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 58(5):904-918
|
| [74] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa1100 pmid: 33416862 |
| [1] | 郑聪慧, 徐振华, 王玉忠, 张蔓蔓, 杜克久, 李向军, 刘春鹏. 四种臭椿不同叶位叶片色素组成及分布变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(32): 56-65. |
| [2] | 王硕, 郑秀文, 刘冠, 张萌萌. 环境因子及内源物质对果树中花青素调控的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(19): 51-57. |
| [3] | 努尔夏提·努尔买买提, 李焕宇, 杨成德. 辣椒根腐病菌拮抗链霉菌的筛选及16S rRNA基因系统发育分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(33): 116-123. |
| [4] | 刘恺媛, 王茂良, 辛海波, 张华, 丛日晨, 黄大庄. 植物花青素合成与调控研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(14): 41-51. |
| [5] | 谢勇飞, 赵钢, 孙娜, 吕银萍, 吴勇, 沈美辰, 吕文犇, 高俊山. 响应面法优化棕色棉纤维原花青素的提取工艺[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(12): 136-143. |
| [6] | 朱玲, 沈学善, 屈会娟, 王平, 蒲志刚, 王晓黎, 黄静玮. 高花青素甘薯新品种‘绵紫薯9号’优化施肥技术研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(17): 26-30. |
| [7] | 卢小草,邱志鹏,李敏,陈楚,孙月婷,邱栋梁. 葡萄果皮花青素提取工艺优化研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(8): 114-121. |
| [8] | 杨阳,张斌武,蓝登明,司建华,谢菲,桂翔. 黑果枸杞果实原花青素含量研究分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(22): 142-146. |
| [9] | 李会珍,谭永兰,夏瑶瑶,张志军. 紫苏籽壳原花青素纯化及抗氧化性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(14): 138-143. |
| [10] | 程志强,雷少楠,熊娟,马荣琴,陈优优,李容丹,路晶晶,吴寒,龚玉杰,田宝玉. 番茄根内生芽孢杆菌的多样性和系统发育研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(8): 37-45. |
| [11] | 姜新强,宫明雪,朱倩玉,刘庆超,王奎玲,刘庆华. 风箱果叶色变化及呈色机理研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(3): 76-81. |
| [12] | 孙美玲,梁月洋,王红朵,张仲鸣. 河南南阳地产绿米稻壳中花青素的提取工艺研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(18): 71-76. |
| [13] | 刘莹,高涵,王丽霞,田益玲. 红树莓花青素的微波辅助提取研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(12): 125-131. |
| [14] | 徐先栋,廖怀生,王海华,朱述淦,张燕萍,吴斌,罗星星. 河川沙塘鳢不同组织6种同工酶分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(25): 152-156. |
| [15] | 王 平,沈学善,屈会娟,王晓黎,黄 钢,王 宏. 灌水时期对川中丘陵区旱地紫色马铃薯产量和花青素含量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(1): 11-17. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||