
中国农学通报 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (31): 102-110.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2025-0065
曾莉莎1( ), 温华强2, 麦进培1, 李燕荷1, 周海琪1, 郑芝波1(
), 温华强2, 麦进培1, 李燕荷1, 周海琪1, 郑芝波1( ), 吕顺1, 周而勋2
), 吕顺1, 周而勋2
收稿日期:2025-02-06
修回日期:2025-08-15
出版日期:2025-11-05
发布日期:2025-11-07
通讯作者:
作者简介:曾莉莎,女,1985年出生,广东海丰人,研究员,硕士,研究方向:植物病理学。通信地址:523086 东莞市南城区绿色路市现代农业科技园东莞市农业科学研究中心,Tel:0769-23668928,E-mail:371924298@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZENG Lisha1( ), WEN Huaqiang2, MAI Jinpei1, LI Yanhe1, ZHOU Haiqi1, ZHENG Zhibo1(
), WEN Huaqiang2, MAI Jinpei1, LI Yanhe1, ZHOU Haiqi1, ZHENG Zhibo1( ), LYU Shun1, ZHOU Erxun2
), LYU Shun1, ZHOU Erxun2
Received:2025-02-06
Revised:2025-08-15
Published:2025-11-05
Online:2025-11-07
摘要:
为构建一种高效、灵敏的荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune)实时荧光环介导等温扩增技术LAMP(Real-time fluorescent LAMP)检测体系,以荷花腐败病菌的翻译延伸因子(TEF-1α)序列作为检测靶标,设计并筛选出4条特异性LAMP引物,成功建立了基于实时荧光监测的LAMP快速检测方法。系统性验证实验表明,该方法具备显著优势,在63℃恒温条件下,60 min即可完成病原菌检测,且具有高度特异性,能精准识别荷花腐败病菌。针对供试菌株的测试结果显示,10株荷花腐败病菌反应结果呈绿色(阳性),电泳结果出现梯度条带,实时荧光扩增正常且熔解曲线为单一尖峰;而其他5株对照菌株反应结果呈橙色(阴性),电泳无梯度条带,实时荧光无扩增。灵敏度实验表明,利用LAMP技术检测F. commune的最低检测限为100 fg/μL,土壤中分生孢子的最低检测限为1×103个/(g·土壤),制作的标准曲线可用于F. commune的定量检测。本方法适用于田间植株受F. commune侵染前后的检测,其地下茎组织F. commune的DNA含量与其发病程度呈正相关。本研究建立的荷花腐败病菌实时荧光LAMP快速检测方法具有较高的特异性和灵敏度,操作简便快捷,适用于F. commune的田间快速检测。
曾莉莎, 温华强, 麦进培, 李燕荷, 周海琪, 郑芝波, 吕顺, 周而勋. 荷花腐败病菌的实时荧光LAMP快速检测技术的建立及应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(31): 102-110.
ZENG Lisha, WEN Huaqiang, MAI Jinpei, LI Yanhe, ZHOU Haiqi, ZHENG Zhibo, LYU Shun, ZHOU Erxun. Establishment and Application of Real-time Fluorescent LAMP Rapid Detection of Lotus Rhizome Rot Pathogen[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2025, 41(31): 102-110.
| 样品编号 | 菌株名称 | 种名 | 寄主 | 来源地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hhgw-2-4 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 广东 |
| 2 | Hhgw-2-6 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 广东 |
| 3 | Hh-21-1 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 江西 |
| 4 | Hh-34-5 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 福建 |
| 5 | Hh-38-5 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 福建 |
| 6 | Hhgw-70-4 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖北 |
| 7 | Hhgw-71-3 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖北 |
| 8 | Hhgw-72-2 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖南 |
| 9 | Hhgw-75-2 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖南 |
| 10 | LTHh-11 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 广西 |
| 11 | XJ-24 | 香蕉枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense) | 香蕉 | 广东 |
| 12 | FOB-5 | 冬瓜枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. benincasae) | 冬瓜 | 广东 |
| 13 | FOV-1 | 棉花枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum) | 棉花 | 广东 |
| 14 | SJH-1-3 | 莲小菌核叶腐病菌(Sclerotium hydrophilum) | 荷花 | 广东 |
| 15 | FJ-22-2 | 甘蔗梢腐病菌(Fusarium sacchari) | 甘蔗 | 福建 |
| 样品编号 | 菌株名称 | 种名 | 寄主 | 来源地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hhgw-2-4 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 广东 |
| 2 | Hhgw-2-6 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 广东 |
| 3 | Hh-21-1 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 江西 |
| 4 | Hh-34-5 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 福建 |
| 5 | Hh-38-5 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 福建 |
| 6 | Hhgw-70-4 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖北 |
| 7 | Hhgw-71-3 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖北 |
| 8 | Hhgw-72-2 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖南 |
| 9 | Hhgw-75-2 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 湖南 |
| 10 | LTHh-11 | 荷花腐败病菌(Fusarium commune) | 荷花 | 广西 |
| 11 | XJ-24 | 香蕉枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense) | 香蕉 | 广东 |
| 12 | FOB-5 | 冬瓜枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. benincasae) | 冬瓜 | 广东 |
| 13 | FOV-1 | 棉花枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum) | 棉花 | 广东 |
| 14 | SJH-1-3 | 莲小菌核叶腐病菌(Sclerotium hydrophilum) | 荷花 | 广东 |
| 15 | FJ-22-2 | 甘蔗梢腐病菌(Fusarium sacchari) | 甘蔗 | 福建 |
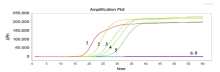
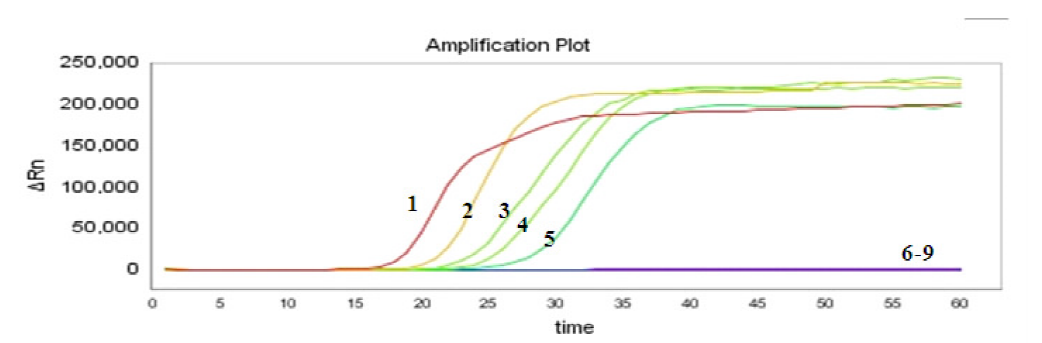
| 样品编号 | 病害级别 | Ct值 | DNA含量/ng |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| 2 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| 3 | 0 | 38.4728 | 2.11985×10-10 |
| 4 | 1 | 33.3232 | 7.70941×10-10 |
| 5 | 1 | 33.3232 | 7.70941×10-10 |
| 6 | 2 | 26.5268 | 1.84773×10-6 |
| 7 | 2 | 25.3468 | 7.135×10-6 |
| 8 | 2 | 25.8775 | 3.886×10-6 |
| 9 | 3 | 18.1149 | 0.028 |
| 10 | 3 | 18.1855 | 0.028 |
| 11 | 3 | 18.2746 | 0.029 |
| 12 | 4 | 18.8747 | 0.030 |
| 13 | 4 | 17.9973 | 0.032 |
| 14 | 5 | 12.2909 | 22.164 |
| 15 | 5 | 13.2689 | 7.233 |
| 16 | 5 | 12.5166 | 17.116 |
| 样品编号 | 病害级别 | Ct值 | DNA含量/ng |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| 2 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| 3 | 0 | 38.4728 | 2.11985×10-10 |
| 4 | 1 | 33.3232 | 7.70941×10-10 |
| 5 | 1 | 33.3232 | 7.70941×10-10 |
| 6 | 2 | 26.5268 | 1.84773×10-6 |
| 7 | 2 | 25.3468 | 7.135×10-6 |
| 8 | 2 | 25.8775 | 3.886×10-6 |
| 9 | 3 | 18.1149 | 0.028 |
| 10 | 3 | 18.1855 | 0.028 |
| 11 | 3 | 18.2746 | 0.029 |
| 12 | 4 | 18.8747 | 0.030 |
| 13 | 4 | 17.9973 | 0.032 |
| 14 | 5 | 12.2909 | 22.164 |
| 15 | 5 | 13.2689 | 7.233 |
| 16 | 5 | 12.5166 | 17.116 |
| [1] |
王兴兰. 莲藕腐败病的发生特点与无公害防治技术[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2007, 27(8):23-24.
|
| [2] |
魏林, 曹福祥, 梁志怀, 等. 莲藕腐败病病原菌人工接种致病性测定方法的研究[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2009(7):74-76.
|
| [3] |
任庆肖, 张金旭, 张木清. 甘蔗根腐病及其致病镰刀菌研究进展[J]. 甘蔗糖业, 2021, 50(3):49-57.
|
| [4] |
任庆肖, 张金旭, 王继华, 等. 果蔗根腐病病原菌分离鉴定及生物学特性分析[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(7):135-142.
|
| [5] |
吴安忠, 程崖芝, 巫升鑫, 等. 烟草镰刀菌根腐病的病原鉴定[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2018, 24(2):135-140.
|
| [6] |
张河庆, 席亚东, 陈玲, 等. 一种新的豇豆根腐病病原菌鉴定及室内药剂筛选[J]. 植物保护, 2018, 44(2):177-183.
|
| [7] |
李润根, 曾慧兰, 卢其能, 等. 百合枯萎病菌Fusarium commune的鉴定及其对杀菌剂敏感性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(1):162-172.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0164 |
| [8] |
朱志贤. 荸荠枯萎病菌病原学、分子检测及防治技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1007/s10327-020-00967-7 |
| [12] |
曾莉莎, 郑芝波, 吕顺, 等. 荷花腐败病病原菌的形态学与多基因分子系统学鉴定[J]. 植物病理学报, 2017, 47(2):162-173.
doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000052 |
| [13] |
曾莉莎, 吕顺, 郑芝波, 等. 不同地区荷花腐败病菌生物学特性及IGS序列分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(1):136-143.
|
| [14] |
温华强, 舒灿伟, 曾莉莎, 等. 荷花腐败病菌的荧光定量PCR检测[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(34):127-132.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0836 |
| [15] |
叶丽芳, 张逸凡, 张连虎, 等. 莲腐败病菌遗传转化体系的构建[J]. 植物保护, 2024, 50(2):211-218.
|
| [16] |
赵媛媛. 强雄腐霉的LAMP检测和瓜果腐霉的RPA检测方法的建立[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学,2018:1-79.
|
| [17] |
徐小刚, 刘雅婷. 实时荧光定量PCR在植物病害中的应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(7):52-56.
|
| [18] |
李宝聚, 陈利达, 袁军海, 等. 镰孢菌属实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(A1):296-301.
|
| [19] |
侯圣凡, 刘峻杰, 李小峰, 等. 基于环介导等温扩增技术的草莓枯萎病检测[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2022, 27(3):172-180.
|
| [20] |
车晓莉, 梁婷婷, 曲媛, 等. 三七根腐病菌茄腐镰刀菌的实时荧光LAMP快速检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2024, 32(4):939-948.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
徐淑菲, 孔繁德, 苗丽, 等. LAMP技术研究进展及其在动物疫病检测中的应用[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2017, 34(1):75-80.
|
| [23] |
徐义刚, 李苏龙, 杨君宏, 等. 水产品中创伤弧菌DNA环介导恒温扩增快速检测方法的建立及初步应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2010, 30(6):96-102.
|
| [24] |
刘旺, 靳晶豪, 陈孝仁. 环介导等温扩增技术的应用进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(2):128-135.
doi: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2020.0152 |
| [25] |
金福姝. 结核分枝杆菌环介导等温扩增实时荧光与反向斑点杂交检测方法的研究[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学,2014:1-65.
|
| [26] |
林惠娇, 牟桂萍, 滕少娜, 等. 苹果壳色单隔孢溃疡病菌TaqMan实时荧光PCR检测方法[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2021, 42(2):65-70.
|
| [27] |
宋必. 应用LAMP检测技术快速诊断大豆根茎部真菌病害[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学,2015:1-68.
|
| [28] |
戴婷婷, 吴小芹. 等温扩增技术快速检测棕榈疫霉[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(10):161-166.
|
| [29] |
刘建利. 沙打旺黄矮根腐病菌分子生物学研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016.
|
| [30] |
王一波, 孙泓希, 史普想, 等. 环介导等温扩增技术在农业病害检测中的应用综述[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(7):17-24.
|
| [31] |
朱志伟, 赵金红. 环介导等温扩增技术在寄生虫检测中的应用进展[J]. 热带病与寄生虫学, 2020, 18(4):234-238.
|
| [32] |
林晶晶, 夏露, 刘旭晖, 等. 环介导等温扩增技术用于结核病诊断的价值评估[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2021, 48(1):104-110.
|
| [33] |
龚建森, 徐敬潇, 付立霞, 等. 印第安纳沙门菌环介导等温扩增检测方法的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52(2):560-564.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.02.029 |
| [34] |
张可欣, 杨思熙, 王丽娜, 等. 环介导等温扩增对人乳头瘤病毒可视化分型检测[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2021, 25(2):236-240.
|
| [35] |
何晋, 刘淑婷, 陈淳, 等. 基于rDNA-ITS序列建立LAMP检测水稻潜根线虫的方法[J]. 植物病理学报, 2021, 51(4):626-635.
doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000538 |
| [36] |
汪少丽, 曲恒华, 王英姿, 等. 苹果轮纹病菌LAMP快速检测方法的建立[J]. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(1):127-133.
|
| [37] |
姜珊珊, 冯佳, 张眉, 等. 甘薯羽状斑驳病毒RT-LAMP快速检测方法的建立[J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(7):1294-1302.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.07.007 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
李欣. 三七主要病害病原菌的快速检测及叶部病害病原菌的鉴定[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学,2020:1-91.
|
| [42] |
朱艳宇, 于文涛, 高水练, 等. 福建安溪茶树种质资源遗传多样性与铁观音衍生品种遗传关系[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7):1591-1601.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20231037 |
| [43] |
陈真真, 申冠宇, 王轲, 等. 小麦遗传构成及重要性状功能基因组成解析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2024, 55(10):2980-2989.
|
| [44] |
黄雯, 徐进, 张昊, 等. 植物青枯菌LAMP检测方法的建立[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(11):2093-2102.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.11.006 |
| [45] |
彭军, 廖孝文, 杨海中, 等. 柑桔黄龙病环介导等温扩增检测方法建立及应用[J]. 热带作物学报, 2013, 34(10):1998-2003.
|
| [46] |
郑艳, 杨玲辉, 马吉湘, 等. 环介导等温扩增实时荧光检测玉米内州萎蔫病菌[J]. 植物检疫, 2015, 29(3):52-56.
|
| [47] |
曾莉莎, 庄华才, 胡规媛, 等. 荷花腐败病生防菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(1):92-99.
|
| [48] |
夏玲, 曾莉莎, 吕顺, 等. 荷花腐败病防治药剂室内筛选及田间药效试验[J]. 南方农业学报, 2016, 47(7):1129-1134.
|
| [49] |
伍文宪, 刘勇, 黄小琴, 等. 尖孢镰刀菌分子检测技术的建立与应用[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5):109-115.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2015335 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2000.90.8.891 URL |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1007/s12600-013-0369-y URL |
| [53] |
王瑜, 马建忠, 张伟杰, 等. 腐皮镰刀菌SYBR Green实时荧光定量PCR快速检测方法的建立[J]. 微生物学免疫学进展, 2018, 46(2):34-39.
|
| [1] | 王华, 余海龙, 任毓忠. 苹果黑星菌LAMP快速检测方法的建立[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(3): 139-144. |
| [2] | 张旻, 景宏丽, 王娜, 吴绍强. 虾肝肠胞虫重组酶聚合酶侧向流试纸条快速检测方法的建立[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(20): 157-164. |
| [3] | 周新裕, 仇梓杰, 黄金恒, 乜晓凤, 杨全, 廖沛然. 镉胁迫下岗梅内参miRNA与基因的筛选与验证[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(11): 31-39. |
| [4] | 杨张青, 辛银平, 赵晴, 王猛, 秦一浪, 胡峰, 李国强. 比浊法快速测定土壤中速效钾的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(9): 83-88. |
| [5] | 田维逵, 董丽英, 资鸿强, 刘树芳, 刘沛, 杨勤忠. 6个抗稻瘟病基因在云南省勐海县水稻主栽品种中的分布[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(20): 130-134. |
| [6] | 王丽, 侯珲, 涂洪涛, 黄天祥, 柳友亮, 袁洪波. 3种葡萄座腔菌的检测方法比较[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(19): 126-132. |
| [7] | 徐英芝, 赵丽梅, 祖未希, 高芬. 黄芪根腐病菌腐皮镰刀菌的实时荧光定量PCR检测方法建立[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(15): 110-116. |
| [8] | 李志明, 许海涛, 高玉平, 蔡德霖, 王相国, 肖龙菲, 安红, 王颖秋, 王骞, 郭勇, 齐晓龙, 倪和民. 牛妊娠相关糖蛋白6快速检测试纸条的制备及应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(2): 75-81. |
| [9] | 陈培华, 鲍涵, 陈培寿, 沈万宽. 果蔗健康种苗田间效果评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(16): 1-5. |
| [10] | 文英, 刘永生. 基于ipaH基因的志贺菌LAMP检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(5): 104-110. |
| [11] | 李楠楠, 李顺成, 韩玉林, 邹少奎, 杜晓宇, 杨光宇, 王丽娜, 张倩, 吕永军. Fhb1基因改良‘周麦’品种赤霉病抗性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(4): 98-104. |
| [12] | 崔贵梅, 李小波, 马樾, 郝曜山, 张欢欢, 孙毅. 玉米预防转基因漂移试纸条快速检测方法[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(36): 19-23. |
| [13] | 温华强, 舒灿伟, 曾莉莎, 周而勋. 荷花腐败病菌的荧光定量PCR检测[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(34): 127-132. |
| [14] | 龙丽坤, 赵宁, 夏蔚, 李葱葱, 董立明, 闫伟, 李飞武. 转基因玉米CM8101特异性定性PCR检测方法[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(23): 23-28. |
| [15] | 郭思依, 孙明娜, 董旭, 褚玥, 童舟, 王梅, 高同春, 段劲生. 免疫分析技术在农药残留快速检测中的应用及研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(23): 106-112. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||