
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (26): 22-29.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0549
刘晓敏( ), 孙志广(
), 孙志广( ), 迟铭, 邢运高, 徐波, 李景芳, 刘艳, 卢百关, 王宝祥, 徐大勇(
), 迟铭, 邢运高, 徐波, 李景芳, 刘艳, 卢百关, 王宝祥, 徐大勇( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-15
修回日期:2023-11-16
出版日期:2024-09-11
发布日期:2024-09-11
通讯作者:
作者简介:刘晓敏,女,1993年出生,江苏连云港人,研究实习员,学士,研究方向:水稻遗传育种。通信地址:222000 江苏省连云港市海州区郁州南路与迎宾大道交叉口 连云港市农业科学院,Tel:0518-83081733,E-mail:824659317@qq.com。
基金资助:
LIU Xiaomin( ), SUN Zhiguang(
), SUN Zhiguang( ), CHI Ming, XING Yungao, XU Bo, LI Jingfang, LIU Yan, LU Baiguan, WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong(
), CHI Ming, XING Yungao, XU Bo, LI Jingfang, LIU Yan, LU Baiguan, WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong( )
)
Received:2023-08-15
Revised:2023-11-16
Published:2024-09-11
Online:2024-09-11
摘要:
本研究旨在对水稻黄绿叶突变体ygl-9108进行表型分析和基因定位,为后续图位克隆该叶色相关基因奠定基础。以黄绿叶突变体ygl-9108为试材,利用突变体ygl-9108和‘五山丝苗’杂交的F2群体进行基因定位。结果表明,与野生型相比,突变体的株高、有效穗数、穗长、每穗粒数、结实率、粒宽、千粒重和单株谷重均显著下降,下降比例分别为21.5%、21.2%、14.6%、19.2%、11.0%、10.2%、12.9%和52.2%。透射电镜观察显示,突变体叶肉细胞的叶绿体数量大量减少,类囊体结构异常。遗传分析表明,突变体的表型由一个隐性核基因控制。利用图位克隆方法,ygl-9108被定位于水稻第11号染色体两InDel标记11Y39和11Y45之间,物理距离约为147 kb,该区间内未见有叶色相关基因的报道,表明ygl-9108是一个新的黄绿叶调控基因。本研究结果为ygl-9108的克隆和功能分析奠定了坚实的基础。
刘晓敏, 孙志广, 迟铭, 邢运高, 徐波, 李景芳, 刘艳, 卢百关, 王宝祥, 徐大勇. 一个新的水稻黄绿叶突变体ygl-9108的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(26): 22-29.
LIU Xiaomin, SUN Zhiguang, CHI Ming, XING Yungao, XU Bo, LI Jingfang, LIU Yan, LU Baiguan, WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong. Identification and Gene Mapping of A Novel Yellow-green Leaf Mutant ygl-9108 in Rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(26): 22-29.
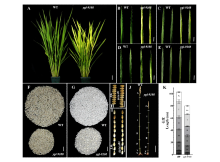
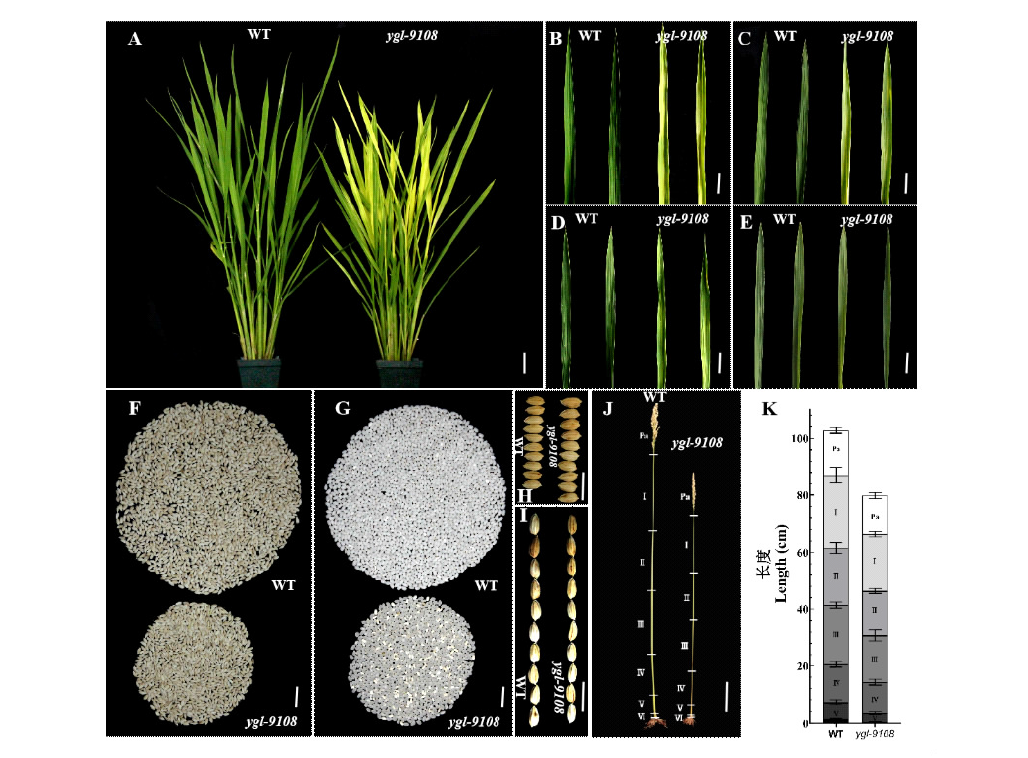
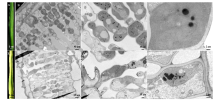

| [1] |
滕炎桐, 叶莲, 何福收, 等. 一个水稻黄叶突变体的叶绿素合成关键基因的表达分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(22):30-35.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17040104 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-2331-3 pmid: 15604725 |
| [3] |
李哲理, 张林金, 谭颖, 等. 水稻白叶白穗突变体wlwp7的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(9):2512-2517.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.09.010 |
| [4] |
孙志广, 代慧敏, 陈庭木, 等. 水稻类病斑突变体lmm7的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4):357-366.
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210711 |
| [5] |
pmid: 14688289 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
欧点点, 赵光伟, 贺玉花, 等. 甜瓜果皮颜色遗传分析及基因定位[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(13):64-69.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18110127 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
刘艳霞, 林冬枝, 董彦君, 等. 水稻温敏感叶色突变体研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4):439-446.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.04.014 |
| [10] |
林秋云, 谢振宇, 龙开意, 等. 水稻黄叶不育系突变体H08S的表型特征与遗传分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2020, 41(7):1321-1325.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.07.006 |
| [11] |
pmid: 10795309 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-201 pmid: 24809003 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.100321 pmid: 17535821 |
| [15] |
doi: S1674-2052(14)60936-9 pmid: 24821718 |
| [16] |
平文超, 徐婧, 曹平平, 等. 外源钾对盐胁迫下植物生长和生理特征影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(9):100-105.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0098 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1453-z pmid: 20872210 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
邓晓梅, 叶胜海, 修芬连, 等. 一个水稻黄绿叶突变性状的遗传分析及基因定位[J]. 核农学报, 2012, 26(2):203-209.
doi: 10.11869/hnxb.2012.02.0203 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2116-0 pmid: 25037719 |
| [30] |
江少华, 周华, 林冬枝, 等. 水稻幼苗叶色温敏感突变体的鉴定及其基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4):359-364.
|
| [31] |
王文娟, 吴兰兰, 雷晓庆, 等. 一个新水稻低温敏感叶色突变体tcm11的鉴定及基因定位[J]. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 46(2):319-325.
|
| [32] |
吴书俊, 王军, 杨杰, 等. 水稻黄绿叶突变体ygl11(t)的生理特性和基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(2):111-118.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2015.02.001 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
李自壮, 徐乾坤, 余海平, 等. 水稻淡黄叶矮化突变体yld的遗传分析及基因定位[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(4):522-529.
|
| [1] | 何国和, 陈海斌, 杜建军, 张伟丽, 郭丽华, 胡益波, 颜肇华, 张婧. 化肥减量配施有机肥对粤西地区水稻产量和养分利用的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(9): 1-8. |
| [2] | 杨小林, 薛敏峰, 张舒, 李进波, 吕亮, 常向前, 张佑宏, 龚艳. 湖北襄阳地区水稻落粒、杆枯等不正常生长现象的解析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(8): 112-118. |
| [3] | 李诚, 王少希, 钱艳杰, 易展平, 严小兵. 叶面调理剂在不同镉污染程度稻田应用效果研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 101-106. |
| [4] | 田宏, 陆姣云, 张鹤山, 熊军波, 刘洋. 烯效唑对扁穗雀麦生长发育和种子产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 29-35. |
| [5] | 查宏波, 赵芳, 吕家锋, 龚林, 陈华, 高顺波, 王文栋, 郑兴琪, 孙浩宸, 张倍. 优化施肥调控对连作烤烟农艺性状和产质量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 53-56. |
| [6] | 乔月, 胡诚, 万建华, 徐化林, 刘茂军, 郭卫红, 戴黎, 张春华, 邓超然. 不同施肥模式对水稻产量及养分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 9-15. |
| [7] | 郭娜, 马建富, 郭英杰, 李爱荣, 刘栋, 张丽丽, 胡杨, 李峰. 胡麻新品系主要农艺性状分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(4): 14-19. |
| [8] | 左雪倩, 谭静, 邓伟, 徐雨然, 吕莹, 张锦文, 余琴, 董维, 管俊娇, 李小林. 云南省杂交籼稻品种试验分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(3): 8-15. |
| [9] | 徐进, 谭建彬, 邓晓瑜, 梁锦炀, 师沛琼, 周鸿凯. 不同浓度镉处理对耐盐水稻生长及斜纹夜蛾酶活的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(3): 120-127. |
| [10] | 张喜娟, 王文龙, 孟英, 唐傲, 董文军, 刘猷红, 徐英哲, 王立志, 姜树坤, 杨贤莉, 刘凯, 姜辉, 任洋, 来永才. 种植方式对寒地水稻抗倒伏性状的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(3): 16-25. |
| [11] | 荀贤玉, 夏阳洋, 钟月华, 孟爱红, 何玲玲, 张军强, 马洪波, 王晓云. 腐熟鸡粪替代氮肥对水稻产量、氮肥利用率和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(25): 1-5. |
| [12] | 窦龙涛, 曲晓军, 胡基华, 姜威, 田缘, 闫更轩, 张淑梅. 一株多粘类芽孢杆菌的鉴定及对水稻稻瘟病菌的抑菌作用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(23): 118-125. |
| [13] | 曹辉, 王峰, 左红娟, 张晓申, 宋涛. 金银花主要农艺性状和光合特性的综合评价研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(22): 47-52. |
| [14] | 赵轶鹏, 赵新勇, 胡婷婷, 罗景升, 王云霞. 浮萍人工培养和调控及其在稻田生态系统中的作用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(22): 72-80. |
| [15] | 高国良, 高发瑞, 张巧玲, 冯雯杰, 王秋云, 黄信诚. 2013—2022年黄淮稻区国审水稻品种的特征特性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(21): 1-11. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||