
中国农学通报 ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 22-29.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0432
刘可可1( ), 李莎莎1, 骆强伟2, 徐炎1, 王跃进1(
), 李莎莎1, 骆强伟2, 徐炎1, 王跃进1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-23
修回日期:2021-09-18
出版日期:2022-04-15
发布日期:2022-05-18
通讯作者:
王跃进
作者简介:刘可可,女,1994年出生,河南周口人,硕士研究生,主要从事果树种质资源及生物技术育种研究。通信地址:712100 陕西省杨凌示范区邰城路3号 西北农林科技大学南校区园艺学院,E-mail: 基金资助:
LIU Keke1( ), LI Shasha1, LUO Qiangwei2, XU Yan1, WANG Yuejin1(
), LI Shasha1, LUO Qiangwei2, XU Yan1, WANG Yuejin1( )
)
Received:2021-04-23
Revised:2021-09-18
Online:2022-04-15
Published:2022-05-18
Contact:
WANG Yuejin
摘要:
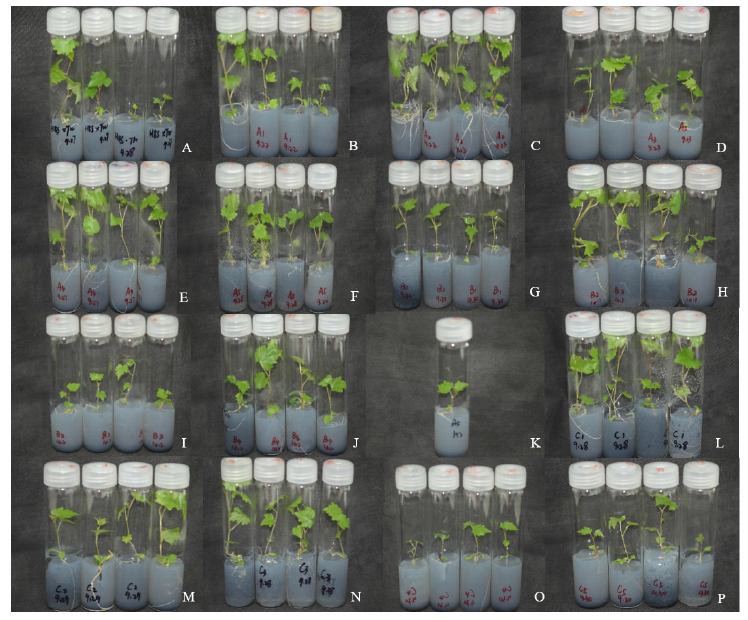
为提高无核抗病、优质葡萄新种质的选育效率,以无核欧洲葡萄品种作母本,中国野生刺葡萄‘塘尾’、‘雪峰’、山葡萄‘双优’及欧山杂交品种‘北醇’做父本,利用胚挽救技术对取样时间和培养基进行优化;用分子标记筛选后代的无核与抗病性状。结果表明:(1)15个杂交组合中共获得杂交果实13341个,接种幼胚珠8589枚,幼胚发育胚1338枚,平均胚发育率15.59%,正常成苗234株,平均成苗率2.73%,‘红宝石无核’ב塘尾’组合胚挽救效果最好,胚发育率为40.17%、成苗率7.76%和成苗植株数178株。(2)‘火焰无核’×北醇’授粉后42天取样,胚发育率(11.37%)和萌发率(3.52%)为最高。‘京可晶’ב北醇’授粉后38天取样,胚发育率(4.3%)和萌发率(1.08%)为最高。(3)以MM3为基础培养基,外源添加3 mmol/L的腐胺,‘红宝石无核’ב塘尾’获得胚发育率(55.83%)和成苗率(20%)为最高。(4)4个自然授粉的品种(‘昆香无核’、‘美丽无核’、‘红宝石无核’、‘赫什无核’),其胚珠在E20A培养基中更有利于幼胚发育率提升。(5)使用葡萄无核标记SCF27-2000和GSLP1-569、抗霜霉病标记S294-369和S382-615及抗白粉病标记OPY13-661进行筛选,杂种后代中有16株同时携带无核且抗霜霉病与抗白粉病特异性条带。该试验为无核葡萄抗病育种提供了新材料,将为进一步开展中国野生葡萄育种相关研究奠定基础。
中图分类号:
刘可可, 李莎莎, 骆强伟, 徐炎, 王跃进. 胚挽救技术创造无核抗病葡萄新种质[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(11): 22-29.
LIU Keke, LI Shasha, LUO Qiangwei, XU Yan, WANG Yuejin. Breeding New Grape Germplasm of Seedless and Disease Resistance by Embryo Rescue Technique[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(11): 22-29.
| 杂交组合 | 去雄时间 | 授粉时间 | 取样时间 | 果粒数/个 | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | ||||||
| 京早晶×双优 | 5月16日 | 5月20日 | 6月25日 | 1317 | 1105 | 22 | 1.99 | 0 | 0 |
| 无核白×双优 | 5月14日 | 5月18日 | 6月24日 | 111 | 65 | 5 | 7.69 | 2 | 3.08 |
| 无核紫×双优 | 5月16日 | 5月18日 | 6月28日 | 790 | 311 | 16 | 5.14 | 0 | 0 |
| 火焰无核×北醇 | 5月12日 | 5月16日 | 6月25日 | 1320 | 1412 | 149 | 10.55 | 28 | 1.98 |
| 赫什无核×北醇 | 5月15日 | 5月19日 | 7月18日 | 579 | 75 | 1 | 1.33 | 0 | 0 |
| 昆香无核×北醇 | 5月5日 | 5月8日 | 6月13日 | 1102 | 210 | 1 | 0.48 | 0 | 0 |
| 美丽无核×北醇 | 5月3日 | 5月6日 | 7月12日 | 1645 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 京可晶×北醇 | 5月6日 | 5月9日 | 6月14日 | 818 | 738 | 20 | 2.71 | 2 | 0.27 |
| 红宝石无核×塘尾 | 5月16日 | 5月19日 | 7月18日 | 1300 | 2295 | 922 | 40.17 | 178 | 7.76 |
| 美丽无核×塘尾 | 5月3日 | 5月6日 | 7月7日 | 1566 | 52 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 火焰无核×塘尾 | 5月4日 | 5月8日 | 6月13日 | 589 | 367 | 62 | 16.89 | 1 | 0.27 |
| 红宝石无核×雪峰 | 5月8日 | 5月10日 | 7月7日 | 253 | 363 | 4 | 1.10 | 1 | 0.28 |
| 昆香无核×火焰无核 | 5月10日 | 5月14日 | 6月28日 | 335 | 87 | 7 | 8.05 | 0 | 0 |
| 火焰无核×昆香无核 | 5月12日 | 5月16日 | 6月25日 | 636 | 897 | 94 | 10.48 | 18 | 2.01 |
| 火州红玉×新郁 | 5月15日 | 5月19日 | 7月1日 | 677 | 550 | 35 | 6.36 | 4 | 0.73 |
| 合计 | 13038 | 8572 | 1338 | 15.61 | 234 | 2.73 | |||
| 杂交组合 | 去雄时间 | 授粉时间 | 取样时间 | 果粒数/个 | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | ||||||
| 京早晶×双优 | 5月16日 | 5月20日 | 6月25日 | 1317 | 1105 | 22 | 1.99 | 0 | 0 |
| 无核白×双优 | 5月14日 | 5月18日 | 6月24日 | 111 | 65 | 5 | 7.69 | 2 | 3.08 |
| 无核紫×双优 | 5月16日 | 5月18日 | 6月28日 | 790 | 311 | 16 | 5.14 | 0 | 0 |
| 火焰无核×北醇 | 5月12日 | 5月16日 | 6月25日 | 1320 | 1412 | 149 | 10.55 | 28 | 1.98 |
| 赫什无核×北醇 | 5月15日 | 5月19日 | 7月18日 | 579 | 75 | 1 | 1.33 | 0 | 0 |
| 昆香无核×北醇 | 5月5日 | 5月8日 | 6月13日 | 1102 | 210 | 1 | 0.48 | 0 | 0 |
| 美丽无核×北醇 | 5月3日 | 5月6日 | 7月12日 | 1645 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 京可晶×北醇 | 5月6日 | 5月9日 | 6月14日 | 818 | 738 | 20 | 2.71 | 2 | 0.27 |
| 红宝石无核×塘尾 | 5月16日 | 5月19日 | 7月18日 | 1300 | 2295 | 922 | 40.17 | 178 | 7.76 |
| 美丽无核×塘尾 | 5月3日 | 5月6日 | 7月7日 | 1566 | 52 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 火焰无核×塘尾 | 5月4日 | 5月8日 | 6月13日 | 589 | 367 | 62 | 16.89 | 1 | 0.27 |
| 红宝石无核×雪峰 | 5月8日 | 5月10日 | 7月7日 | 253 | 363 | 4 | 1.10 | 1 | 0.28 |
| 昆香无核×火焰无核 | 5月10日 | 5月14日 | 6月28日 | 335 | 87 | 7 | 8.05 | 0 | 0 |
| 火焰无核×昆香无核 | 5月12日 | 5月16日 | 6月25日 | 636 | 897 | 94 | 10.48 | 18 | 2.01 |
| 火州红玉×新郁 | 5月15日 | 5月19日 | 7月1日 | 677 | 550 | 35 | 6.36 | 4 | 0.73 |
| 合计 | 13038 | 8572 | 1338 | 15.61 | 234 | 2.73 | |||
| 杂交组合 | 授粉后天数/天 | 果粒数/个 | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | ||||
| 火焰无核×北醇 | 37 | 121 | 179 | 11 | 6.15 | 1 | 0.56 |
| 38 | 129 | 201 | 16 | 7.96 | 1 | 0.50 | |
| 39 | 122 | 146 | 20 | 13.70 | 3 | 2.01 | |
| 40 | 136 | 189 | 26 | 13.76 | 6 | 3.17 | |
| 41 | 190 | 313 | 31 | 9.91 | 6 | 1.92 | |
| 42 | 341 | 255 | 29 | 11.37 | 9 | 3.52 | |
| 43 | 170 | 120 | 16 | 13.33 | 2 | 1.18 | |
| 京可晶×北醇 | 34 | 118 | 132 | 3 | 2.27 | 1 | 0.76 |
| 36 | 158 | 222 | 10 | 4.50 | 2 | 0.90 | |
| 38 | 143 | 93 | 4 | 4.30 | 1 | 1.08 | |
| 40 | 187 | 133 | 3 | 2.26 | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 42 | 105 | 53 | 1 | 1.87 | 0 | 0 | |
| 44 | 107 | 105 | 1 | 0.95 | 0 | 0 | |
| 杂交组合 | 授粉后天数/天 | 果粒数/个 | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | ||||
| 火焰无核×北醇 | 37 | 121 | 179 | 11 | 6.15 | 1 | 0.56 |
| 38 | 129 | 201 | 16 | 7.96 | 1 | 0.50 | |
| 39 | 122 | 146 | 20 | 13.70 | 3 | 2.01 | |
| 40 | 136 | 189 | 26 | 13.76 | 6 | 3.17 | |
| 41 | 190 | 313 | 31 | 9.91 | 6 | 1.92 | |
| 42 | 341 | 255 | 29 | 11.37 | 9 | 3.52 | |
| 43 | 170 | 120 | 16 | 13.33 | 2 | 1.18 | |
| 京可晶×北醇 | 34 | 118 | 132 | 3 | 2.27 | 1 | 0.76 |
| 36 | 158 | 222 | 10 | 4.50 | 2 | 0.90 | |
| 38 | 143 | 93 | 4 | 4.30 | 1 | 1.08 | |
| 40 | 187 | 133 | 3 | 2.26 | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 42 | 105 | 53 | 1 | 1.87 | 0 | 0 | |
| 44 | 107 | 105 | 1 | 0.95 | 0 | 0 | |
| 母本 | 培养基 | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | |||
| 红宝石无核 | ER | 300 | 14 | 4.67±0.33c | 1 | 0.33±0.33a |
| MM3 | 300 | 26 | 8.67±0.33b | 1 | 0.33±0.33a | |
| E20A | 300 | 43 | 14.33±0.33a | 2 | 0.67±0.33a | |
| 美丽无核 | ER | 200 | 2 | 0.33±0.33c | 0 | 0 |
| MM3 | 200 | 5 | 2.5±0.5b | 0 | 0 | |
| E20A | 200 | 9 | 4.5±0a | 1 | 0.5±0.5a | |
| 昆香无核 | ER | 200 | 2 | 1.01±0.5b | 0 | 0 |
| MM3 | 200 | 9 | 4.5±0.87a | 1 | 0.5±0.5a | |
| E20A | 200 | 12 | 6.1±0a | 1 | 0.5±0.5a | |
| 赫什无核 | ER | 200 | 14 | 7.07±0.5b | 1 | 0.5±0.5b |
| MM3 | 200 | 13 | 6.57±0.5b | 0 | 0 | |
| E20A | 200 | 21 | 10.61±0a | 4 | 2.53±0.5a | |
| 母本 | 培养基 | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | |||
| 红宝石无核 | ER | 300 | 14 | 4.67±0.33c | 1 | 0.33±0.33a |
| MM3 | 300 | 26 | 8.67±0.33b | 1 | 0.33±0.33a | |
| E20A | 300 | 43 | 14.33±0.33a | 2 | 0.67±0.33a | |
| 美丽无核 | ER | 200 | 2 | 0.33±0.33c | 0 | 0 |
| MM3 | 200 | 5 | 2.5±0.5b | 0 | 0 | |
| E20A | 200 | 9 | 4.5±0a | 1 | 0.5±0.5a | |
| 昆香无核 | ER | 200 | 2 | 1.01±0.5b | 0 | 0 |
| MM3 | 200 | 9 | 4.5±0.87a | 1 | 0.5±0.5a | |
| E20A | 200 | 12 | 6.1±0a | 1 | 0.5±0.5a | |
| 赫什无核 | ER | 200 | 14 | 7.07±0.5b | 1 | 0.5±0.5b |
| MM3 | 200 | 13 | 6.57±0.5b | 0 | 0 | |
| E20A | 200 | 21 | 10.61±0a | 4 | 2.53±0.5a | |
| 杂交组合 | 多胺种类 | 浓度/(mmol/L) | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | ||||
| 红宝石无核×塘尾 | 对照CK | 0 | 135 | 61 | 44.81±10.59abc | 9 | 9.63±0.37bcd |
| 亚精胺 | 1 | 135 | 67 | 50.37±5.79a | 17 | 12.78±1.47b | |
| 2 | 120 | 55 | 45.83±4.17abc | 13 | 10.83±3.33bc | ||
| 3 | 135 | 46 | 33.52±4.45cdef | 10 | 7.39±0.39bcde | ||
| 4 | 150 | 52 | 34.67±2.91bcde | 17 | 11.33±1.33b | ||
| 5 | 150 | 36 | 24±3.06ef | 7 | 4.67±1.33def | ||
| 精胺 | 1 | 150 | 84 | 56±4.16a | 11 | 7.33±1.33bcde | |
| 2 | 120 | 35 | 29.17±2.2def | 6 | 5±0cdef | ||
| 3 | 150 | 36 | 24±2.31ef | 5 | 3.33±1.33ef | ||
| 4 | 150 | 39 | 26±3.06ef | 6 | 4±1.15def | ||
| 5 | 135 | 26 | 19.26±0.74f | 1 | 0.67±0.67f | ||
| 腐胺 | 1 | 120 | 59 | 49.17±3.0ab | 10 | 8.33±2.2bcde | |
| 2 | 120 | 50 | 41.67±7.12abcd | 10 | 8.33±1.67bcde | ||
| 3 | 120 | 67 | 55.83±4.64a | 24 | 20±4.33a | ||
| 4 | 135 | 66 | 48.96±0.58ab | 13 | 9.53±1.07bcd | ||
| 5 | 150 | 85 | 56.67±3.33a | 6 | 4±1.15def | ||
| 杂交组合 | 多胺种类 | 浓度/(mmol/L) | 胚珠数/枚 | 发育胚 | 成苗 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/枚 | 占比/% | 数量/棵 | 占比/% | ||||
| 红宝石无核×塘尾 | 对照CK | 0 | 135 | 61 | 44.81±10.59abc | 9 | 9.63±0.37bcd |
| 亚精胺 | 1 | 135 | 67 | 50.37±5.79a | 17 | 12.78±1.47b | |
| 2 | 120 | 55 | 45.83±4.17abc | 13 | 10.83±3.33bc | ||
| 3 | 135 | 46 | 33.52±4.45cdef | 10 | 7.39±0.39bcde | ||
| 4 | 150 | 52 | 34.67±2.91bcde | 17 | 11.33±1.33b | ||
| 5 | 150 | 36 | 24±3.06ef | 7 | 4.67±1.33def | ||
| 精胺 | 1 | 150 | 84 | 56±4.16a | 11 | 7.33±1.33bcde | |
| 2 | 120 | 35 | 29.17±2.2def | 6 | 5±0cdef | ||
| 3 | 150 | 36 | 24±2.31ef | 5 | 3.33±1.33ef | ||
| 4 | 150 | 39 | 26±3.06ef | 6 | 4±1.15def | ||
| 5 | 135 | 26 | 19.26±0.74f | 1 | 0.67±0.67f | ||
| 腐胺 | 1 | 120 | 59 | 49.17±3.0ab | 10 | 8.33±2.2bcde | |
| 2 | 120 | 50 | 41.67±7.12abcd | 10 | 8.33±1.67bcde | ||
| 3 | 120 | 67 | 55.83±4.64a | 24 | 20±4.33a | ||
| 4 | 135 | 66 | 48.96±0.58ab | 13 | 9.53±1.07bcd | ||
| 5 | 150 | 85 | 56.67±3.33a | 6 | 4±1.15def | ||
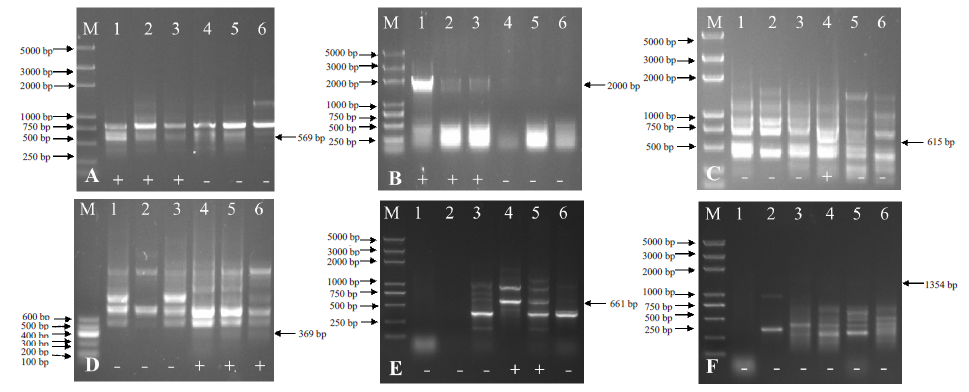
| 杂交组合 | 鉴定 株系数 | 无核标记 SCF27-2000 | 无核标记 GSLP1-569 | 抗霜霉病标记 S294-369 | 抗霜霉病标记 S382-615 | 抗白粉病标记 OPY13-661 | 无核、抗霜霉病、 抗白粉病标记 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | |||||||
| 火焰无核×北醇 | 24 | 19 | 79.17 | - | - | 13 | 54.17 | - | - | 18 | 75.0 | 7 | 29.17 | |||||
| 红宝石无核×塘尾 | 178 | 126 | 70.79 | - | - | - | - | 63 | 35.39 | 25 | 14.04 | 6 | 3.37 | |||||
| 火焰无核×昆香无核 | 18 | 9 | 50 | 12 | 66.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| 火焰无核×塘尾 | 4 | - | - | 4 | 100 | - | - | 3 | 75 | 4 | 100 | 3 | 75 | |||||
| 红宝石无核×雪峰 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 100 | - | - | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | - | - | |||||
| 总计 | 225 | 154 | 68.44 | 17 | 7.56 | 13 | 5.78 | 66 | 29.33 | 48 | 21.33 | 16 | 7.11 | |||||
| 杂交组合 | 鉴定 株系数 | 无核标记 SCF27-2000 | 无核标记 GSLP1-569 | 抗霜霉病标记 S294-369 | 抗霜霉病标记 S382-615 | 抗白粉病标记 OPY13-661 | 无核、抗霜霉病、 抗白粉病标记 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | 株系数 | 占比/% | |||||||
| 火焰无核×北醇 | 24 | 19 | 79.17 | - | - | 13 | 54.17 | - | - | 18 | 75.0 | 7 | 29.17 | |||||
| 红宝石无核×塘尾 | 178 | 126 | 70.79 | - | - | - | - | 63 | 35.39 | 25 | 14.04 | 6 | 3.37 | |||||
| 火焰无核×昆香无核 | 18 | 9 | 50 | 12 | 66.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| 火焰无核×塘尾 | 4 | - | - | 4 | 100 | - | - | 3 | 75 | 4 | 100 | 3 | 75 | |||||
| 红宝石无核×雪峰 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 100 | - | - | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | - | - | |||||
| 总计 | 225 | 154 | 68.44 | 17 | 7.56 | 13 | 5.78 | 66 | 29.33 | 48 | 21.33 | 16 | 7.11 | |||||
| [1] | 贺普超, 罗国光. 葡萄学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1999:5-7. |
| [2] | FAO. Focus 2019 Table and dried grapes: non-alcoholic products of the Vitivinicultural sector intended for human consumption. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/.FAO-OIV. 2019-4-16. |
| [3] |
DAVID W., RAMMING, et al. A stenospermocarpic, seedless Vitis vinifera × Vitis rotundifolia hybrid developed by embryo rescue[J]. HortScience, 2000, 35(4):732-734.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.35.4.732 URL |
| [4] |
LEDBETTER C A, BURGOS L. Inheritance of stenospermocarpic seedlessness in Vitis vinifera L[J]. Journal of Heredity, 1994, 85(2):157-160.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111419 URL |
| [5] | RAMMING D W, EMERSHAD R L. In ovulo embryo culture of seeded and seedless Vitis vinifera L[J]. Horticultural Science, 1982, 17(3):487. |
| [6] | CAIN D W, EMERSHAD R L, TARAILO R E. In-ovulo embryo culture and seedling development of seeded and seedless grapes (Vitis vinifera L.)[J]. Vitis, 1983, 22:9-14. |
| [7] | 李莎莎, 王跃进. 葡萄无核基因及无核育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(9):1711-1726. |
| [8] |
EMERSHAD R L, RAMMING D W, SERPE M D. In ovulo embryo development and plant formation from stenospermic genotypes of Vitis Vinifera[J]. American Journal of Botany, 1989, 76(3):397-402.
doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1989.tb11327.x URL |
| [9] | EMERSHAD R L, RAMMING D W. Somatic embryogenesis and plant development from immature zygotic embryos of seedless grapes (Vitis vinifera L.)[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 1994, 14:6-12. |
| [10] | SINGH N V, SINGH S K, SINGH A K. Standardization of embryo rescue technique and bio-hardening of grape hybrids (Vitis vinifera L.) using Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) under sub-tropical conditions[J]. Vitis Journal of Grapevine Research, 2011, 50(3):115-118. |
| [11] |
JI W, WANG Y. Breeding for seedless grapes using Chinese wild Vitis spp. II. In vitro embryo rescue and plant development[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2013, 93(15):3870-3875.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6342 URL |
| [12] | MINEMURA M, IZUMI K, YAMASHITA H, et al. Breeding a new grape cultivar 'Nagano Purple' and its characteristics[J]. Horticultural Research, 2009, 8(1):115-122. |
| [13] | 陈烁, 李莎莎, 骆强伟, 等. 无核玫瑰香味葡萄种质创新及胚挽救技术优化[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2021(3):8-17. |
| [14] | 蒋爱丽, 李世诚, 金佩芳, 等. 胚培无核葡萄新品种--沪培1号的选育[J]. 果树学报, 2007, 24(3):402-403. |
| [15] | 蒋爱丽, 李世诚, 杨天仪, 等. 无核葡萄新品种--沪培2号的选育[J]. 果树学报, 2008, 25(4):618-619. |
| [16] | 郝燕, 杨瑞, 王玉安, 等. 无核葡萄新品种‘紫丰’的选育[J]. 果树学报, 2019, 36(4):533-536. |
| [17] | 李桂荣, 王跃进, 唐冬梅, 等. 无核白葡萄胚挽救育种技术研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2001, 21(3):432-436. |
| [18] | 唐冬梅, 王跃进, 赵荣华, 等. 无核葡萄胚挽救中影响胚发育的因子[J]. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(7):2449-2457. |
| [19] |
LI S, LIU K, YU S et al. The process of embryo abortion of stenospermocarpic grape and it develops into plantlet in vitro using embryo rescue[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2020, 143(2):389-409.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-020-01926-y URL |
| [20] | MEJía N, HINRICHSEN P. A new, highly assertive SCAR marker potentially useful to assist selection for seedlessness in table grape breeding[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2003,(603):559-564. |
| [21] | 王跃进, LAMIKANRA, OLUSOLA. 检测葡萄无核基因DNA探针的合成与应用[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 30(3):42-45. |
| [22] | 张艳艳, 张剑侠, 王跃进. 中国野生葡萄抗霜霉病基因RAPD标记的筛选[J]. 果树学报, 2008, 25(6):816-820. |
| [23] | 张剑侠, 王跃进, 周邦军, 等. 中国野生葡萄抗白粉病基因RAPD标记的克隆及序列分析[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2008, 16(3):481-485. |
| [24] | 田莉莉. 抗病无核葡萄胚挽救育种及种质创新[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2007:76-80. |
| [25] |
UGUR B, NEBAHAT S, HALE Y. Effects of E20 and Ms based media on in vitro induction of axillary buds and shoot development from haploid Cucumis melo microcuttings[J]. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2003, 6(13):1130-1138.
doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2003.1130.1138 URL |
| [26] | 王跃进, 王西平, 周鹏, 等. 中国野生葡萄抗黑痘病基因的RAPD标记[J]. 园艺学报, 2000, 18(5):68-71. |
| [27] | 杨有龙. 美国和日本的葡萄育种[J]. 北方果树, 1992, 2(1):1-2. |
| [28] | RAMMING D W, TARAILO R, BADR S A. 'Crimson Seedless': A new late-maturing, red seedless grape[J]. HortScience: a publication of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 1995, 30(7):1473-1474. |
| [29] |
RAMMING D W, TARAILO R. 'Fantasy Seedless': A new black seedless grape[J]. Hortscience, 1995, 30(1):152-153.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.30.1.152 URL |
| [30] | SPIEGEL P, BARON Y, SAHAR N. Inheritance of seedlessness in seeded × seedless progeny of Vitis vinifera L[J]. Vitis, 1990, 29:79-83. |
| [31] | WEINBERGER J H, HARMON F N. Seedlessness in vinifera grapes[J]. Proceedings of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 1964, 85:270-274. |
| [32] |
TUKEY H B. Artificial culture of sweet cherry embryos[J]. Journal of Heredity, 1933, 24(1):7-12.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a103677 URL |
| [33] | RAMMING D W, LEDBETTER C A, TARAILO R. Hybridization of seedless grapes[J]. Vitis, 1990,(1):439-444. |
| [34] | NOTSUKA K, TSURU T, SHIRAISHI M. Seedless-Seedless grape hybridization via in-ovulo embryo culture[J]. Journal of the Japanese Society for Horticultural Science, 2001, 70(1):7-15. |
| [35] | BURGER P, GERBER C, GERBER A, et al. Breeding seedless grapes in South Africa by means of embryo rescue[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2003(603):565-569. |
| [36] | TIAN L, WANG Y. Seedless grape breeding for disease resistance by using embryo rescue[J]. Vitis, 2015, 47(1):15-19. |
| [37] |
AKKURT M, WELTER L, MAUL E, et al. Development of SCAR markers linked to powdery mildew (Uncinula necator) resistance in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. and Vitis sp.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2007, 19(2):103-111.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-006-9047-9 URL |
| [38] | WANG Y, LIU Y, HE P, et al. Evaluation of foliar resistance to Uncinula necator in Chinese wild Vitis spp. species[J]. Vitis, 1995, 34(3):159-164. |
| [39] |
WANG Y, LIU Y, HE P, et al. Resistance of Chinese Vitis species to Elsinoë ampelina (de Bary) Shear[J]. Hortscience, 1998, 33(1):123-126.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.33.1.123 URL |
| [40] | 张剑侠. 中国野生葡萄抗病基因标记及辅助育种应用研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2006:104-106. |
| [1] | 卢倩倩, 冯琳骄, 王爽, 古力扎提·包尔汗, 褚韧, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫对鲜食葡萄生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 62-70. |
| [2] | 胡军, 多吉扎西, 拉巴, 格桑卓玛, 洛松曲珍. 西藏昌都市芒康县盐井葡萄生育期界定及气象条件分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 103-106. |
| [3] | 吴炫柯, 汪仁军, 黄维, 刘永裕, 姚裕群. 基于SURFER技术的广西葡萄高温热害空间分布研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 118-121. |
| [4] | 任曙霞, 郝玲, 董京铭, 胡冬莉, 魏怡坤. 连云港市灌南县葡萄种植气象灾害分析和气候区划[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 122-128. |
| [5] | 郑碧霞, 戢小梅, 李长林, 龚林忠, 方林川. 不同复合保鲜处理对‘夏黑’果实贮藏效果的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 135-143. |
| [6] | 郝建宇, 王伟军, 陈文朝, 刘景坤, 王岩, 寇宏立, 王尊文. 不同处理方式对‘蜜光’葡萄生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 48-57. |
| [7] | 梁长梅, 王建伟, 温鹏飞, 杨华. 高压静电场诱导采后葡萄果实总黄烷-3-醇积累模型构建[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(5): 152-156. |
| [8] | 张雯, 马依努尔·加马力, 李贺平, 王敏, 韩守安, 谢辉, 麦合木提·图如普, 周雪薇, 艾尔买克·才卡斯木, 潘明启. 80份葡萄品种叶片包裹和食用特性评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(34): 130-137. |
| [9] | 韩佳希, 范中菡, 董义霞, 吕昕芮, 李红春, 陈庆华, 李洪浩, 林立金, 胡容平. 脱落酸对葡萄幼苗镉积累的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(34): 46-51. |
| [10] | 查倩, 奚晓军, 殷向静, 蒋爱丽. 转色期补光处理对鲜食葡萄‘巨峰’和‘巨玫瑰’果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(31): 55-59. |
| [11] | 张紫卿, 韩守安, 王敏, 谢辉, 张雯, 周龙. 叶幕整形方式对新疆主要红色酿酒葡萄生长和果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(28): 58-67. |
| [12] | 赵永锋, 余开, 宋迁红, 戈贤平, 刘乐丹, 罗红, 陈倩, 徐树晨. 中国淡水池塘养殖发展战略研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(23): 135-142. |
| [13] | 黄艳玲, 严志, 申广勒, 王慧, 张从合, 杨韦, 陈琳, 张云虎, 庞战士, 乔木, 李方宝, 杨力. 分子标记辅助选择改良水稻不育系‘荃211S’白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(18): 133-139. |
| [14] | 鲍远放, 张绿萍, 郑伟, 王彬. BTH处理对火龙果采后抗病性及贮藏品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(10): 134-140. |
| [15] | 刘大章, 毛丽萍, 李志超, 郑崇兰, 巫玲琳, 祝铭谦, 巫登峰. 水肥一体化滴灌对西昌设施‘克瑞森’无核葡萄果实膨大的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(35): 34-37. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||