
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (24): 100-106.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0432
罗秀芹1,2( ), 韦卓文1,2, 蔡杰1,2, 安飞飞1,2, 陈松笔1,2, 薛晶晶1,2(
), 韦卓文1,2, 蔡杰1,2, 安飞飞1,2, 陈松笔1,2, 薛晶晶1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-07
修回日期:2023-09-15
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-08-20
通讯作者:
作者简介:罗秀芹,女,1986年出生,广东兴宁人,副研究员,硕士,研究方向:木薯遗传育种。通信地址:571101 海南省海口市龙华区学院路4号,Tel:0898-66961663,E-mail:xiuqinluo@163.com。
基金资助:
LUO Xiuqin1,2( ), WEI Zhuowen1,2, CAI Jie1,2, AN Feifei1,2, CHEN Songbi1,2, XUE Jingjing1,2(
), WEI Zhuowen1,2, CAI Jie1,2, AN Feifei1,2, CHEN Songbi1,2, XUE Jingjing1,2( )
)
Received:2023-06-07
Revised:2023-09-15
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-08-20
摘要:
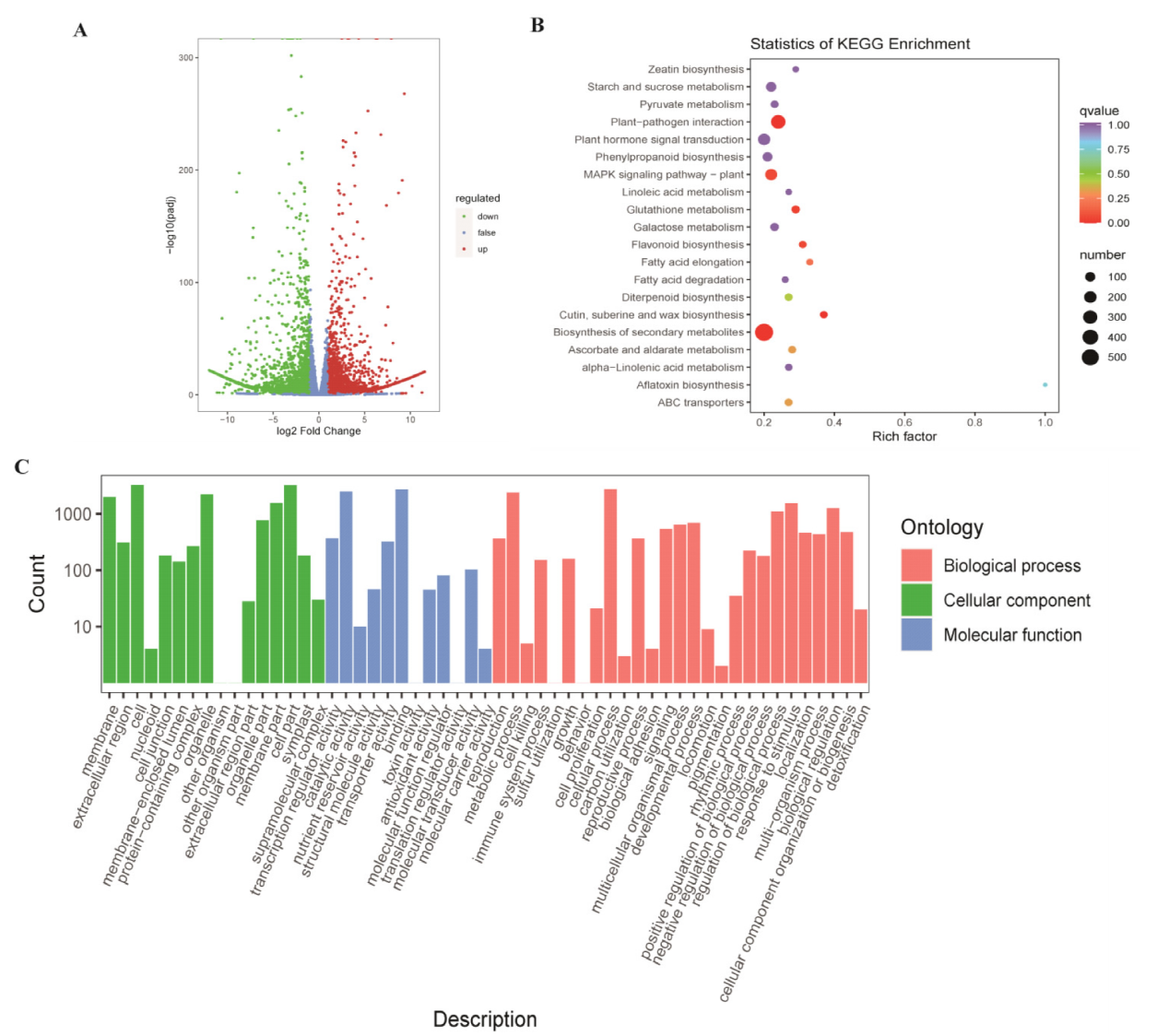
木薯是世界上第六大粮食作物,其块根富含淀粉但缺乏蛋白质、花青素、胡萝卜素等营养物质。为了探索木薯花青素生物合成机制,本研究选取了两种不同颜色木薯种质资源叶片(FL与PL)为材料,进行转录组和花青素靶向代谢组及其联合分析。转录组分析结果显示在FL和PL中6864个差异表达基因,其中包含4112个上调表达和2752个下调表达。代谢组分析结果显示26种显著差异代谢物在PL中显著高于FL,其中21种属于花青素类。联合分析结果显示,其中7个差异表达的基因与花青素生物合成相关,且花青素含量与差异基因的表达呈正相关,尤其是MeANS1的表达差异最大。本研究结果为阐明木薯花青素的生物合成机制提供了候选基因,同时也为提高木薯花青素含量奠定科学基础。
罗秀芹, 韦卓文, 蔡杰, 安飞飞, 陈松笔, 薛晶晶. 转录组和代谢组联合分析阐释木薯叶片花青素合成机制[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 100-106.
LUO Xiuqin, WEI Zhuowen, CAI Jie, AN Feifei, CHEN Songbi, XUE Jingjing. Explanation of Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Transcriptome for Anthocyanins Synthesis Mechanism in Cassava Leaves[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(24): 100-106.
| 样品 | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Base(G) | 错误率/% | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量t/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL | 49851289.33 | 48392253 | 7.26 | 0.03 | 97.50667 | 92.95333 | 43.75333 |
| PL | 48613812.67 | 47113263 | 7.066667 | 0.03 | 97.42333 | 92.80667 | 43.31 |
| 样品 | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Base(G) | 错误率/% | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量t/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL | 49851289.33 | 48392253 | 7.26 | 0.03 | 97.50667 | 92.95333 | 43.75333 |
| PL | 48613812.67 | 47113263 | 7.066667 | 0.03 | 97.42333 | 92.80667 | 43.31 |
| 物质 | 物质类别 | FL/(ng/g) | PL/(ng/g) | 倍数(FL&PL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 矢车菊素-3-(6-O-p-咖啡酰)-葡萄糖苷 | 矢车菊素 | 2.7196±0.7705B | 26.2989±0.7705A | 9.6701 | ||||
| 矢车菊素-3,5-O-二葡萄糖苷 | 0.0828±0.0021B | 2.6097±0.0685A | 31.5192 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 0.4664±0.0188B | 11.9382±0.1446A | 25.5939 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 1.7501±0.0720B | 24.9373±0.4226A | 14.2494 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-桑布双糖苷 | 0.0160±0.0013B | 0.4867±0.0411A | 30.3952 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-槐糖苷 | 0.0445±0.0017B | 1.8697±0.0323A | 41.9972 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-木糖苷 | 0.0115±0.0008B | 0.1795±0.0030A | 15.5381 | |||||
| 飞燕草素 | 飞燕草素 | 0.17204±0.0034B | 1.2881±0.0175A | 7.4873 | ||||
| 飞燕草素-3,5-O-二葡萄糖苷 | 0.1259±0.0028B | 8.7282±0.2205A | 69.3402 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 1.0915±0.0287B | 9.3198±0.3368A | 8.5386 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-鼠李糖苷 | 0.06500±0.0009B | 0.3599±0.0473A | 5.5384 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 5.0056±0.1091B | 295.9350±6.2067A | 59.1209 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷-5-O-葡萄糖苷 | 0.1837±0.0122B | 0.5204±0.0295A | 2.8338 | |||||
| 锦葵色素-3-O-半乳糖苷 | 锦葵色素 | 0.0011±0.0001B | 0.0107±0.0009A | 9.8393 | ||||
| 锦葵色素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 0.0119±0.0003B | 0.05289±0.0011A | 4.4336 | |||||
| 天竺葵素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 天竺葵素 | 0.0057±0.0004B | 0.0764±0.0023A | 13.4108 | ||||
| 天竺葵素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 0.3995±0.00259B | 15.8928±0.3032A | 39.7795 | |||||
| 芍药花素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 芍药花素 | 0.0012±0.0001B | 0.1918±0.0058A | 166.2545 | ||||
| 芍药花素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 0.1620±0.0045B | 9.6148±0.2802A | 59.3364 | |||||
| 矮牵牛素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 矮牵牛素 | 0.0380±0.0006B | 0.2716±0.0106A | 7.1428 | ||||
| 矮牵牛素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 0.1446±0.0025B | 3.6052±0.0914A | 24.9263 | |||||
| 总花青素 | 12.4987±0.0474B | 414.1877±6.9967A | 33.1385 | |||||
| 物质 | 物质类别 | FL/(ng/g) | PL/(ng/g) | 倍数(FL&PL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 矢车菊素-3-(6-O-p-咖啡酰)-葡萄糖苷 | 矢车菊素 | 2.7196±0.7705B | 26.2989±0.7705A | 9.6701 | ||||
| 矢车菊素-3,5-O-二葡萄糖苷 | 0.0828±0.0021B | 2.6097±0.0685A | 31.5192 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 0.4664±0.0188B | 11.9382±0.1446A | 25.5939 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 1.7501±0.0720B | 24.9373±0.4226A | 14.2494 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-桑布双糖苷 | 0.0160±0.0013B | 0.4867±0.0411A | 30.3952 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-槐糖苷 | 0.0445±0.0017B | 1.8697±0.0323A | 41.9972 | |||||
| 矢车菊素-3-O-木糖苷 | 0.0115±0.0008B | 0.1795±0.0030A | 15.5381 | |||||
| 飞燕草素 | 飞燕草素 | 0.17204±0.0034B | 1.2881±0.0175A | 7.4873 | ||||
| 飞燕草素-3,5-O-二葡萄糖苷 | 0.1259±0.0028B | 8.7282±0.2205A | 69.3402 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 1.0915±0.0287B | 9.3198±0.3368A | 8.5386 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-鼠李糖苷 | 0.06500±0.0009B | 0.3599±0.0473A | 5.5384 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 5.0056±0.1091B | 295.9350±6.2067A | 59.1209 | |||||
| 飞燕草素-3-O-芸香糖苷-5-O-葡萄糖苷 | 0.1837±0.0122B | 0.5204±0.0295A | 2.8338 | |||||
| 锦葵色素-3-O-半乳糖苷 | 锦葵色素 | 0.0011±0.0001B | 0.0107±0.0009A | 9.8393 | ||||
| 锦葵色素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 0.0119±0.0003B | 0.05289±0.0011A | 4.4336 | |||||
| 天竺葵素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 天竺葵素 | 0.0057±0.0004B | 0.0764±0.0023A | 13.4108 | ||||
| 天竺葵素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 0.3995±0.00259B | 15.8928±0.3032A | 39.7795 | |||||
| 芍药花素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 芍药花素 | 0.0012±0.0001B | 0.1918±0.0058A | 166.2545 | ||||
| 芍药花素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 0.1620±0.0045B | 9.6148±0.2802A | 59.3364 | |||||
| 矮牵牛素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 矮牵牛素 | 0.0380±0.0006B | 0.2716±0.0106A | 7.1428 | ||||
| 矮牵牛素-3-O-芸香糖苷 | 0.1446±0.0025B | 3.6052±0.0914A | 24.9263 | |||||
| 总花青素 | 12.4987±0.0474B | 414.1877±6.9967A | 33.1385 | |||||
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
王硕, 郑秀文, 王琪, 等. 果树中花青素合成及其分子调控机制研究进展[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2022(7), https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220728.1710.014.html.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00046 pmid: 31322881 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules17032378 pmid: 22370524 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
王定美, 王伟, 麦力文, 等. HPLC法同时测定不同采收期木薯叶片中6种类黄酮的含量[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2017, 38(18):133-137.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.3007 pmid: 24908251 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.06.007 pmid: 34171572 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00222 pmid: 23060891 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: S0882-4010(18)31278-6 pmid: 30145251 |
| [16] |
|
| [1] | 杨敏, 周陈平, 李庆萌, 邝瑞彬, 吴夏明, 魏岳荣. ‘黄花佑’和‘金锤’番木瓜贮藏期品质、贮藏特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 57-66. |
| [2] | 金辽, 刘银松, 林建枫, 张文伟, 顾钢, 魏恕文, 汪睿琪, 谢小芳, 张炳辉. 基于代谢组学解析‘翠碧一号’烟叶烘烤过程中多酚类代谢物动态变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 135-142. |
| [3] | 王莹, 李娟, 孙雪梅. 菊芋HtMYB2基因VIGS体系构建与功能验证[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 116-121. |
| [4] | 李佳颖, 刘乃新, 韩广源. 红甜菜根中萜类代谢物的比较代谢组学分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(2): 137-142. |
| [5] | 罗燕春, 赵鑫鑫, 盘欢, 廖琦, 俞奔驰, 劳赏业, 范锡恩, 刘翠娟, 李荣云, 曾新华, 付海天. 9个不同使用类型木薯品系在合浦县的适应性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 31-37. |
| [6] | 朱明霞, 张玉红. 隆子黑青稞花青素提取及体外抗氧化活性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(14): 142-147. |
| [7] | 陈丽丽, 吕平, 吕少杰, 房明志, 李斌, 胡跃高, 薛绪掌, 康文艺. 不同波长LEDs光源对苦荞芽菜生长、生物活性物积累及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(12): 45-52. |
| [8] | 梁展图, 全林发, 梁盛曦, 陈炳旭, 马群, 姚琼. 基于CiteSpace的鳞翅目昆虫转录组学研究态势分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(8): 142-148. |
| [9] | 孙保娟, 李涛, 游倩, 宫超, 黎振兴, 李植良. 茄科植物花青素合成相关的MYB转录因子研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(36): 102-111. |
| [10] | 薛守宇, 李涛涛, 李冰冰. 组学技术在葱属植物中的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(34): 22-31. |
| [11] | 郑聪慧, 徐振华, 王玉忠, 张蔓蔓, 杜克久, 李向军, 刘春鹏. 四种臭椿不同叶位叶片色素组成及分布变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(32): 56-65. |
| [12] | 梅瑜, 王继华, 蔡时可. 金线莲应答高温胁迫的转录组学特征分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 97-103. |
| [13] | 洪森荣, 朱盈盈, 李紫莹, 胡明艳, 欧阳克蕙. 盐胁迫下金花菜和紫花苜蓿试管苗的转录组分析及其耐盐基因筛选[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 111-118. |
| [14] | 秦贺兰, 梁芳, 金莹杉, 李子敬, 张华, 胡雪凡. 赛菊芋花叶突变体转录组测序分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(29): 1-7. |
| [15] | 徐珺, 董颖, 朱华, 崔金腾, 张蓉. 培养模式对水芹叶片药用成分代谢物的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(28): 33-39. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||