
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (18): 73-82.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0604
张凯1,2( ), 程彦弟3, 胡皓楠1, 冯海萍2(
), 程彦弟3, 胡皓楠1, 冯海萍2( ), 吴宏亮1(
), 吴宏亮1( ), 康建宏1
), 康建宏1
收稿日期:2023-08-15
修回日期:2023-12-22
出版日期:2024-06-25
发布日期:2024-06-18
通讯作者:
作者简介:张凯,男,1998年出生,宁夏固原人,硕士研究生,研究方向:农作制度理论与技术。通信地址:750021 宁夏银川市西夏区贺兰山西路489号,E-mail:12022131461@nxu.edu.cn。
基金资助:
ZHANG Kai1,2( ), CHENG Yandi3, HU Haonan1, FENG Haiping2(
), CHENG Yandi3, HU Haonan1, FENG Haiping2( ), WU Hongliang1(
), WU Hongliang1( ), KANG Jianhong1
), KANG Jianhong1
Received:2023-08-15
Revised:2023-12-22
Published:2024-06-25
Online:2024-06-18
摘要:
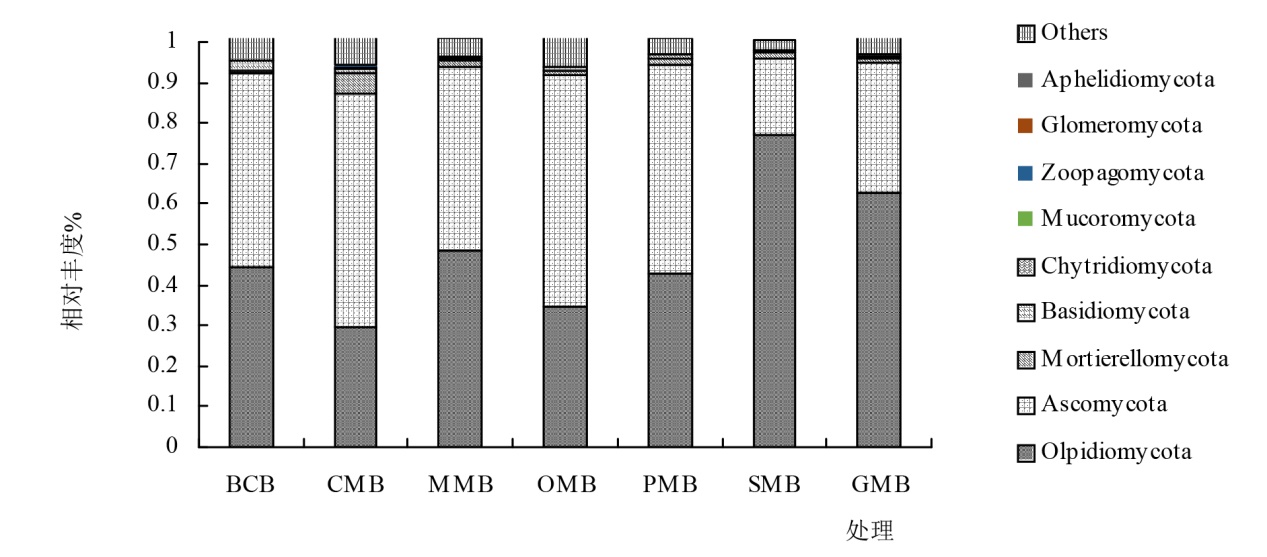
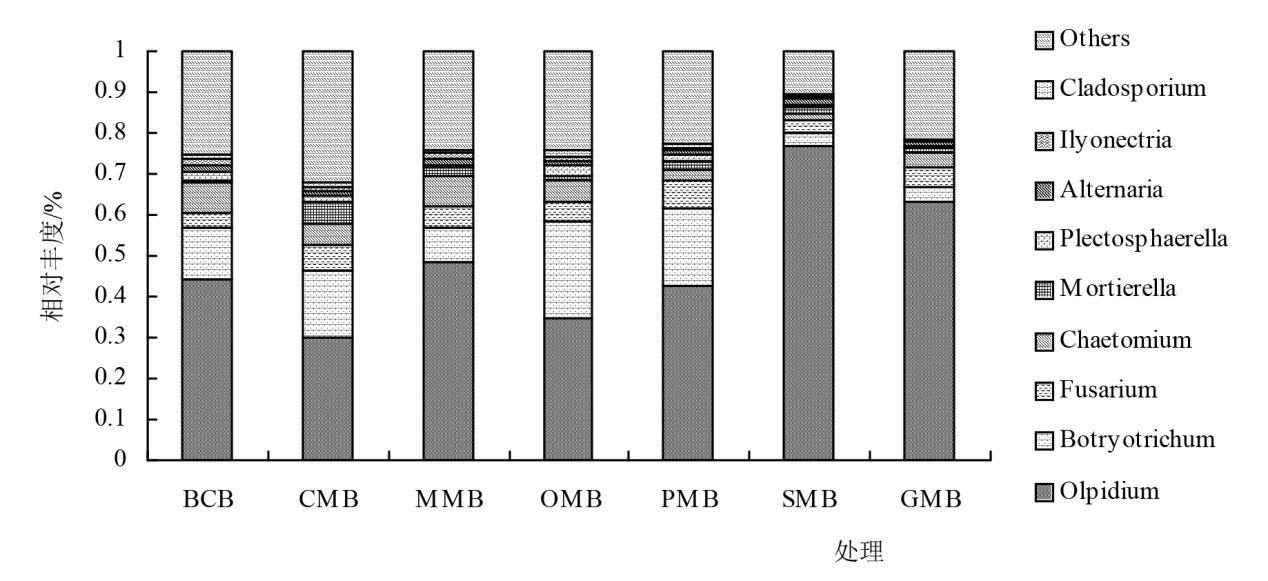
为解决耕地资源利用与管理的不合理因素导致的肥力下降,质量退化等土壤健康问题;通过田间试验,研究不同轮作模式下种植西兰花后对土壤养分,真菌群落结构和多样性的影响。以不同轮作模式后西兰花根际土壤为研究对象,测定并分析土壤化学性质、酶活性,Illumina MiSeq高通量测序技术分析真菌群落结构及多样性在6种轮作模式:西兰花分别与谷子、洋葱、大豆、马铃薯、大葱进行轮作,以西兰花连作为对照。西兰花连作(BB)、谷西轮作(MB)、洋西轮作(OB)、豆西轮作(SB)、马西轮作(PB)、葱西轮作(GB)的变化。结果表明:相较于西兰花连作,轮作后各处理土壤根际化学性质差异明显,pH无明显差异,处理MB化学性质均有明显的增加。Alpha多样性分析下,较处理BB,其他处理的Chao1指数和观察到的物种数指数都显示上升趋势,而辛普森指数则呈下降趋势。至于香农指数和Pielou’s evenness指数表现为SB<GB<MB<BB<PB<OB。真菌群落丰度和组成结果显示,优势菌群有油壶菌群、子囊菌门、被孢菌群、毛壳菌属。相关性分析表明全磷、硝态氮是影响土壤有益菌的主要因素。综合比较后,谷子轮作西兰花可明显优化土壤化学性质,增强酶活性,以及提升有益微生物群落的丰度和多样性,从而增强土壤养分的调节和植物病害的抵抗性,在各方面指标中都表现为最佳,能有效缓解西兰花的连作和改善土壤健康问题,建议推广种植。
张凯, 程彦弟, 胡皓楠, 冯海萍, 吴宏亮, 康建宏. 不同轮作模式通过改善西兰花土壤养分和真菌群落在土壤健康中的应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 73-82.
ZHANG Kai, CHENG Yandi, HU Haonan, FENG Haiping, WU Hongliang, KANG Jianhong. Improving Broccoli Soil Nutrients and Fungal Community: Application of Different Rotation Patterns in Soil Health[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(18): 73-82.
| pH | EC/(mS/cm) | SOM/(g/kg) | TN/(g/kg) | TP/(g/kg) | AK/(mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 8.78 | 0.20 | 11.38 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 124.71 |
| M | 8.73 | 0.19 | 13.21 | 0.58 | 0.29 | 160.64 |
| S | 8.73 | 0.19 | 13.50 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 139.16 |
| O | 8.85 | 0.19 | 9.40 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 107.10 |
| G | 8.74 | 0.18 | 18.14 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 224.28 |
| P | 8.75 | 0.22 | 13.06 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 199.24 |
| AP/(g/kg) | NO3--N/(mg/kg) | NH4+-N/(mg/kg) | 脲酶Urease/[mg/(d·g)] | 蔗糖酶Sucrase/[mg/(d·g)] | 过氧化氢酶Catalase/[mg/(d·g)] | |
| B | 16.75 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 2.71 | 0.94 | 1.11 |
| M | 36.83 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 2.77 | 0.86 | 1.05 |
| S | 31.44 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 3.99 | 1.49 | 1.10 |
| O | 14.05 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 3.22 | 1.29 | 0.97 |
| G | 30.86 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 7.41 | 3.44 | 1.17 |
| P | 11.99 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 3.12 | 1.70 | 1.12 |
| pH | EC/(mS/cm) | SOM/(g/kg) | TN/(g/kg) | TP/(g/kg) | AK/(mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 8.78 | 0.20 | 11.38 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 124.71 |
| M | 8.73 | 0.19 | 13.21 | 0.58 | 0.29 | 160.64 |
| S | 8.73 | 0.19 | 13.50 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 139.16 |
| O | 8.85 | 0.19 | 9.40 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 107.10 |
| G | 8.74 | 0.18 | 18.14 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 224.28 |
| P | 8.75 | 0.22 | 13.06 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 199.24 |
| AP/(g/kg) | NO3--N/(mg/kg) | NH4+-N/(mg/kg) | 脲酶Urease/[mg/(d·g)] | 蔗糖酶Sucrase/[mg/(d·g)] | 过氧化氢酶Catalase/[mg/(d·g)] | |
| B | 16.75 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 2.71 | 0.94 | 1.11 |
| M | 36.83 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 2.77 | 0.86 | 1.05 |
| S | 31.44 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 3.99 | 1.49 | 1.10 |
| O | 14.05 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 3.22 | 1.29 | 0.97 |
| G | 30.86 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 7.41 | 3.44 | 1.17 |
| P | 11.99 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 3.12 | 1.70 | 1.12 |
| 处理 | Chao1 指数 | 物种观察数 | 辛普森指数 | 香农指数 | Pielou均匀度 | 覆盖度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BB | 242.11±26.89b | 235.08±23.50b | 0.76±0.14a | 3.75±0.79a | 0.48±0.11a | 100 |
| GB | 274.65±50.63ab | 268.12±50.00ab | 0.55±0.24a | 2.76±1.42a | 0.348±0.16a | 100 |
| MB | 352.59±56.33a | 342.82±57.14a | 0.72±0.20a | 3.70±1.11a | 0.44±0.13a | 100 |
| OB | 250.90±87.66b | 247.02±86.56ab | 0.73±0.25a | 3.92±1.57a | 0.50±0.19a | 100 |
| PB | 261.84±38.91ab | 255.68±34.85ab | 0.75±0.196a | 3.80±1.02a | 0.48±0.13a | 100 |
| SB | 292.89±14.12ab | 277.04±34.85ab | 0.38±0.28a | 1.98±1.42a | 0.24±0.17a | 100 |
| 处理 | Chao1 指数 | 物种观察数 | 辛普森指数 | 香农指数 | Pielou均匀度 | 覆盖度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BB | 242.11±26.89b | 235.08±23.50b | 0.76±0.14a | 3.75±0.79a | 0.48±0.11a | 100 |
| GB | 274.65±50.63ab | 268.12±50.00ab | 0.55±0.24a | 2.76±1.42a | 0.348±0.16a | 100 |
| MB | 352.59±56.33a | 342.82±57.14a | 0.72±0.20a | 3.70±1.11a | 0.44±0.13a | 100 |
| OB | 250.90±87.66b | 247.02±86.56ab | 0.73±0.25a | 3.92±1.57a | 0.50±0.19a | 100 |
| PB | 261.84±38.91ab | 255.68±34.85ab | 0.75±0.196a | 3.80±1.02a | 0.48±0.13a | 100 |
| SB | 292.89±14.12ab | 277.04±34.85ab | 0.38±0.28a | 1.98±1.42a | 0.24±0.17a | 100 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
冯海萍. 宁南山区露地西兰花高产高效栽培技术[J]. 长江蔬菜, 2022(9):4-6.
|
| [4] |
李旭霞. 宁夏地区冷凉蔬菜栽培现状调查研究[J]. 蔬菜, 2022(11):54-57.
|
| [5] |
张卫信, 申智锋, 邵元虎, 等. 土壤生物与可持续农业研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(10):3183-3206.
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02120-6 pmid: 33794774 |
| [7] |
翁佩莹, 郑红艳. 作物连作障碍的成因与机制及其消减策略[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 2020, 49(2):157-162.
|
| [8] |
耿文丛, 马悦, 张玉雪, 等. 设施农业的土壤健康调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(12):1973-1984.
|
| [9] |
覃潇敏, 蒋娟娟, 韦巧云, 等. 轮作与生物有机肥对菠萝连作土壤微生物特性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023(6):1-10.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
程国亭, 王延峰, 姜文婷, 等. 设施番茄土壤障碍综合防控研究进展[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2023(2):16-24.
|
| [13] |
王东, 句梦娜, 赵远征, 等. 西兰花轮作及其残体还田对土壤中病原菌微菌核数量、黄萎病发生及马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(6):1297-1303.
|
| [14] |
朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 等. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5):909-917.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.006 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
陈海生, 刘守平, 梁国钱, 等. 3种西兰花种植方式对根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响研究[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(6):1457-1465.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1457 |
| [17] |
杨子峰, 陈伟强, 王伟, 等. 轮作模式对西兰花耕作土壤微生物和酶活性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(5):818-823.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2017.05.19 |
| [18] |
李丹, 李小霞, 李万星, 等. 谷子不同轮作模式对土壤理化性质及细菌群落的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(6):1500-1509.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
高群, 孟宪志, 于洪飞. 连作障碍原因分析及防治途径研究[J]. 山东农业科学, 2006(3):60-63.
|
| [21] |
徐宁. 稻田复种轮作系统的作物生产力、生态环境效应及能流物流特征研究[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2013(2):48.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
孙倩, 吴宏亮, 陈阜, 等. 不同轮作模式下作物根际土壤养分及真菌群落组成特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(10):4682-4689.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
陈爱萍, 周逢芳. 连作对草莓根际土壤指标及优势真菌的影响[J]. 宁德师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2018, 30(1):66-70.
|
| [30] |
张邦喜, 顾小凤, 张萌, 等. 轮作对贵州烤烟农艺和经济性状及真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(9):81-87.
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2013.01.014 pmid: 23403226 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1007/s10661-020-08556-z pmid: 32857216 |
| [34] |
刘会芳, 韩宏伟, 王强, 等. 不同蔬菜与番茄轮作对设施土壤微生物多样性、酶活性及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(1):167-182.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
陈倬, 冯海萍, 程彦弟, 等. 不同茬口对娃娃菜根际土壤养分和真菌群落的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(7):141-152.
|
| [1] | 郑剑超, 李明, 董飞. 减施化肥增施有机肥和菌肥对番茄产量及土壤微生物和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(9): 48-54. |
| [2] | 陈睿, 崔泽远, 李志, 耿贵, 於丽华. AM真菌对连作土壤上作物生长影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(6): 1-8. |
| [3] | 朱诗君, 罗幼君, 金树权, 周金波, 汪峰. 灵芝—水稻轮作体系中土壤微生物群落的演替[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(5): 39-46. |
| [4] | 林思远, 袁军委, 侯俊, 何文祥, 蔡亮, 吴俊达, 刘超, 刘翔. 有机肥小分子化促进作物增产增效的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(15): 59-65. |
| [5] | 胡皓楠, 冯海萍, 张凯, 吴宏亮, 康建宏. 土壤微生物对种植模式的响应——基于CiteSpace的文献计量分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(13): 146-156. |
| [6] | 黄金玲, 覃丽萍, 刘志明, 刘峥嵘, 李红芳, 陆秀红. 广西水稻产区稻-菜轮作田水稻根结线虫病发生情况调查及病原鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(12): 126-133. |
| [7] | 付斌, 胡万里, 倪明, 李枝武, 王炽, 陈安强, 闫辉, 赵新梅, 陈兴位, 杨树明. 等氮量有机替代对水稻田面水氮素动态变化特征研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(11): 36-43. |
| [8] | 施林林, 柳开楼, 董林林, 沈园, 陈培峰, 沈明星, 王海侯. 太湖地区稻麦轮作系统有机氮肥替代率的演变特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(1): 1-6. |
| [9] | 殷丽萍, 刘思远, 蔡成梅, 石小丽, 朱小娟, 袁国明, 汪吉东, 张辉, 徐聪, 马洪波. 嘉博文土壤调理剂对萝卜产量品质、土壤理化性质的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(6): 64-71. |
| [10] | 平晓帆, 魏云敏, 宋小双, 遇文婧. 火干扰对森林和草原土壤影响的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(35): 75-80. |
| [11] | 杨东, 刘晓霞, 陈红金, 虞轶俊. 定额制施肥对土壤及生态环境影响的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(32): 91-98. |
| [12] | 郭巨先, 李桂花, 符梅, 刘县明, 罗文龙, 骆善伟, 刘玉涛. 微生物有机肥对芋头产量品质性状及土壤微生物类群的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 20-27. |
| [13] | 武明雅, 陈俊强, 马海林, 刘方春, 刘丙花, 刘幸红, 司东霞. 印度梨形孢定殖策略和促生机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 119-126. |
| [14] | 黄颖博, 罗凡, 龚雪蛟, 王迎春, 李兰英, 刘东娜, 尧渝. 有机肥对土壤微生物群落特征影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 88-96. |
| [15] | 蔡雅琪, 包天莉, 焦晓光. 东北黑土区生物结皮对土壤微生物量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(29): 39-45. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||