
中国农学通报 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (29): 21-30.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2024-0141
翟玉凤1( ), 丁兰2, 余叶敏3, 贾巧君1, 梁宗锁1, 汪得凯1(
), 丁兰2, 余叶敏3, 贾巧君1, 梁宗锁1, 汪得凯1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-29
修回日期:2024-05-15
出版日期:2024-10-15
发布日期:2024-10-14
通讯作者:
作者简介:翟玉凤,女,1997年出生,山东德州人,硕士研究生,主要从事药用植物资源研究。通信地址:310018 浙江杭州钱塘区下沙2号大街928号 浙江理工大学生命科学与医药学院,Tel:0571-86843303,E-mail: 276109167@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHAI Yufeng1( ), DING Lan2, YU Yemin3, JIA Qiaojun1, LIANG Zongsuo1, WANG Dekai1(
), DING Lan2, YU Yemin3, JIA Qiaojun1, LIANG Zongsuo1, WANG Dekai1( )
)
Received:2024-02-29
Revised:2024-05-15
Published:2024-10-15
Online:2024-10-14
摘要:
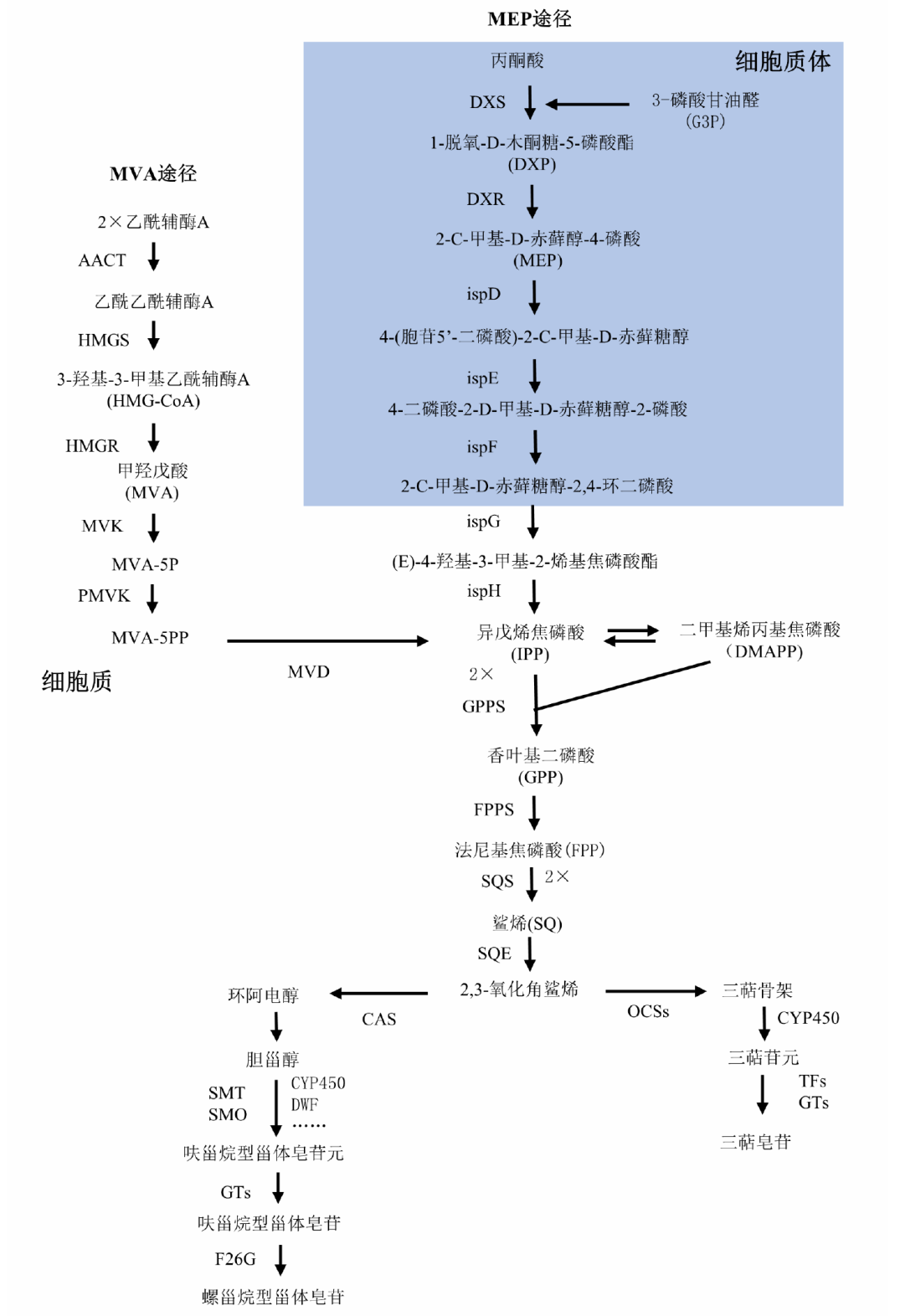
黄精(Polygonatum spp.)是药食同源植物,其活性成分如多糖、黄酮和皂苷具有显著的药理作用。近年来的研究主要集中在从黄精中提取具有抗疲劳、抗氧化、降血糖、降血脂及增强免疫力的皂苷类成分。尽管对黄精皂苷的结构解析取得了一定进展,但其生物合成途径尚需深入研究。黄精中的皂苷通过甲羟戊酸途径和2-C-甲基-D-赤藓醇-4-磷酸途径合成,涉及多个酶催化步骤。本研究提出,黄精皂苷在抗肿瘤、抗菌抗炎、抗病毒及提高免疫调节方面具有多种生物功效,并在药品、食品、化妆品等领域有广泛应用。然而,当前研究还存在以下不足:结构解析不够深入、生物合成途径未完全阐明及药理作用机制不明。未来的研究应加强黄精皂苷的分离、结构解析、合成生物学及药理学研究,以推动其科学研究和产品开发,为新型治疗药物的开发提供科学依据。
翟玉凤, 丁兰, 余叶敏, 贾巧君, 梁宗锁, 汪得凯. 黄精皂苷的化学成分、生物合成及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(29): 21-30.
ZHAI Yufeng, DING Lan, YU Yemin, JIA Qiaojun, LIANG Zongsuo, WANG Dekai. The Chemical Constituents, Biological Synthesis and Pharmacological Effects of the genus Polygonatum Saponins: A Review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(29): 21-30.
| 来源 | 皂苷类化合物名称 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 滇黄精 Polygonatum kingianum | kingianosides A,kingianosides B,kingianosides C,kingianosides D | [ |
| 6-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-3β,6α,12β,25-tetrahydroxy-(20S,24R)-epoxy-dammarane | [ | |
| kingianoside H、kingianoside I、ginsenoside-Rc、(25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17a-diol-3-O-a-L-rhamnopyra-nosyl-(1→4)-a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-[a-L-rhamnopy-ranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; (25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17a-diol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-[a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; polygonatoside C1; ophiopogonin C’; | [ | |
| kingianoside K,(3β,23S,25R)-23-hydroxy-12-oxospirost-5-en-3-yl 4-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-galactopyranoside | [ | |
| 黄精 Polygonatum sibiricum | Huangjinoside A,Huangjinoside B,Huangjinoside C,Huangjinoside D,Huangjinoside E,Huangjinoside F; Huangjinoside G; Huangjinoside H; Huangjinoside I; Huangjinoside J; Huangjinoside K; Huangjinoside L; Huangjinoside M; Huangjinoside N; Huangjinoside O; Huangjinoside P; Huangjinoside Q; Huangjinoside R; | [ |
| asiaticoside,Oleanane-type saponins,madecassoside,3β(OH)-(3→1)glucose-(4→1)glucose(28→1)arabinose-(2→1)arabinose-oleanolic acid; | [ | |
| 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl-diosgenin; 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl-diosgenin; | [ | |
| 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-fucopyranosyl -(25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17α-diol, 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D- fucopyranosyl-(25S)-spirost-5-en-3β,17α-diol; 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-fucopyranosyl-(25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17α-diol;3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-fucopyranosyl-(25R/S)-spirost-5-en-3β,12β-diol; | [ | |
| polygonoside 1,polygonoside 2,polygonoside 3,polygonoside,polygonoside 5,polygonoside 6,polygonoside 7 | [ | |
| polygodoside F,yamogenin 3-O-β-lycotetraoside,gentrogenin 3-O-β-lycotetraoside,neoprazerigenin A 3-O-β-lycotetraoside; diosgenin 3-O-β-lycotetraoside; madecassoside; diosgenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; prosapogenin B of dioscin; neoprazerigenin A; (25R)-kingianoside G; acutoside A; diosgenin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | [ | |
| Polygonoides C (1),Polygonoides D (2),Polygonoides E (3) | [ | |
| 点花黄精 Polygonatum punctatum | Polypunctatoside A,PolypunctatosideB,PolypunctatosideC,PolypunctatosideD,Polypunctatoside E,dioscin;protodioscin; 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)[α-L-arabinofuranosyl(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; prosapogenin A of dioscin; proto-type of prosapogenin A of dioscin; | [ |
| 轮叶黄精 Polygonatum verticillatum | 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-22ξ-hydroxy-(25R)-furost-5-en-3β,26-diol,3-O-β[xylopyranosyl(1→3)α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)β-D-glucopyranoside]; 3-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→3)α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)β-D-glucopyranoside diosgenin; | [ |
| 多花黄精 Polygonatum cyrtonema | (25R)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside; (25S)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside (25R)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→3)]-O-β-Dglucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside; (25S)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→3)]-O-β-Dglucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside 25R-3-β-hydroxyspirost-5-en-12-one; 25S-3-β-hydroxyspirost-5-en-12-one | [ |
| 来源 | 皂苷类化合物名称 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 滇黄精 Polygonatum kingianum | kingianosides A,kingianosides B,kingianosides C,kingianosides D | [ |
| 6-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-3β,6α,12β,25-tetrahydroxy-(20S,24R)-epoxy-dammarane | [ | |
| kingianoside H、kingianoside I、ginsenoside-Rc、(25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17a-diol-3-O-a-L-rhamnopyra-nosyl-(1→4)-a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-[a-L-rhamnopy-ranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; (25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17a-diol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-[a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; polygonatoside C1; ophiopogonin C’; | [ | |
| kingianoside K,(3β,23S,25R)-23-hydroxy-12-oxospirost-5-en-3-yl 4-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-galactopyranoside | [ | |
| 黄精 Polygonatum sibiricum | Huangjinoside A,Huangjinoside B,Huangjinoside C,Huangjinoside D,Huangjinoside E,Huangjinoside F; Huangjinoside G; Huangjinoside H; Huangjinoside I; Huangjinoside J; Huangjinoside K; Huangjinoside L; Huangjinoside M; Huangjinoside N; Huangjinoside O; Huangjinoside P; Huangjinoside Q; Huangjinoside R; | [ |
| asiaticoside,Oleanane-type saponins,madecassoside,3β(OH)-(3→1)glucose-(4→1)glucose(28→1)arabinose-(2→1)arabinose-oleanolic acid; | [ | |
| 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl-diosgenin; 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl-diosgenin; | [ | |
| 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-fucopyranosyl -(25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17α-diol, 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D- fucopyranosyl-(25S)-spirost-5-en-3β,17α-diol; 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-fucopyranosyl-(25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,17α-diol;3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-fucopyranosyl-(25R/S)-spirost-5-en-3β,12β-diol; | [ | |
| polygonoside 1,polygonoside 2,polygonoside 3,polygonoside,polygonoside 5,polygonoside 6,polygonoside 7 | [ | |
| polygodoside F,yamogenin 3-O-β-lycotetraoside,gentrogenin 3-O-β-lycotetraoside,neoprazerigenin A 3-O-β-lycotetraoside; diosgenin 3-O-β-lycotetraoside; madecassoside; diosgenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; prosapogenin B of dioscin; neoprazerigenin A; (25R)-kingianoside G; acutoside A; diosgenin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | [ | |
| Polygonoides C (1),Polygonoides D (2),Polygonoides E (3) | [ | |
| 点花黄精 Polygonatum punctatum | Polypunctatoside A,PolypunctatosideB,PolypunctatosideC,PolypunctatosideD,Polypunctatoside E,dioscin;protodioscin; 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)[α-L-arabinofuranosyl(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside; prosapogenin A of dioscin; proto-type of prosapogenin A of dioscin; | [ |
| 轮叶黄精 Polygonatum verticillatum | 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-22ξ-hydroxy-(25R)-furost-5-en-3β,26-diol,3-O-β[xylopyranosyl(1→3)α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)β-D-glucopyranoside]; 3-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→3)α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)β-D-glucopyranoside diosgenin; | [ |
| 多花黄精 Polygonatum cyrtonema | (25R)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside; (25S)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside (25R)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→3)]-O-β-Dglucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside; (25S)spirostan-5-en-12-one-3-O-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl(1→3)]-O-β-Dglucopyranosyl(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside 25R-3-β-hydroxyspirost-5-en-12-one; 25S-3-β-hydroxyspirost-5-en-12-one | [ |

| [1] |
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China:Vol I (中华人民共和国药典:第一部)[M]. Beijing: China medical science press, 2020:319-320.
|
| [2] |
杨冰峰, 胥峰, 李淑立, 等. 黄精化学成分-生理功能及产业发展研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(11):8-12.
|
| [3] |
王彩霞. 黄精中三萜皂苷和活性多糖的分离与鉴定[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2008.
|
| [4] |
胡康棣, 李昌林, 李昌素, 等. 黄精功能成分的研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(12):16-18.
|
| [5] |
陈晔, 孙晓生. 黄精的药理研究进展[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2010, 21(3):328-330.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2018.01.003 pmid: 29629289 |
| [8] |
罗攀, 吕春明, 周文斌, 等. 薯蓣皂苷药理作用、潜在肝毒性及药代动力学研究进展[J]. 中国药物警戒, 2018, 15(8):493-498.
|
| [9] |
唐翩翩, 徐德平. 黄精中甾体皂苷的分离与结构鉴定[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2008(4):34-37.
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)00992-x pmid: 11762770 |
| [11] |
宋玮, 郑伟, 张洁, 等. 中药皂苷类成分的体内代谢研究进展[J]. 药学学报, 2018, 53(10):1609-1619.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
马百平, 张洁, 康利平, 等. 滇黄精中一个三萜皂苷的NMR研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2007, 19(1):7-10.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
孙隆儒. 黄精化学成分及生物活性的研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳科技大学, 1999.
|
| [17] |
徐德平, 孙婧, 齐斌, 等. 黄精中三萜皂苷的提取分离与结构鉴定[J]. 中草药, 2006, 37(10):1470-1472.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
李宁, 李巍, 陈刚, 等. 甾体皂苷类化合物及其制备方法和应用.中国:CN 111303231 B[P].2021-8-24.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
尹艳, 关红雨, 张夏楠. 甾体皂苷生物合成相关酶及基因研究进展[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2016, 28(8):1332-1336.
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2911-0 pmid: 29748819 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
张雪, 王希付, 赵荣华, 等. 药用植物甾体皂苷生物合成途径研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(14):225-234.
|
| [29] |
廖荣俊, 杨阳, 叶碧欢, 等. 多花黄精根茎的转录组分析与甾体皂苷生物合成相关基因发掘[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(7):1648-1656.
|
| [30] |
单春苗, 王晨凯, 施圆圆, 等. 多花黄精甾体皂苷生物合成途径分析及关键酶基因研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(12):2847-2857.
|
| [31] |
徐惠龙, 孟静, 范世明, 等. 基于转录组的多花黄精与长梗黄精代谢途径分析[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(11):2663-2668.
|
| [32] |
doi: S1875-5364(20)30049-2 pmid: 32503733 |
| [33] |
周宸, 巩婷, 陈晶晶, 等. 三萜皂苷生物合成相关糖基转移酶研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(4):1-21.
|
| [34] |
朱源, 李检秀, 李坚斌, 等. 药用植物中四环三萜皂苷合成生物学研究进展[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2020, 36(3):309-316.
|
| [35] |
张召宝, 侯林, 崔清华, 等. 中药三萜皂苷合成通路的生物信息学分析[J]. 中成药, 2015, 37(6):1255-1261.
|
| [36] |
牛云云, 朱孝轩, 罗红梅, 等. 三萜皂苷合成生物学元件的开发:三七鲨烯环氧酶编码基因克隆及表达模式分析[J]. 药学学报, 2013, 48(2):211-218.
|
| [37] |
李诺楠, 李春. 糖基转移酶在三萜皂苷合成中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10):3869-3879.
doi: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190607 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
赵水平. 血脂第3讲高脂血症的病因[J]. 中国临床医生, 2003, 31(11):15-17.
|
| [41] |
彭静. 黄精皂苷对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾损伤的保护作用及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J]. 中成药, 2019, 41(10):2518-2521.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: S0031-9422(19)30019-6 pmid: 31158602 |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.024 pmid: 33878610 |
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
梁玉琼, 黄庆, 陈梁可, 等. 薯蓣皂苷对HepG2肝癌细胞增殖的抑制作用[J]. 现代食品科技, 2021, 37(8):62-66,213.
|
| [50] |
武豪杰, 张明辉, 洪成智. 薯蓣皂苷对滑膜炎大鼠症状的改善作用和对TLR2-NF-κB信号通路的调节作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021, 47(4):943-950.
|
| [51] |
刘彦东. 不同生长期黔产黄精中化学成分研究及质量评价[D]. 贵州: 贵州师范大学, 2017.
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
徐维平, 祝凌丽, 魏伟, 等. 黄精总皂苷对慢性应激性抑郁模型大鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国临床保健杂志, 2011, 14(1):59-61.
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
郭纪芬, 刘艳菊, 杨筱. 薯蓣皂苷元抑制宫颈癌免疫逃逸的作用及机制探讨[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2021, 37(15):1830-1835.
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
张明晓, 方峰, 杨艳, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1对幼龄大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤和神经元凋亡的保护作用[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 42(5):693-699.
|
| [58] |
孙隆儒, 李铣, 郭月英, 等. 黄精改善学习记忆障碍等作用的研究[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2001, 18(4):286-288.
|
| [59] |
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1921 pmid: 25189808 |
| [60] |
|
| [1] | 程功, 章建红, 袁虎威, 郑炳松, 闫道良. 冬青属常用药用植物化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(8): 30-37. |
| [2] | 施锘, 朱宏强, 王圣丰, 关辉, 周艳宾, 杜宇, 代惠娟. 植物生长调节剂对烤烟生长发育及产质量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(28): 10-16. |
| [3] | 艾仄宜, 胡振民, 叶禹彤, 穆兵, 李荣林, 杨亦扬. 不同茶树品种绿杨春茶的适制性评价及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(28): 148-156. |
| [4] | 杨玉玲, 王灿, 屈用函, 茹瑞红, 孙宏伟, 李雪萍, 杨清松, 陶永宏. 文山地区三七根际真菌群落多样性及与土壤类型的关系研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(28): 94-101. |
| [5] | 侯冰清, 王硕立, 张友杰, 曹阳, 时向东, 丁松爽, 刘冰洋, 王以慧. 基于BP神经网络的雪茄原料感官质量预测模型构建[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(27): 126-133. |
| [6] | 苏海兰, 江保东, 朱雁鸣, 郑梅霞, 陈宏, 丁明月, 牛雨晴, 朱育菁. 黄精转录组SSR分子标记开发及种质遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(26): 30-37. |
| [7] | 杨艳, 赵伟金, 谢益燕, 马骏洁, 彭仁, 杨德海, 郑仕方, 孙永华, 李晓婷, 李先才. 大理州植烟区‘KRK26’烟叶化学成分与感官质量特征和土壤养分的关系[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(25): 132-139. |
| [8] | 罗秀芹, 韦卓文, 蔡杰, 安飞飞, 陈松笔, 薛晶晶. 转录组和代谢组联合分析阐释木薯叶片花青素合成机制[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 100-106. |
| [9] | 王莹, 李娟, 孙雪梅. 菊芋HtMYB2基因VIGS体系构建与功能验证[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 116-121. |
| [10] | 张辉红, 张亚恒, 沈勰, 王唯, 刘胜传, 吴方莲, 张仕祥, 陈发元. 黔西南州烤烟烟叶化学成分与外观质量、感官质量的相关性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(22): 149-157. |
| [11] | 王慧芳, 张希, 王智慧, 郭创江, 文俊明, 杨照, 刘云. 不同湿度条件对雪茄烟叶晾制过程中酶促棕色化反应及品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(21): 131-138. |
| [12] | 李宛儒, 关昕, 祁可香, 张赫, 曾伟民, 郑春英. 刺五加叶精油的制备及挥发性成分分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 157-164. |
| [13] | 张杨, 孔德才, 董小卫, 孙延国, 曲远凯, 闫慧峰. 主成分分析法在山东上部烟质量评价中的应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 53-57. |
| [14] | 朱明霞, 张玉红. 隆子黑青稞花青素提取及体外抗氧化活性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(14): 142-147. |
| [15] | 陈丽丽, 吕平, 吕少杰, 房明志, 李斌, 胡跃高, 薛绪掌, 康文艺. 不同波长LEDs光源对苦荞芽菜生长、生物活性物积累及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(12): 45-52. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||