
中国农学通报 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (17): 115-125.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2025-0135
金永萍1( ), 刘连金1, 任静1, 法泽1, 李金华1, 王慧玲1, 吴文涛1, 朱有勇1, 何霞红1,2(
), 刘连金1, 任静1, 法泽1, 李金华1, 王慧玲1, 吴文涛1, 朱有勇1, 何霞红1,2( ), 郭力维1(
), 郭力维1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-28
修回日期:2025-04-15
出版日期:2025-06-15
发布日期:2025-06-15
通讯作者:
作者简介:金永萍,女,1999年出生,云南玉溪人,在读硕士研究生,研究方向:生物多样性与植物病害控制。通信地址:650500 云南省昆明市盘龙区沣源路452号 云南农业大学,E-mail:2508190091@qq.com。
基金资助:
JIN Yongping1( ), LIU Lianjin1, REN Jing1, FA Ze1, LI Jinhua1, WANG Huiling1, WU Wentao1, ZHU Youyong1, HE Xiahong1,2(
), LIU Lianjin1, REN Jing1, FA Ze1, LI Jinhua1, WANG Huiling1, WU Wentao1, ZHU Youyong1, HE Xiahong1,2( ), GUO Liwei1(
), GUO Liwei1( )
)
Received:2025-02-28
Revised:2025-04-15
Published:2025-06-15
Online:2025-06-15
摘要:
为了探明外源物质对茄腐镰刀菌(Fusarium solani)引发的三七根腐病的协同防治效果,本研究采用L-赖氨酸和哈茨木霉菌(Trichoderma harzianum)配合施用,开展室内带药平板和室外盆栽试验,明确不同处理对F. solani菌株、三七幼苗生长、根腐病防控及其对三七根际微生物多样性调控的影响。结果表明:1 μmol/L L-赖氨酸对F. solani的抑制率仅有13.32%,但显著促进了T. harzianum生长(23.05%)和产孢(173.61%);盆栽试验中,以LTF1处理(1 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani)应用效果最好;与CK(F. solani)相比,三七存苗率、根鲜重和根干重分别提高45.83%、27.45%和33.33%,根腐病发病率降低88.89%。根际微生物高通量测序分析表明,对土壤真菌和细菌多样性均有影响,其中,真菌群落丰度降低最为显著。子囊菌门(Ascomycota,87.27%)和放线菌门(Actinobacteriota,24.54%)为优势菌群,木霉属(Trichoderma,28.57%)、厌氧粘细菌属(Anaeromyxobacter,2.47%)及类芽孢杆菌属(Paenibacillus,1.96%)等功能菌属显著富集,与根腐病发病率呈负相关。本实验结果为L-赖氨酸和哈茨木霉菌(Trichoderma harzianum)联用防控三七根腐病提供生态治理新策略。
金永萍, 刘连金, 任静, 法泽, 李金华, 王慧玲, 吴文涛, 朱有勇, 何霞红, 郭力维. L-赖氨酸和哈茨木霉菌联用对三七生长、根腐病及根际微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(17): 115-125.
JIN Yongping, LIU Lianjin, REN Jing, FA Ze, LI Jinhua, WANG Huiling, WU Wentao, ZHU Youyong, HE Xiahong, GUO Liwei. Effects of Growth, Root Rot Disease, and Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure of Panax notoginseng: A Combined Application of L-Lysine and Trichoderma harzianum[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2025, 41(17): 115-125.
| 序号 | 试验处理 | 单次灌根用量/(mL/盆) | 单次灌水量/(mL/盆) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | F. solani(茄腐镰刀菌) | 50 | 150 |
| TF | T. harzianum+F. solani(哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LF1 | 1 μmol/L L-Lysine+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LF10 | 10 μmol/L L-Lysine+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LF100 | 100 μmol/L L-Lysine+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LTF1 | 1 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50+50 | 50 |
| LTF10 | 10 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50+50 | 50 |
| LTF100 | 100 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50+50 | 50 |
| 序号 | 试验处理 | 单次灌根用量/(mL/盆) | 单次灌水量/(mL/盆) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | F. solani(茄腐镰刀菌) | 50 | 150 |
| TF | T. harzianum+F. solani(哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LF1 | 1 μmol/L L-Lysine+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LF10 | 10 μmol/L L-Lysine+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LF100 | 100 μmol/L L-Lysine+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50 | 100 |
| LTF1 | 1 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50+50 | 50 |
| LTF10 | 10 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50+50 | 50 |
| LTF100 | 100 μmol/L L-Lysine+T. harzianum+F. solani(L-赖氨酸+哈茨木霉菌+茄腐镰刀菌) | 50+50+50 | 50 |
| L-赖氨酸供试浓度/(μmol/L) | 菌落直径/cm | 抑制率/% | 产孢量/(×106CFU/mL) | 孢子产生抑制率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.47±0.10 a | — | 0.26±0.02 b | — |
| 1 | 3.86±0.06 b | 13.32±1.7 a | 0.41±0.02 a | -60.37±17.75 b |
| 10 | 4.43±0.03 a | 0.18±2.48 b | 0.17±0.02 c | 32.69±11.87 a |
| 100 | 4.03±0.08 b | 9.61±2.06 a | 0.15±0.02 c | 38.82±12.95 a |
| L-赖氨酸供试浓度/(μmol/L) | 菌落直径/cm | 抑制率/% | 产孢量/(×106CFU/mL) | 孢子产生抑制率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.47±0.10 a | — | 0.26±0.02 b | — |
| 1 | 3.86±0.06 b | 13.32±1.7 a | 0.41±0.02 a | -60.37±17.75 b |
| 10 | 4.43±0.03 a | 0.18±2.48 b | 0.17±0.02 c | 32.69±11.87 a |
| 100 | 4.03±0.08 b | 9.61±2.06 a | 0.15±0.02 c | 38.82±12.95 a |
| L-赖氨酸供试浓度/(μmol/L) | 菌落直径/cm | 促进率/% | 产孢量/(×106CFU/mL) | 孢子产生促进率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.00±0.08 c | — | 40.00±4.62 b | — |
| 1 | 8.61±0.15 a | 23.05±2.19 a | 106.67±6.67 a | 173.61±32.84 a |
| 10 | 8.03±0.15 b | 14.79±2.49 b | 86.67±12.02 a | 118.06±22.35 a |
| 100 | 7.93±0.06 b | 13.49±1.55 b | 116.67±17.64 a | 202.08±58.00 a |
| L-赖氨酸供试浓度/(μmol/L) | 菌落直径/cm | 促进率/% | 产孢量/(×106CFU/mL) | 孢子产生促进率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.00±0.08 c | — | 40.00±4.62 b | — |
| 1 | 8.61±0.15 a | 23.05±2.19 a | 106.67±6.67 a | 173.61±32.84 a |
| 10 | 8.03±0.15 b | 14.79±2.49 b | 86.67±12.02 a | 118.06±22.35 a |
| 100 | 7.93±0.06 b | 13.49±1.55 b | 116.67±17.64 a | 202.08±58.00 a |
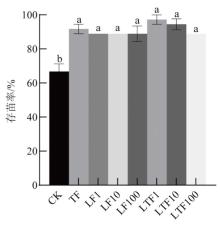
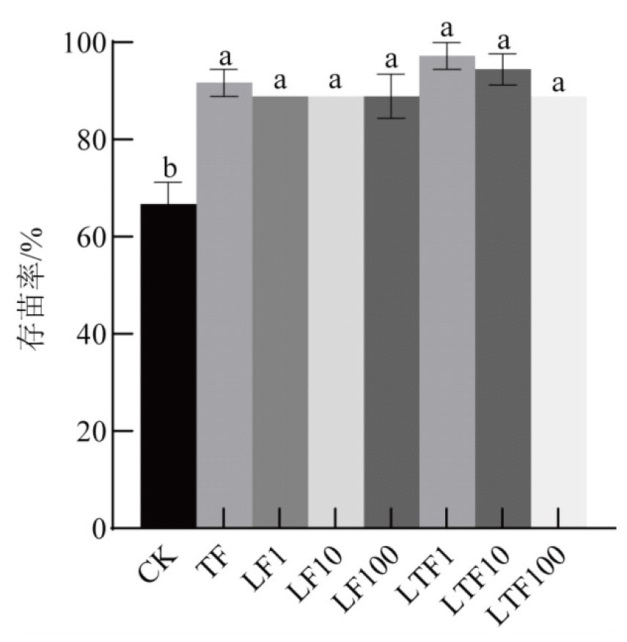
| 处理 | 地上部分鲜重/(g/株) | 地上部分干重/(g/株) | 根鲜重/(g/株) | 根干重/(g/株) | 株高/(cm/株) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.37±0.01 b | 0.07±0.01 b | 0.51±0.02 b | 0.12±0.00 c | 8.82±0.28 c |
| TF | 0.49±0.02 a | 0.08±0.01 ab | 0.55±0.02 b | 0.15±0.01 ab | 9.96±0.04 ab |
| LF1 | 0.42±0.01 ab | 0.07±0.00 b | 0.52±0.02 b | 0.12±0.00 bc | 8.79±0.06 c |
| LF10 | 0.39±0.02 b | 0.06±0.01 b | 0.52±0.01 b | 0.12±0.00 c | 9.30±0.16 bc |
| LF100 | 0.49±0.04 a | 0.08±0.01 ab | 0.57±0.03 b | 0.14±0.01 abc | 9.48±0.53 abc |
| LTF1 | 0.49±0.02 a | 0.08±0.00 ab | 0.65±0.04 a | 0.16±0.01 a | 10.00±0.04 ab |
| LTF10 | 0.43±0.01 ab | 0.09±0.02 a | 0.49±0.02 b | 0.12±0.00 c | 9.24±0.12 bc |
| LTF100 | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.08±0.01 ab | 0.56±0.02 b | 0.13±0.01 abc | 10.23±0.23 a |
| 处理 | 地上部分鲜重/(g/株) | 地上部分干重/(g/株) | 根鲜重/(g/株) | 根干重/(g/株) | 株高/(cm/株) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.37±0.01 b | 0.07±0.01 b | 0.51±0.02 b | 0.12±0.00 c | 8.82±0.28 c |
| TF | 0.49±0.02 a | 0.08±0.01 ab | 0.55±0.02 b | 0.15±0.01 ab | 9.96±0.04 ab |
| LF1 | 0.42±0.01 ab | 0.07±0.00 b | 0.52±0.02 b | 0.12±0.00 bc | 8.79±0.06 c |
| LF10 | 0.39±0.02 b | 0.06±0.01 b | 0.52±0.01 b | 0.12±0.00 c | 9.30±0.16 bc |
| LF100 | 0.49±0.04 a | 0.08±0.01 ab | 0.57±0.03 b | 0.14±0.01 abc | 9.48±0.53 abc |
| LTF1 | 0.49±0.02 a | 0.08±0.00 ab | 0.65±0.04 a | 0.16±0.01 a | 10.00±0.04 ab |
| LTF10 | 0.43±0.01 ab | 0.09±0.02 a | 0.49±0.02 b | 0.12±0.00 c | 9.24±0.12 bc |
| LTF100 | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.08±0.01 ab | 0.56±0.02 b | 0.13±0.01 abc | 10.23±0.23 a |
| 评价对象 | 正理想解距离D+ | 负理想解距离D- | 相对接近度C | 排序结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.37 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| TF | 0.293 | 1.081 | 0.786 | 3 |
| LF1 | 0.441 | 0.937 | 0.68 | 6 |
| LF10 | 0.441 | 0.937 | 0.68 | 7 |
| LF100 | 0.44 | 0.937 | 0.68 | 5 |
| LTF1 | 0 | 1.37 | 1 | 1 |
| LTF10 | 0.147 | 1.225 | 0.893 | 2 |
| LTF100 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.737 | 4 |
| 评价对象 | 正理想解距离D+ | 负理想解距离D- | 相对接近度C | 排序结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.37 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| TF | 0.293 | 1.081 | 0.786 | 3 |
| LF1 | 0.441 | 0.937 | 0.68 | 6 |
| LF10 | 0.441 | 0.937 | 0.68 | 7 |
| LF100 | 0.44 | 0.937 | 0.68 | 5 |
| LTF1 | 0 | 1.37 | 1 | 1 |
| LTF10 | 0.147 | 1.225 | 0.893 | 2 |
| LTF100 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.737 | 4 |
| 样品 | Chao指数 | ACE指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 577.00±9.21 a | 577.10±7.72 a | 3.16±0.07 a | 0.18±0.01 d |
| TF | 328.24±9.99 b | 327.39±11.43 b | 1.51±0.02 c | 0.41±0.00 b |
| LF1 | 311.21±13.92 b | 312.54±14.68 b | 1.36±0.10 c | 0.54±0.04 a |
| LTF1 | 310.50±13.13 b | 314.62±15.67 b | 1.81±0.03 b | 0.34±0.01 c |
| 样品 | Chao指数 | ACE指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 577.00±9.21 a | 577.10±7.72 a | 3.16±0.07 a | 0.18±0.01 d |
| TF | 328.24±9.99 b | 327.39±11.43 b | 1.51±0.02 c | 0.41±0.00 b |
| LF1 | 311.21±13.92 b | 312.54±14.68 b | 1.36±0.10 c | 0.54±0.04 a |
| LTF1 | 310.50±13.13 b | 314.62±15.67 b | 1.81±0.03 b | 0.34±0.01 c |
| 样品 | Chao指数 | ACE指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2682.78±19.44 a | 2704.46±24.11 a | 5.48±0.03 b | 0.03±0.00 ab |
| TF | 2730.69±10.60 a | 2757.90±11.86 a | 5.59±0.05 a | 0.02±0.00 b |
| LF1 | 2589.97±91.74 a | 2613.68±95.01 a | 5.60±0.02 a | 0.01±0.00 c |
| LTF1 | 2368.02±32.15 b | 2398.25±29.58 b | 5.25±0.03 c | 0.03±0.00 a |
| 样品 | Chao指数 | ACE指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2682.78±19.44 a | 2704.46±24.11 a | 5.48±0.03 b | 0.03±0.00 ab |
| TF | 2730.69±10.60 a | 2757.90±11.86 a | 5.59±0.05 a | 0.02±0.00 b |
| LF1 | 2589.97±91.74 a | 2613.68±95.01 a | 5.60±0.02 a | 0.01±0.00 c |
| LTF1 | 2368.02±32.15 b | 2398.25±29.58 b | 5.25±0.03 c | 0.03±0.00 a |
| [1] |
崔秀明, 黄璐琦, 郭兰萍, 等. 中国三七产业现状及发展对策[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(4):553-557.
|
| [2] |
张希, 王文倩, 许旭东, 等. 三七素的药理作用研究进展[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2019, 34(10):3192-3196.
|
| [3] |
毛忠顺, 龙月娟, 朱书生, 等. 三七根腐病研究进展[J]. 中药材, 2013, 36(12):2051-2054.
|
| [4] |
王景旭, 黄直俊, 梁传新, 等. 三七人工栽培研究现状与展望[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2021, 60(S2):8-12.
|
| [5] |
王勇, 马承铸, 陈昱君, 等. 土壤处理对三七根腐病控制作用研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2008(10):1213-1214.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
于新, 田淑慧, 徐文兴, 等. 木霉菌生防作用的生化机制研究进展[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2005(2):86-90.
|
| [8] |
庄敬华, 刘淑花, 王传世, 等. 木霉菌多功能生防菌剂对瓜类枯萎病的防治效果[J]. 北方园艺, 2005(5):90-91.
|
| [9] |
曹秋林, 李菁菁, 廉华, 等. 防治花生白绢病木霉菌的筛选及生防特性研究[J/OL]. 中国油料作物学报, 2025:1-10. https://doi.org/10.19802/j.issn.1007-9084.2024175.
|
| [10] |
常峻嘉, 盖佳鑫, 陶刚, 等. 哈茨木霉菌对烟草的促生及其黑胫病的诱导抗性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10):168-176.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
王敏. ε-聚赖氨酸对链格孢菌致病力和毒素合成的影响及其机制研究[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2023.
|
| [17] |
杨诺林, 邵改革, 张瑞颖, 等. 木质素磺酸钙对食用菌菌丝生长影响初探[J]. 食用菌, 2024, 46(1):11-14.
|
| [18] |
张玉锦, 周文丽, 崔梦娇, 等. 抗、感西瓜根系分泌物鉴定及对枯萎病菌生长的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2022, 35(12):33-39.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
李欣, 崔秀明, 刘迪秋, 等. 三七根中茄腐镰刀菌的实时荧光定量PCR检测[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(5):1302-1307.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604 pmid: 23955772 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
丁兆建, 漆艳香, 曾凡云, 等. 氨基酸影响尖孢镰孢菌古巴专化型厚垣孢子的形成[J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(6):1413-1426.
doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.200317 |
| [28] |
张璐, 赵心雨, 郭宇燕, 等. L-半胱氨酸对稻曲病菌菌丝生长的抑制作用及其转录组分析[J]. 植物病理学报, 2022, 52(3):352-363.
doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000581 |
| [29] |
康慧芳, 乔勇进, 刘晨霞, 等. L-半胱氨酸对葡萄交链孢霉腐病的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41(23):228-235.
|
| [30] |
令阳, 邓丽莉, 姚世响, 等. L-半胱氨酸处理对采后李果实褐腐菌的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(9):256-261.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181109-098 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
苏仪梅. 根系分泌物影响促生长细菌对甘蔗生长的效应[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2023.
|
| [34] |
赵卫松, 郭庆港, 崔钠淇, 等. 外源添加L-脯氨酸对棉花黄萎病发生及其根际土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2024, 57(11):2143-2160.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2024.11.008 |
| [35] |
韩佳怡, 周景芝, 林凯特, 等. 根腐病对白术内生菌及根际土壤微生物群多样性的影响[A].中国植物病理学会. 中国植物病理学会2024年学术年会论文集[C]. 浙江中医药大学药学院, 2024:71.
|
| [36] |
王馨. 木霉菌肥与氨基酸混施对防控苹果连作障碍效果的研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
于文清, 肖俊杰, 刘文志, 等. 类芽胞杆菌(Paenibacillus)对植物促生御病机理研究进展[J]. 微生物学杂志, 2020, 40(6):102-112.
|
| [1] | 王晨龙, 闵杰, 梁睿, 谭熊宇, 王烁, 吾木提·艾山江. 水稻根际土壤微生物细菌群落组成及多样性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(4): 84-93. |
| [2] | 唐旭, 田辉, 张浩冉, 柴国华, 吴秀文. 外源L-天门冬氨酸纳米钙对镉污染土壤理化性质及微生物群落分布的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(2): 98-108. |
| [3] | 刘东海, 戴志刚, 梅亮贤, 乔艳, 张智, 肖卓熙, 李菲, 胡诚. 短期施肥对麦田土壤细菌群落组成和多样性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(2): 43-48. |
| [4] | 刘艳超, 翁仕洋, 魏聪. 怒江西藏段3种鱼类肠道微生物多样性比较研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(2): 149-156. |
| [5] | 李芳, 邓杰, 戈秀梅, 都斌斌. 药用植物与根际微生物相互作用的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(16): 99-107. |
| [6] | 黄欢, 樊娅萍, 宋柏权, 王倡宪. 摩西球囊霉与强还原灭菌对黄瓜幼苗连作障碍的缓解作用研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(1): 55-62. |
| [7] | 王佳, 周德宝, 张军生, 钱莹莹, Mansoor HAYAT, 王占斌. 基于高通量测序的樟子松叶部病害分析及叶际真菌群落多样性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(5): 27-33. |
| [8] | 郎涛, 杨飞洋, 蒲志刚, 张聪, 李明, 余马, 屈会娟, 伍竞宇, 张璐, 刁杜, 冯俊彦. 转录组测序技术在甘薯研究中的应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(30): 94-102. |
| [9] | 杨玉玲, 王灿, 屈用函, 茹瑞红, 孙宏伟, 李雪萍, 杨清松, 陶永宏. 文山地区三七根际真菌群落多样性及与土壤类型的关系研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(28): 94-101. |
| [10] | 王灿, 杨玉玲, 彭翠仙, 赵大伟, 李玲, 杨清松, 孙宏伟, 屈用函, 陶永宏. 三七籽条对文山红壤土真菌群落结构的影响研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 87-91. |
| [11] | 石博, 谢媛媛, 关峰, 杨雪桐, 张景云, 王凯, 万新建. 苦瓜枯萎病抗病与感病品种根际土壤的微生物数量消长动态分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(22): 118-124. |
| [12] | 倪霞, 龚林, 陈华, 宋明健, 周玉忠, 陈敏, 付业明, 龚浩瀚, 盘文政, 张孟升, 罗启鹏, 李建云, 鲍宏明, 李德文, 张海鹍. 基于高通量测序的昭通核心烟区植烟土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(2): 61-70. |
| [13] | 缪凡, 刘鑫, 林岗, 陈燕婷, 刘燕飞, 郑怡. 坛紫菜贝壳丝状体白斑病附生细菌及藻际细菌群落特征分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(5): 154-164. |
| [14] | 寇佩雯, 刘长乐, 许祎珂, 宋忠兴, 李铂, 张永生, 黄文静, 唐志书. 蒙东地区三种药用植物根际微生物群落特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(33): 58-67. |
| [15] | 秦贺兰, 梁芳, 金莹杉, 李子敬, 张华, 胡雪凡. 赛菊芋花叶突变体转录组测序分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(29): 1-7. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||