
中国农学通报 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (21): 145-155.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2025-0271
万婷婷( ), 何浩, 程李洋, 李帅, 余梦梦, 秦洁, 李铈阔, 李俊华(
), 何浩, 程李洋, 李帅, 余梦梦, 秦洁, 李铈阔, 李俊华( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-30
修回日期:2025-07-24
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-05
通讯作者:
作者简介:万婷婷,女,1999年出生,甘肃庆阳人,硕士研究生,研究方向:盐碱地改良技术。通信地址:832003 新疆石河子北五路石河子大学北苑新区,E-mail:2994847860@qq.com。
基金资助:
WAN Tingting( ), HE Hao, CHENG Liyang, LI Shuai, YU Mengmeng, QIN Jie, LI Shikuo, LI Junhua(
), HE Hao, CHENG Liyang, LI Shuai, YU Mengmeng, QIN Jie, LI Shikuo, LI Junhua( )
)
Received:2025-03-30
Revised:2025-07-24
Published:2025-07-25
Online:2025-08-05
摘要: 本研究探讨了哈茨木霉菌与不同改良剂配施对盐碱土的协同改良效应及其对棉花生长的影响。通过盆栽试验,设置对照组(CK)、哈茨木霉菌单施(T)、哈茨木霉菌配施生物炭(BT)、腐植酸(HT)、有机肥(AT)和微生物菌剂(MT)共6个处理,研究其对盐碱土壤理化性质和棉花生长生理状况的影响。结果表明:AT处理使土壤pH降低2.58%,显著优于其他处理,同时显著增加土壤有机质、速效磷、速效钾和碱解氮含量,这说明改良处理显著改善了土壤理化性质;在棉花生长指标方面,AT处理显著提高株高(+36.40%)、茎粗(+49.50%)、地上部生物量(+68.67%)和地下部生物量(+89.29%),增幅最大;生理生化指标显示,T、AT和MT处理显著提高棉花叶片中超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性,降低丙二醛、可溶性蛋白和脯氨酸含量,表明其抗逆性提升;相关性分析揭示了土壤理化性质与棉花生长指标之间的显著相关性,为改良措施的优化提供了科学依据。研究发现,哈茨木霉菌配施有机肥(AT处理)在改善土壤理化性质和促进棉花生长方面效果最优,为新疆盐碱地高效利用和棉花优质高产提供了科学依据及实践指导。
万婷婷, 何浩, 程李洋, 李帅, 余梦梦, 秦洁, 李铈阔, 李俊华. 哈茨木霉菌配施改良剂对盐碱土理化特性及棉花抗盐碱响应的协同机制[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(21): 145-155.
WAN Tingting, HE Hao, CHENG Liyang, LI Shuai, YU Mengmeng, QIN Jie, LI Shikuo, LI Junhua. Synergistic Mechanism of Application of Trichoderma harzianum and Amendments on Physicochemical Properties of Saline-alkali Soil and Cotton’s Salt Alkali Resistance Response[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2025, 41(21): 145-155.
| 处理 | 株高/cm | 茎粗/mm | 地上部生物量/(g/pot) | 地下部生物量/(g/pot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.21±0.49c | 3.03±0.08d | 0.83±0.01c | 0.28±0.01cd |
| T | 13.20±0.15b | 3.55±0.10c | 0.90±0.01bc | 0.33±0.02c |
| BT | 13.80±0.12b | 3.65±0.11bc | 0.92±0.05b | 0.30±0.03cd |
| HT | 10.46±1.06c | 3.06±0.07d | 0.71±0.02d | 0.25±0.01d |
| AT | 15.29±0.72a | 4.53±0.36a | 1.40±0.04a | 0.53±0.04a |
| MT | 13.83±0.51b | 3.95±0.04b | 0.97±0.04b | 0.41±0.04b |
| 处理 | 株高/cm | 茎粗/mm | 地上部生物量/(g/pot) | 地下部生物量/(g/pot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.21±0.49c | 3.03±0.08d | 0.83±0.01c | 0.28±0.01cd |
| T | 13.20±0.15b | 3.55±0.10c | 0.90±0.01bc | 0.33±0.02c |
| BT | 13.80±0.12b | 3.65±0.11bc | 0.92±0.05b | 0.30±0.03cd |
| HT | 10.46±1.06c | 3.06±0.07d | 0.71±0.02d | 0.25±0.01d |
| AT | 15.29±0.72a | 4.53±0.36a | 1.40±0.04a | 0.53±0.04a |
| MT | 13.83±0.51b | 3.95±0.04b | 0.97±0.04b | 0.41±0.04b |
| 处理 | 叶绿素a含量 | 叶绿素b含量 | 类胡萝卜素含量 | 叶绿素总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.833±0.086d | 2.203±0.156c | 0.637±0.028c | 6.037±0.137d |
| T | 4.430±0.268cd | 2.596±0.139bc | 0.838±0.031b | 7.027±0.155cd |
| BT | 4.831±0.161c | 2.564±0.219bc | 0.839±0.019b | 7.395±0.058c |
| HT | 5.851±0.173b | 3.104±0.207ab | 0.928±0.078ab | 8.954±0.142b |
| AT | 7.016±0.184a | 3.389±0.193a | 1.053±0.115a | 10.406±0.177a |
| MT | 4.938±0.130c | 2.470±0.100bc | 0.813±0.017b | 7.408±0.227c |
| 处理 | 叶绿素a含量 | 叶绿素b含量 | 类胡萝卜素含量 | 叶绿素总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.833±0.086d | 2.203±0.156c | 0.637±0.028c | 6.037±0.137d |
| T | 4.430±0.268cd | 2.596±0.139bc | 0.838±0.031b | 7.027±0.155cd |
| BT | 4.831±0.161c | 2.564±0.219bc | 0.839±0.019b | 7.395±0.058c |
| HT | 5.851±0.173b | 3.104±0.207ab | 0.928±0.078ab | 8.954±0.142b |
| AT | 7.016±0.184a | 3.389±0.193a | 1.053±0.115a | 10.406±0.177a |
| MT | 4.938±0.130c | 2.470±0.100bc | 0.813±0.017b | 7.408±0.227c |
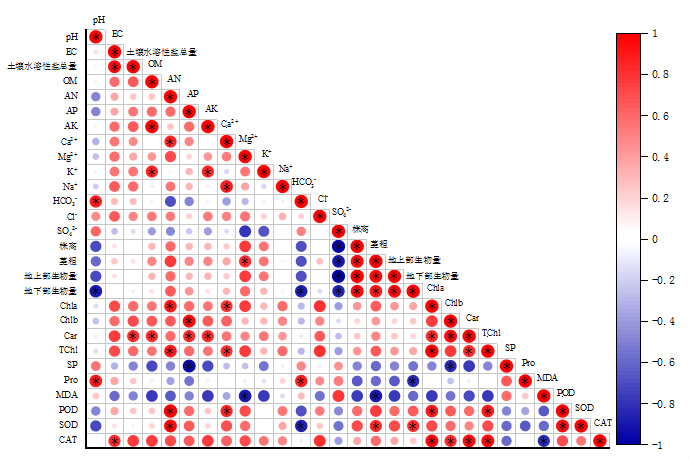
| [1] |
姚应上, 孙晓雷, 柳维扬, 等. 秸秆还田与沼液配施对盐渍化土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2024, 42(4):117-126.
|
| [2] |
王丹, 赵亚光, 张凤华. 耐盐促生菌筛选、鉴定及对盐胁迫小麦的效应[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(1):110-117.
|
| [3] |
李少朋, 陈昢圳, 刘惠芬, 等. 丛枝菌根提高滨海盐碱地植物耐盐性的作用机制及其生态效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(2):411-418.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.02.024 |
| [4] |
李颖, 陶军, 钞锦龙, 等. 滨海盐碱地“台田-浅池”改良措施的研究进展[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2014, 32(5):154-160.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-073009-114450 pmid: 20192757 |
| [9] |
付健, 王玉凤, 张翼飞, 等. 不同木霉菌对寒地盐碱土壤玉米杂交种光合特性及活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2021, 33(1):7-14.
|
| [10] |
赵政, 陈巍, 王欢, 等. 木霉微生物肥与减量化肥配施对番茄产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(5):1243-1253.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
吴丹, 孙萍, 路鹏展, 等. 浒苔生物炭对滨海盐碱土壤改良的效果及途径[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(4):1941-1949.
|
| [13] |
武慧, 刘畅, 樊航, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌与哈茨木霉对黄瓜幼苗生长的协同促进作用[J]. 吉林师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 42(3):95-99.
|
| [14] |
任志超, 穆耀辉, 匡志豪, 等. 哈茨木霉配施高碳基肥对植烟土壤理化性质和细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(8):223-231.
|
| [15] |
孔涛, 马瑜, 刘民, 等. 生物有机肥对土壤养分和土壤微生物的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(4):884-891.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [19] |
李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000.
|
| [20] |
林植芳, 李双顺, 林桂珠, 等. 水稻叶片的衰老与超氧物歧化酶活性及脂质过氧化作用的关系[J]. Journal of integrative plant biology, 1984(6):605-615.
|
| [21] |
胡秉芬, 黄华梨, 季元祖, 等. 分光光度法测定叶绿素含量的提取液的适宜浓度[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(8):1965-1974.
|
| [22] |
钟华, 董洁, 董宽虎. 盐胁迫对扁蓿豆幼苗脯氨酸积累及其代谢关键酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4):189-194.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017464 |
| [23] |
pmid: 942051 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
展文洁, 周犇, 朱林星, 等. 木霉生物有机肥对盐渍化土壤肥力及杭白菜产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(7):108-117.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0130 |
| [28] |
姚少雄, 周蓓蓓, 李晓晴, 等. 哈茨木霉菌与有机肥复配强化植物修复强酸性重金属污染土壤的效果及机理[J]. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(4):937-946.
|
| [29] |
罗洋, 张桂玲, 王芳, 等. 辣椒秸秆生物炭对黄壤化学特性及小白菜生长的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2022, 40(6):847-852.
|
| [30] |
刘荣林, 葛菁萍. 丛枝菌根真菌和硫氧化细菌对土壤理化性质和植物生长影响的研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(10):3355-3363.
|
| [31] |
蒋志洋, 周育智, 陈道坤, 等. 微生物菌剂与大豆秸秆生物炭配施对砂姜黑土养分及小白菜品质的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2024, 37(4):133-139.
|
| [32] |
李梦瑶, 胡兆羽, 刘洋, 等. 微生物菌肥及其应用研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2024(21):115-123.
|
| [33] |
刘峰, 阮盈盈. 哈茨木霉菌剂对玉米苗期生长和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2021, 62(8):1507-1510.
doi: 10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20210813 |
| [34] |
韩冰, 高文瑞, 孙艳军, 等. 哈茨木霉菌不同接种方法对番茄种子萌发和幼苗生长生理的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(5):165-169.
|
| [35] |
杨晓娟, 何浩, 程李洋, 等. 盐渍土施用有机物料对作物生长及土壤盐碱指标的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2025, 46(3):1751-1761.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
霍雪雪, 张豪, 黄艳华, 等. 绿色木霉Tv-1511及其生物有机肥对盐碱地小麦、玉米生长及其产量的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(11):103-111.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.12096 pmid: 26157352 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0061-6 pmid: 18379856 |
| [42] |
赵忠娟, 杨凯, 扈进冬, 等. 盐胁迫条件下哈茨木霉ST02对椒样薄荷生长及根区土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(7):224-235.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-1251 |
| [1] | 汪峰, 朱诗君, 应虹, 柴伟纲, 戴瑶璐, 袁晴, 金树权. 有机改良剂配合适度深耕对丘陵复垦稻田生产力提升效果[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(9): 91-98. |
| [2] | 顾鑫, 任翠梅, 冯鹏, 王丽娜, 张宏宇, 李娜, 宋敏超, 王迪. 不同改良剂对苏打盐碱地土壤细菌群落结构及燕麦生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(21): 107-113. |
| [3] | 刘洋, 刘冲, 徐培智, 王丹, 解开治, 李雅莹, 张坤, 孙丽丽, 黎婉玲, 谷峻, 顾文杰, 卢钰升. 有机无机配施改良剂对滨海盐渍土及冰菜生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(21): 123-130. |
| [4] | 孙毅, 王腾, 傅云洁, 鲍奎, 王金贵. 改良剂对柴达木盆地盐碱土有机碳组分和团聚体稳定性的影响研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(21): 131-138. |
| [5] | 孔令羽, 吴则蒽, 孟云杉, 胡树文. 新型复合改良剂对土默川盐碱耕地性质及玉米产量影响研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(21): 85-95. |
| [6] | 赵明明, 杜付荣, 胡新燕, 李可, 陈晓光. 江苏省早熟棉花区试品种皮棉产量性状和试验点鉴别力综合分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(20): 10-17. |
| [7] | 李健鹏, 张丛志, 潘慧, 马学伟, 赵占辉. 天然腐殖质材料型土壤改良剂在新垦耕地改良中的应用与效果分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(2): 63-68. |
| [8] | 房佰涵, 刘晶晶, 郭晓雯, 叶扬, 杨茂琪, 张楠, 郭慧娟, 闵伟. 等碳量秸秆和秸秆炭还田对棉田土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(2): 69-82. |
| [9] | 顾嘉诚, 王家平, 张增成, 蒋贵菊, 李鲁华, 程志博. 耕作方式对土壤团聚体稳定性、土壤质量和玉米产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(17): 78-87. |
| [10] | 曹文洋, 陈小康, 杨涛, 陈民志, 马兴旺, 王则玉, 梅磊, 郑胤建, 阿尔祖娜·阿布力米提, 安杰. 南疆棉花“干播湿出”模式适应性评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(17): 96-102. |
| [11] | 金永萍, 刘连金, 任静, 法泽, 李金华, 王慧玲, 吴文涛, 朱有勇, 何霞红, 郭力维. L-赖氨酸和哈茨木霉菌联用对三七生长、根腐病及根际微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(17): 115-125. |
| [12] | 董晓庆, 陈铭, 唐治博, 牛小天, 陈秀梅, 王桂芹. 复合微生物菌剂在池塘养殖水质调控上的应用及研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(15): 148-153. |
| [13] | 牛源丰, 熊茜, 林云红, 康前真, 刘正万, 吴昱聪, 周桂夙. 配施土壤改良剂对烤烟田间生长发育的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(15): 45-50. |
| [14] | 刘武, 邹庆娴, 张佛熠, 钟嘉琳, 樊雨鹭, 刘玮, 王琼. 南昌城市森林土壤动物群落组成及多样性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(13): 80-88. |
| [15] | 李星星, 阿布都艾尼·阿布都维力, 周仑, 马辉, 欧欢, 艾麦尔江·阿布力提甫, 田立文, 刘燕, 罗单, 阿孜古丽·阿布力孜. 基于壤土含水量的南疆“干播湿出”棉田出苗水调控研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(1): 25-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||