
中国农学通报 ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 60-68.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0564
王岩1,2( ), 王丽伟1,2, 赵洪颜3, 赵敏1,2(
), 王丽伟1,2, 赵洪颜3, 赵敏1,2( ), 杨洪岩1,2(
), 杨洪岩1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-27
修回日期:2021-07-18
出版日期:2022-02-15
发布日期:2022-03-17
通讯作者:
赵敏,杨洪岩
作者简介:王岩,女,1997年出生,河北石家庄人,硕士研究生,研究方向:土壤微生物。通信地址:150040 黑龙江省哈尔滨市东北林业大学生命科学学院,Tel:0451-82191737,E-mail: 基金资助:
WANG Yan1,2( ), WANG Liwei1,2, ZHAO Hongyan3, ZHAO Min1,2(
), WANG Liwei1,2, ZHAO Hongyan3, ZHAO Min1,2( ), YANG Hongyan1,2(
), YANG Hongyan1,2( )
)
Received:2021-05-27
Revised:2021-07-18
Online:2022-02-15
Published:2022-03-17
Contact:
ZHAO Min,YANG Hongyan
摘要:
为减轻参地需求压力,促进农田栽参的深度发展,本研究以农田、林地和4年参地土壤为研究对象,以常规分析为基础,结合高通量测序技术解析土壤养分及微生物群落特征,为农田栽参土壤定向改良提供依据。理化分析结果表明:4年参地土壤的pH最低,但其铵态氮、有效磷、全氮、全磷以及有机质含量显著高于农田及林地土壤。高通量测序结果揭示农田土壤细菌与真菌群落丰富度和多样性均高于参地且低于林地土壤。不同类型土壤中细菌门类组成基本相同,主要包括Proteobacteria,Acidobacteria,Actinobacteria,Chloroflexi等。Mortierella为林地土壤中的优势菌属,Fusarium大量存在于农田土壤中,参地检测到病原菌Sclerotinia的大量富集。db-RDA分析表明土壤pH、氮、磷和有机质含量对微生物群落结构均有影响,且环境因子与真菌群落相关性更强。因此对农田土壤进行有效改良应以控制真菌群落为主。
中图分类号:
王岩, 王丽伟, 赵洪颜, 赵敏, 杨洪岩. 不同人参栽培土壤养分及微生物群落组成特征解析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(5): 60-68.
WANG Yan, WANG Liwei, ZHAO Hongyan, ZHAO Min, YANG Hongyan. Characteristics of Nutrients and Microbial Community Composition of Different Panax ginseng Cultivation Soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(5): 60-68.
| 样品名称 | pH | NO3--N/ (mg/kg) | NH4+-N/ (mg/kg) | AP/ (mg/kg) | TN/ (g/kg) | TP/ (g/kg) | TK/ (g/kg) | OM/ (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 林地土壤 | 6.12±0.08a | 11.57±2.11b | 9.12±1.05b | 0.42±0.01c | 3.89±0.17b | 1.32±0.25b | 5.80±0.53a | 163.92±1.20b |
| 农田土壤 | 5.54±0.09b | 23.66±0.62a | 1.47±1.44c | 1.88±0.14b | 2.81±0.16c | 1.15±0.12b | 4.93±0.41a | 150.09±4.46c |
| 4年参地土壤 | 4.93±0.03c | 0.11±0.06c | 93.88±1.26a | 7.71±0.12a | 5.44±0.06a | 2.41±0.09a | 5.64±0.85a | 174.39±2.61a |
| 样品名称 | pH | NO3--N/ (mg/kg) | NH4+-N/ (mg/kg) | AP/ (mg/kg) | TN/ (g/kg) | TP/ (g/kg) | TK/ (g/kg) | OM/ (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 林地土壤 | 6.12±0.08a | 11.57±2.11b | 9.12±1.05b | 0.42±0.01c | 3.89±0.17b | 1.32±0.25b | 5.80±0.53a | 163.92±1.20b |
| 农田土壤 | 5.54±0.09b | 23.66±0.62a | 1.47±1.44c | 1.88±0.14b | 2.81±0.16c | 1.15±0.12b | 4.93±0.41a | 150.09±4.46c |
| 4年参地土壤 | 4.93±0.03c | 0.11±0.06c | 93.88±1.26a | 7.71±0.12a | 5.44±0.06a | 2.41±0.09a | 5.64±0.85a | 174.39±2.61a |
| 微生物类型 | 样品名称 | ACE | Chao 1 | Simpson | Shannon | Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 | 林地土壤 | 2131±42.6a | 2116±41.5a | 0.0069±0.0010a | 6.120±0.065a | 98.02±0.05b |
| 农田土壤 | 2034±76.4b | 2007±29.0b | 0.0066±0.0004a | 6.042±0.072ab | 98.05±0.05b | |
| 4年参地土壤 | 1909±62.8c | 1895±70.9c | 0.0085±0.0010a | 5.981±0.068b | 98.20±0.07a | |
| 真菌 | 林地土壤 | 1315±19.7A | 1293±18.1A | 0.0610±0.0046C | 4.358±0.045A | 99.47±0.03B |
| 农田土壤 | 781±30.2B | 778±30.1B | 0.1055±0.0079A | 3.725±0.092B | 99.79±0.03A | |
| 4年参地土壤 | 546±31.8C | 542±38.6C | 0.0756±0.0065B | 3.407±0.083C | 99.79±0.04A |
| 微生物类型 | 样品名称 | ACE | Chao 1 | Simpson | Shannon | Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 | 林地土壤 | 2131±42.6a | 2116±41.5a | 0.0069±0.0010a | 6.120±0.065a | 98.02±0.05b |
| 农田土壤 | 2034±76.4b | 2007±29.0b | 0.0066±0.0004a | 6.042±0.072ab | 98.05±0.05b | |
| 4年参地土壤 | 1909±62.8c | 1895±70.9c | 0.0085±0.0010a | 5.981±0.068b | 98.20±0.07a | |
| 真菌 | 林地土壤 | 1315±19.7A | 1293±18.1A | 0.0610±0.0046C | 4.358±0.045A | 99.47±0.03B |
| 农田土壤 | 781±30.2B | 778±30.1B | 0.1055±0.0079A | 3.725±0.092B | 99.79±0.03A | |
| 4年参地土壤 | 546±31.8C | 542±38.6C | 0.0756±0.0065B | 3.407±0.083C | 99.79±0.04A |
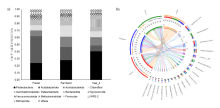
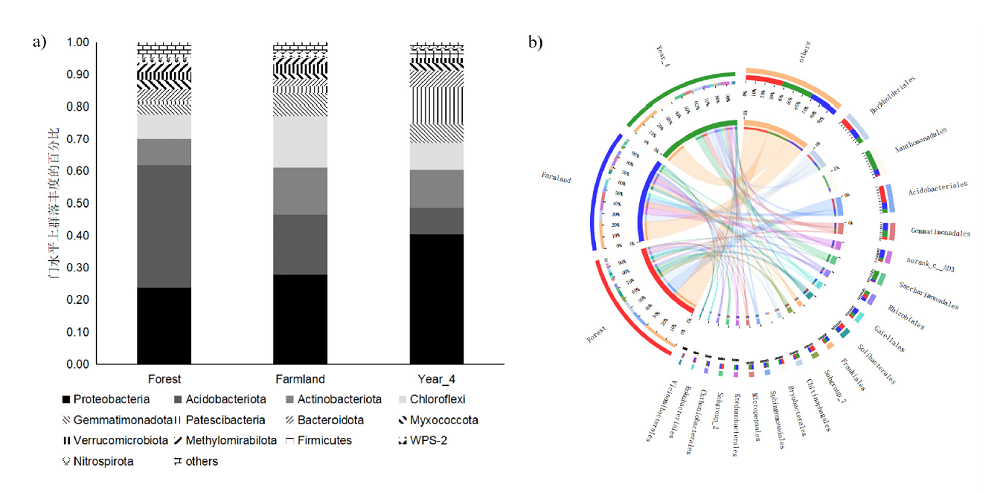
| [1] | FAN S S, ZHANG Z P, SU H, et al. Panax ginseng clinical trials: Current status and future perspectives[J]. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy, 2020, 132:1-8. |
| [2] | 徐江, 沈亮, 陈士林, 等. 无公害人参农田栽培技术规范及标准[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2018, 20(7):102-111. |
| [3] | 金慧, 于树莲, 曹志强. 老参地、农田地改造,连续栽培人参、西洋参[J]. 世界科学技术:中医药现代化, 2006, 8(1):84-87. |
| [4] | 赵洪颜, 傅民杰, 邹吉祥, 等. 老参地土壤改良的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(21):12-15. |
| [5] | 胡秀艳. 改良措施对农田土壤微生态及人参存苗率的影响探讨[J]. 农业与技术, 2018, 38(12):32-32. |
| [6] | 杨莉, 文子伟, 付婧, 等. 生物质炭对连作参地人参种苗与土壤质量的影响[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(4):791-796. |
| [7] |
CESARANO G, DE FILIPPIS F, LA STORIA A, et al. Organic amendment type and application frequency affect crop yields, soil fertility and microbiome composition[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2017, 120:254-264.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.08.017 URL |
| [8] | 孙海, 张亚玉, 孙长伟, 等. 多功能微生物制剂对农田栽参土壤养分状况的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(18):116-120. |
| [9] | 刘晨阳, 王二欢, 高成林, 等. 农田栽参土壤改良技术研究现状[J]. 人参研究, 2019, 31(2):37-40. |
| [10] | 孙婉薷, 沈健林, 李勇, 等. 不同水肥处理对稻麦轮作农田土壤氮磷肥力特征的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2021, 60(6):23-26,30. |
| [11] | 王婷婷, 刘双, 赵洪颜, 等. 农田栽参和伐林栽参土壤养分及酶活性比较分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2014(34):12075-12077. |
| [12] | XU Z W, ZHANG T Y, WANG S Z, et al. Soil ph and c/n ratio determines spatial variations in soil microbial communities and enzymatic activities of the agricultural ecosystems in northeast china: Jilin province case[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2020, 155:1-12. |
| [13] | KANG E, LI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Soil ph and nutrients shape the vertical distribution of microbial communities in an alpine wetland[J]. Science of the total environment, 2021, 774:1-12. |
| [14] | LIU N, SHAO C, SUN H, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi biofertilizer improves american ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) growth under the continuous cropping regime[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 363:1-10. |
| [15] | 王敏, 周犇, 曾吉兴, 等. 硝态氮抑制尖孢镰刀菌侵染促进黄瓜生长的内在生理机制[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(11):26-34. |
| [16] |
SUN H, WANG Q X, ZHANG L L, et al. Distinct leaf litter drive the fungal communities in Panax ginseng-growing soil[J]. Ecological indicators, 2019, 104:184-194.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.04.083 URL |
| [17] | LI F, ZHANG S Q, WANG Y, et al. Rare fungus, Mortierella capitata, promotes crop growth by stimulating primary metabolisms related genes and reshaping rhizosphere bacterial community[J]. Soil biology and biochemistry, 2020, 151:1-11. |
| [18] | DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, REICH P B, TRIVEDI C, et al. Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes[J]. Nature ecology & evolution, 2020, 4(2):210-220. |
| [19] | XIA Q, RUFTY T, SHI W. Soil microbial diversity and composition: Links to soil texture and associated properties[J]. Soil biology and biochemistry, 2020, 149:1-13. |
| [20] |
HERNANDEZ D J, DAVID A S, MENGES E S, et al. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks[J]. The Isme journal, 2021,doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00882-x.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00882-x |
| [21] |
EICHORST S A, KUSKE C R, SCHMIDT T M. Influence of plant polymers on the distribution and cultivation of bacteria in the Phylum Acidobacteria[J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 2011, 77(2):586-596.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01080-10 URL |
| [22] | HONG S, JV H L, LU M, et al. Significant decline in banana Fusarium wilt disease is associated with soil microbiome reconstruction under chilli pepper-banana rotation[J]. European journal of soil biology, 2020, 97:1-10. |
| [23] | WU H M, QIN X J, WANG J Y, et al. Rhizosphere responses to environmental conditions in Radix pseudostellariae under continuous monoculture regimes[J]. Agriculture ecosystems and environment, 2019, 270:19-31. |
| [24] |
XIAO C P, YANG L M, ZHANG L X, et al. Effects of cultivation ages and modes on microbial diversity in the rhizosphere soil of Panax ginseng[J]. Journal of ginseng research, 2016, 40(1):28-37.
doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.04.004 URL |
| [25] |
DONG L L, XU J, ZHANG L J, et al. Rhizospheric microbial communities are driven by Panax ginseng at different growth stages and biocontrol bacteria alleviates replanting mortality[J]. Acta pharmaceutica sinica B, 2018, 8(2):272-282.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2017.12.011 URL |
| [26] | SUN Z, YANG L M, HAN M, et al. Biological control ginseng grey mold and plant colonization by antagonistic bacteria isolated from rhizospheric soil of Panax ginseng meyer[J]. Biological control, 2019, 138:1-7. |
| [27] | LIU L L, HUANG X Q, ZHANG J B, et al. Deciphering the relative importance of soil and plant traits on the development of rhizosphere microbial communities[J]. Soil biology and biochemistry, 2020, 148:1-13. |
| [28] | EGIDI E, DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, PLETT J M, et al. A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide[J]. Nature communications, 2019, 10(7717):6506-6511. |
| [29] | DE CORATO U, PATRUNO L, AVELLA N, et al. Soil management under tomato -wheat rotation increases the suppressive response against Fusarium wilt and tomato shoot growth by changing the microbial composition and chemical parameters[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2020, 154:1-18. |
| [30] |
LI T, KIM J H, JUNG B, et al. Transcriptome analyses of the ginseng root rot pathogens Cylindrocarpon destructans and Fusarium solani to identify radicicol resistance mechanisms[J]. Journal of Ginseng Research, 2020, 44(1):161-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2018.11.005 URL |
| [31] | LIU X, ZHANG Y. Exploring the communities of bacteria, fungi and ammonia oxidizers in rhizosphere of Fusarium -diseased greenhouse cucumber[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2021, 161:1-12. |
| [32] | TIAN G L, BI Y M, CHENG J D, et al. High concentration of ferulic acid in rhizosphere soil accounts for the occurrence of Fusarium wilt during the seedling stages of strawberry plants[J]. Physiological and molecular plant pathology, 2019, 108:1-8. |
| [33] | BREUNIG M, CHILVERS M I. Baseline sensitivity of Fusarium graminearum from wheat, corn, dry bean and soybean to pydiflumetofen in michigan, USA[J]. Crop protection, 2021, 140:1-6. |
| [34] | 王丹, 傅俊范, 尹海波, 等. 人参核盘菌菌核分泌液致病性及生物学特性研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2020(4):439-445. |
| [35] |
WANG G S, YIN C M, PAN F B, et al. Analysis of the fungal community in apple replanted soil around bohai gulf[J]. Horticultural plant journal, 2018, 4(5):175-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2018.05.003 URL |
| [36] | NING Q, CHEN L, JIA Z J, et al. Multiple long-term observations reveal a strategy for soil ph-dependent fertilization and fungal communities in support of agricultural production[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, 293:1-10. |
| [37] | GUO N, LI L, CUI J, et al. Effects of Funneliformis mosseae on the fungal community in and soil properties of a continuously cropped soybean system[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2021, 164(1):1-11. |
| [38] |
BADAWI N, RONHEDE S, OLSSON S, et al. Metabolites of the phenylurea herbicides chlorotoluron, diuron, isoproturon and linuron produced by the soil fungus Mortierella sp.[J] Environmental pollution, 2009, 157(10):2806-2812.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.04.019 URL |
| [39] |
CUI Z J, ZHANG X, YANG H H, et al. Bioremediation of heavy metal pollution utilizing composite microbial agent of Mucor circinelloides, Actinomucor sp. and Mortierella sp.[J] Journal of environmental chemical engineering, 2017, 5(4):3616-3621.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.021 URL |
| [40] |
KATAOKA R, TAKAGI K, SAKAKIBARA F. Biodegradation of endosulfan by Mortieralla sp strain W8 in soil: Influence of different substrates on biodegradation[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(3):548-552.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.08.021 URL |
| [41] |
DENG X, ZHANG N, SHEN Z, et al. Soil microbiome manipulation triggers direct and possible indirect suppression against Ralstonia solanacearum and Fusarium oxysporum[J]. NPJ biofilms microbiomes, 2021, 7(1):1-10.
doi: 10.1038/s41522-020-00173-5 URL |
| [1] | 崔莹莹, 周波, 陈义勇, 刘嘉裕, 黎健龙, 唐颢, 唐劲驰. 广东茶区土壤肥力时空变化分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 85-95. |
| [2] | 孙树晴, 丁炜, 孙瑞, 张希财, 兰国玉, 陈伟, 杨川, 吴志祥. 不同林龄橡胶林土壤细菌群落组成及多样性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 93-100. |
| [3] | 曾婕, 余浪, 达布希拉图, 李云驹. 磷基土壤调理剂在低磷红壤上对小白菜生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 81-87. |
| [4] | 黄浩, 谢晋, 袁文彬, 王初亮, 陈坤华, 曾繁东, 梁增发, 苏诏, 王维. 不同有机物料对烤烟根系特征及氮磷钾积累量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 51-57. |
| [5] | 秦乃群, 马巧云, 高敬伟, 杨璞, 蔡金兰, 郝迎春, 李艳梅, 冀洪策, 廖祥政. 沼渣施用对花生小麦轮作作物产量及土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 58-63. |
| [6] | 卢丽兰, 王玉萍, 尹欣幸, 黄英凯, 范海阔. 海南省水果型椰子园土壤养分调查与评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 72-80. |
| [7] | 王丽娜, 杨瑛, 杜苏. 生物炭施入对盐碱土壤影响的研究现状[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 81-87. |
| [8] | 赵双梅, 刘宪斌, 李红梅, 董文彩, 沈健萍, 包金美, 梁芳, 鲁美. 云南哀牢山湿性常绿阔叶林土壤碳分布特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(8): 88-95. |
| [9] | 邓裕帅, 王宇光, 於丽华, 耿贵. 水涝胁迫对不同土壤盐碱度下甜菜幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 18-23. |
| [10] | 张梦佳, 文方芳, 张雪莲, 赵青春, 郭建明, 廖洪, 刘自飞, 朱文, 韩宝, 葛瑶科, 廖上强, 卢静. 田块尺度设施菜田土壤健康评价方法的初步构建与应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 74-79. |
| [11] | 陈慧, 周晓月, 谭诚, 张永春, 汪吉东, 马洪波. 紫云英还田对土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 80-85. |
| [12] | 鲍广灵, 陶荣浩, 杨庆波, 胡含秀, 李丁, 马友华. 微生物修复农田土壤重金属污染技术研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 69-74. |
| [13] | 孙养存, 尹紫良, 葛菁萍. 土壤中重金属污染物的来源及治理方式[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 75-79. |
| [14] | 陈道, 王新, 江山, 张洁, 吴祖建, 丁新伦. 福建地区草莓斑驳病毒全基因组测序和分子变异分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(6): 94-101. |
| [15] | 张洪芬, 杨丽杰, 赵玉娟, 张峰. 陇东2020年“强凉夏”气候特征及对农业影响分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(5): 117-123. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||