
中国农学通报 ›› 2022, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (30): 108-117.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-1170
所属专题: 生物技术
曹永清1,2( ), 刘艳1,2, 张丽慧1,2, 晋婷婷2, 任嘉红2(
), 刘艳1,2, 张丽慧1,2, 晋婷婷2, 任嘉红2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-06
修回日期:2022-03-15
出版日期:2022-10-25
发布日期:2022-10-27
通讯作者:
任嘉红
作者简介:曹永清,女,1996年出生,山西大同人,硕士研究生,研究方向:资源微生物。通信地址:046011 山西省长治市潞州区太行东街街道长治学院北校区 长治学院,Tel:13994361141,E-mail: 基金资助:
CAO Yongqing1,2( ), LIU Yan1,2, ZHANG Lihui1,2, JIN Tingting2, REN Jiahong2(
), LIU Yan1,2, ZHANG Lihui1,2, JIN Tingting2, REN Jiahong2( )
)
Received:2021-12-06
Revised:2022-03-15
Online:2022-10-25
Published:2022-10-27
Contact:
REN Jiahong
摘要:
探讨根际促生长细菌荧光假单胞菌(Pseudomonas fluorescens)CLW17对草甘膦的降解作用及其分子机制。利用平板培养法和钼锑抗比色法对CLW17菌株降解草甘膦能力进行研究。采用Plackett-Burman(PB)与Central Composite Design(CCD)试验联用确定CLW17降解草甘膦的最佳条件。对降解草甘膦关键基因thiO进行生物信息学分析,并构建敲除株(CLW17ΔthiO)及回补株(ΔthiO/thiO),研究其对草甘膦降解的影响。荧光假单胞菌CLW17菌株耐受草甘膦的最大浓度为0.7%。在降解草甘膦最优条件下,野生株CLW17、敲除株CLW17ΔthiO和回补株ΔthiO/thiO对草甘膦降解率分别为72.81%、32.78%和54.33%。生物信息学分析显示thiO基因编码366个氨基酸,拥有信号肽和跨膜结构域。CLW17具有较强的降解草甘膦能力,且thiO基因与降解草甘膦能力密切相关。研究结果可为草甘膦污染的治理及土壤修复提供良好的菌种资源。
中图分类号:
曹永清, 刘艳, 张丽慧, 晋婷婷, 任嘉红. 荧光假单胞CLW17菌株对草甘膦的降解及其机制初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(30): 108-117.
CAO Yongqing, LIU Yan, ZHANG Lihui, JIN Tingting, REN Jiahong. Pseudomonas fluorescens Strain CLW17: Degradation of Glyphosate and Its Mechanism[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(30): 108-117.
| Primers | Sequences (5’→3’) |
|---|---|
| CLW17_04770FW (Hind Ⅲ) | CCCAAGCTTCTGAGTCCAGTGGCAACATCAC |
| CLW17_Del04770FW | AGGAAGAAAAACTGACTAGATGGTCATGTTTGATCCAACCGT |
| CLW17_Del04770RV | ACGGTTGGATCAAACATGACCATCTAGTCAGTTTTTCTTCCT |
| CLW17_04770RV (EcoR I) | CCGGAATTCACGTGATCGAACTGCGTGTG |
| CLW17_04770SQFW | ACTACGCGGTGCTCGACACTAACGCTGAT |
| CLW17_04770SQRV | CCAACAGGAAACCGTGGTCGATGTG |
| CLW17_Comp04770FW -EcoR Ⅰ | CCGGAATTCACGGTTGGATCAAACATG |
| CLW17_Comp04770RV -Spe I | CGGACTAGTCTAGATCCGTCCGGCCGGTG |
| pBAD-Forward | ATGCCATAGCATTTTTATCC |
| T7 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG |
| Primers | Sequences (5’→3’) |
|---|---|
| CLW17_04770FW (Hind Ⅲ) | CCCAAGCTTCTGAGTCCAGTGGCAACATCAC |
| CLW17_Del04770FW | AGGAAGAAAAACTGACTAGATGGTCATGTTTGATCCAACCGT |
| CLW17_Del04770RV | ACGGTTGGATCAAACATGACCATCTAGTCAGTTTTTCTTCCT |
| CLW17_04770RV (EcoR I) | CCGGAATTCACGTGATCGAACTGCGTGTG |
| CLW17_04770SQFW | ACTACGCGGTGCTCGACACTAACGCTGAT |
| CLW17_04770SQRV | CCAACAGGAAACCGTGGTCGATGTG |
| CLW17_Comp04770FW -EcoR Ⅰ | CCGGAATTCACGGTTGGATCAAACATG |
| CLW17_Comp04770RV -Spe I | CGGACTAGTCTAGATCCGTCCGGCCGGTG |
| pBAD-Forward | ATGCCATAGCATTTTTATCC |
| T7 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG |
| 实验组 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | 降解率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 10.2175 |
| 2 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 7.7161 |
| 3 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 56.8252 |
| 4 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | 14.1815 |
| 5 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 13.3826 |
| 6 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 26.5896 |
| 7 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 50.2848 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 37.3735 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 62.5904 |
| 10 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 58.4321 |
| 11 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 42.4330 |
| 12 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 28.4748 |
| 实验组 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | 降解率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 10.2175 |
| 2 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 7.7161 |
| 3 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 56.8252 |
| 4 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | 14.1815 |
| 5 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 13.3826 |
| 6 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 26.5896 |
| 7 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 50.2848 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 37.3735 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 62.5904 |
| 10 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 58.4321 |
| 11 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 42.4330 |
| 12 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 28.4748 |
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 效果 | 平方和 | 贡献值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| intercept | 34.04 | |||
| X1 | 9.25 | 18.49 | 1025.78 | 23.09 |
| X2 | -2.29 | -4.58 | 62.92 | 1.42 |
| X3 | 6.19 | 12.38 | 459.52 | 10.34 |
| X4 | 0.74 | 1.48 | 6.54 | 0.15 |
| X5 | -11.01 | -22.01 | 1453.54 | 32.72 |
| X6 | -8.69 | -17.38 | 906.4 | 20.40 |
| X7 | 2.32 | 4.65 | 64.75 | 1.46 |
| X8 | 4.37 | 8.74 | 229.32 | 5.16 |
| X9 | -1.28 | -2.57 | 19.76 | 0.44 |
| X10 | 2.87 | 5.75 | 99.15 | 2.23 |
| X11 | 3.10 | 6.19 | 115.05 | 2.59 |
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 效果 | 平方和 | 贡献值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| intercept | 34.04 | |||
| X1 | 9.25 | 18.49 | 1025.78 | 23.09 |
| X2 | -2.29 | -4.58 | 62.92 | 1.42 |
| X3 | 6.19 | 12.38 | 459.52 | 10.34 |
| X4 | 0.74 | 1.48 | 6.54 | 0.15 |
| X5 | -11.01 | -22.01 | 1453.54 | 32.72 |
| X6 | -8.69 | -17.38 | 906.4 | 20.40 |
| X7 | 2.32 | 4.65 | 64.75 | 1.46 |
| X8 | 4.37 | 8.74 | 229.32 | 5.16 |
| X9 | -1.28 | -2.57 | 19.76 | 0.44 |
| X10 | 2.87 | 5.75 | 99.15 | 2.23 |
| X11 | 3.10 | 6.19 | 115.05 | 2.59 |
| 实验组数 | 编码/预测值 | 实际值 | 预测值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1/℃ | X5/(g/L) | X6/(g/L) | |||
| 1 | -1/26 | -1/8 | -1/0.3 | 61.2962 | 59.81 |
| 2 | 1/30 | -1/8 | -1/0.3 | 64.2350 | 64.62 |
| 3 | -1/26 | 1/12 | -1/0.3 | 64.0738 | 64.43 |
| 4 | 1/30 | 1/12 | -1/0.3 | 67.1785 | 65.49 |
| 5 | -1/26 | -1/8 | 1/0.7 | 67.0071 | 67.93 |
| 6 | 1/30 | -1/8 | 1/0.7 | 66.0919 | 64.97 |
| 7 | -1/26 | 1/12 | 1/0.7 | 68.8709 | 67.73 |
| 8 | 1/30 | 1/12 | 1/0.7 | 60.3094 | 61.03 |
| 9 | -2/24.64 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 66.3589 | 66.80 |
| 10 | 2/31.36 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 64.5662 | 65.21 |
| 11 | 0/28 | -2/6.64 | 0/0.5 | 63.2265 | 63.63 |
| 12 | 0/28 | 2/13.36 | 0/0.5 | 63.5127 | 64.18 |
| 13 | 0/28 | 0/10 | -2/0.16 | 62.4065 | 63.49 |
| 14 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 2/0.84 | 66.5652 | 66.56 |
| 15 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 73.4263 | 72.78 |
| 16 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 74.3185 | 72.78 |
| 17 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 70.0747 | 72.78 |
| 18 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 73.5353 | 72.78 |
| 19 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 72.5685 | 72.78 |
| 20 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 72.9370 | 72.78 |
| 实验组数 | 编码/预测值 | 实际值 | 预测值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1/℃ | X5/(g/L) | X6/(g/L) | |||
| 1 | -1/26 | -1/8 | -1/0.3 | 61.2962 | 59.81 |
| 2 | 1/30 | -1/8 | -1/0.3 | 64.2350 | 64.62 |
| 3 | -1/26 | 1/12 | -1/0.3 | 64.0738 | 64.43 |
| 4 | 1/30 | 1/12 | -1/0.3 | 67.1785 | 65.49 |
| 5 | -1/26 | -1/8 | 1/0.7 | 67.0071 | 67.93 |
| 6 | 1/30 | -1/8 | 1/0.7 | 66.0919 | 64.97 |
| 7 | -1/26 | 1/12 | 1/0.7 | 68.8709 | 67.73 |
| 8 | 1/30 | 1/12 | 1/0.7 | 60.3094 | 61.03 |
| 9 | -2/24.64 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 66.3589 | 66.80 |
| 10 | 2/31.36 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 64.5662 | 65.21 |
| 11 | 0/28 | -2/6.64 | 0/0.5 | 63.2265 | 63.63 |
| 12 | 0/28 | 2/13.36 | 0/0.5 | 63.5127 | 64.18 |
| 13 | 0/28 | 0/10 | -2/0.16 | 62.4065 | 63.49 |
| 14 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 2/0.84 | 66.5652 | 66.56 |
| 15 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 73.4263 | 72.78 |
| 16 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 74.3185 | 72.78 |
| 17 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 70.0747 | 72.78 |
| 18 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 73.5353 | 72.78 |
| 19 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 72.5685 | 72.78 |
| 20 | 0/28 | 0/10 | 0/0.5 | 72.9370 | 72.78 |
| 差异来源 | 平方和 | df | 自由度 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 342.46 | 9 | 38.05 | 17.01 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 3.04 | 1 | 3.04 | 1.36 | 0.2705 |
| X5 | 0.39 | 1 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.6842 |
| X6 | 11.42 | 1 | 11.42 | 5.11 | 0.0474 |
| X1X5 | 6.99 | 1 | 6.99 | 3.13 | 0.1075 |
| X1X6 | 30.11 | 1 | 30.11 | 13.46 | 0.0043 |
| X5X6 | 11.62 | 1 | 11.62 | 5.19 | 0.0459 |
| X12 | 82.75 | 1 | 82.75 | 36.99 | 0.0001 |
| X52 | 141.80 | 1 | 141.80 | 63.38 | <0.0001 |
| X62 | 108.32 | 1 | 108.32 | 48.42 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 22.37 | 10 | 2.24 | ||
| Lack of fit | 11.64 | 5 | 2.33 | 1.08 | 0.4660 |
| Pure error | 10.74 | 5 | 2.15 | ||
| Cor total | 364.84 | 19 |
| 差异来源 | 平方和 | df | 自由度 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 342.46 | 9 | 38.05 | 17.01 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 3.04 | 1 | 3.04 | 1.36 | 0.2705 |
| X5 | 0.39 | 1 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.6842 |
| X6 | 11.42 | 1 | 11.42 | 5.11 | 0.0474 |
| X1X5 | 6.99 | 1 | 6.99 | 3.13 | 0.1075 |
| X1X6 | 30.11 | 1 | 30.11 | 13.46 | 0.0043 |
| X5X6 | 11.62 | 1 | 11.62 | 5.19 | 0.0459 |
| X12 | 82.75 | 1 | 82.75 | 36.99 | 0.0001 |
| X52 | 141.80 | 1 | 141.80 | 63.38 | <0.0001 |
| X62 | 108.32 | 1 | 108.32 | 48.42 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 22.37 | 10 | 2.24 | ||
| Lack of fit | 11.64 | 5 | 2.33 | 1.08 | 0.4660 |
| Pure error | 10.74 | 5 | 2.15 | ||
| Cor total | 364.84 | 19 |
| 基因编号 | 蛋白 | KO号 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE04770 | 甘氨酸氧化酶thiO | K03153 | 甘氨酸氧化酶活性 |
| GE04748 | phnA | K06193 | 磷酸酯水解酶活性 |
| GE01859 | phnB | K04750 | 乙醛酶/博莱霉素抗性蛋白/双加氧酶 |
| GE01316 | phnC | K02041 | ABC转运系统,核苷酸结合蛋白 |
| GE01318 | phnE | K02042 | ABC转运系统跨膜蛋白 |
| GE05347 | phnN | K05774 | 核糖1,5-二磷酸磷酸激酶 |
| GE02201 | phnR | – | 参与2-氨基乙基膦酸酯降解操纵子的转录调控 |
| GE00269 | phnX | K05306 | 磷酸酯水解酶活性 |
| GE01317 | htxC | K02042 | 磷酸酯ABC转运蛋白渗透酶 |
| GE04402 | 肌氨酸氧化酶SoxD | K00304 | 肌氨酸氧化酶活性 |
| GE03301 | 草甘膦乙酰转移酶gat | K03823 | N-乙酰基转移酶活性 |
| 基因编号 | 蛋白 | KO号 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE04770 | 甘氨酸氧化酶thiO | K03153 | 甘氨酸氧化酶活性 |
| GE04748 | phnA | K06193 | 磷酸酯水解酶活性 |
| GE01859 | phnB | K04750 | 乙醛酶/博莱霉素抗性蛋白/双加氧酶 |
| GE01316 | phnC | K02041 | ABC转运系统,核苷酸结合蛋白 |
| GE01318 | phnE | K02042 | ABC转运系统跨膜蛋白 |
| GE05347 | phnN | K05774 | 核糖1,5-二磷酸磷酸激酶 |
| GE02201 | phnR | – | 参与2-氨基乙基膦酸酯降解操纵子的转录调控 |
| GE00269 | phnX | K05306 | 磷酸酯水解酶活性 |
| GE01317 | htxC | K02042 | 磷酸酯ABC转运蛋白渗透酶 |
| GE04402 | 肌氨酸氧化酶SoxD | K00304 | 肌氨酸氧化酶活性 |
| GE03301 | 草甘膦乙酰转移酶gat | K03823 | N-乙酰基转移酶活性 |
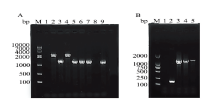
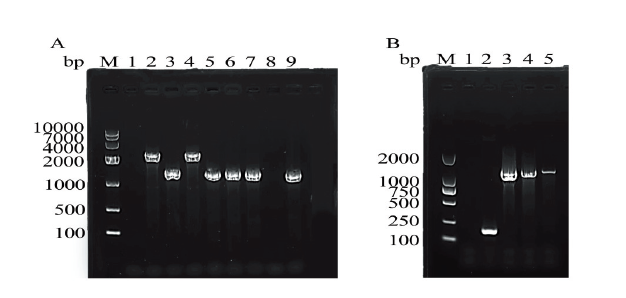
| [1] | KACYNSKI P, LOZOWICKA B, WOLEJKO E, et al. Complex study of glyphosate and metabolites influence on enzymatic activity and microorganisms association in soil enriched with Pseudomonas fluorescens and sewage sludge[J]. Journal of hazard mater, 2020, 393(122443). |
| [2] | FENG D, SORIC A, BOUTIN O. Treatment technologies and degradation pathways of glyphosate: a critical review[J]. The science of the total environment, 2020, 742(140559). |
| [3] | MASOTTI F, GARAVAGLIA B S, PIAZZA A, et al. Bacterial isolates from Argentine pampas and their ability to degrade glyphosate[J]. The science of the total environment, 2021, 774(145761). |
| [4] | VAN BRUGGEN A H C, HE M M, SHIN K, et al. Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate[J]. The science of the total environment, 2018, 616-617:255-268. |
| [5] | ESPINOZA-MONTERO P J, VEGA-VERDUGA C, ALULEMA-PULLUPAXI P, et al. Technologies employed in the treatment of water contaminated with glyphosate: a review[J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 25(23). |
| [6] |
WANG S, SEIWERT B, KÄSTNER M, et al. (Bio)degradation of glyphosate in water-sediment microcosms - a stable isotope co-labeling approach[J]. Water research, 2016, 99:91-100.
doi: S0043-1354(16)30239-1 pmid: 27140906 |
| [7] |
SIHTMÄE M, BLINOVA I, KŰNNIS-BERES K, et al. A. Ecotoxicological effects of different glyphosate formulations[J]. Applied soil ecology, 2013, 72:215-224.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.07.005 URL |
| [8] |
ZHAN H, FENG Y, FAN X, et al. Recent advances in glyphosate biodegradation[J]. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 2018, 102:5033-5043.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9035-0 pmid: 29705962 |
| [9] |
SINGH S, KUMAR V, GILL J P K, et al. Herbicide glyphosate: toxicity and microbial degradation[J]. International journal of environmental research and public health, 2020, 17(20):7519.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph17207519 URL |
| [10] | 沙纪莹, 金丹, 陆伟, 等. 极端污染环境草甘膦抗性菌株的分离、鉴定及特性[J]. 微生物学报, 2008, 48(6):824-828. |
| [11] | 王军华, 王易芬, 陈蕾蕾, 等. 除草剂草甘膦微生物降解技术研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(4):8-12. |
| [12] | ROSSI F, CARLES L, DONNADIEU F, et al. Glyphosate-degrading behavior of five bacterial strains isolated from stream biofilms[J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 2021, 420(126651). |
| [13] | 任嘉红, 刘辉, 吴晓蕙, 等. 南方红豆杉根际溶无机磷细菌的筛选、鉴定及其促生效果[J]. 微生物学报, 2012, 52(3):295-303. |
| [14] | BAI B X, YANG X, ZHAO Q S, et al. Inoculations with Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus cereus affect the soil enzyme activity, growth and rhizosphere microbial diversity of Taxus chinensis var. mairei[J]. Plant and soil, 2020, 455(1):45-52. |
| [15] | 刘邮洲, 张婷婷, 周亚秋, 等. sacB介导的绿针假单胞菌YL-1遗传操作方法[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2019, 35(4):622-629. |
| [16] | 康纪婷. 有机磷农药草甘膦降解菌的筛选、分离及鉴定[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2010. |
| [17] | 卢晓雪, 胡治强, 梅国徽, 等. 类鼻疽伯克霍尔德菌bopA基因敲除株的构建及生物学特征[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(2):233-242. |
| [18] | 张乐, 丁宁, 海燕, 等. 产姜黄素大肠杆菌工程菌的构建[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(6):2077-2084. |
| [19] | 李冠喜, 吴小芹, 叶建仁. 多噬伯克霍尔德氏菌WS-FJ9对草甘膦的降解特性[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(21):6885-6894. |
| [20] |
MANOGARAN M, SHUKOR M Y, YASID N A, et al. Optimisation of culture composition for glyphosate degradation by Burkholderia vietnamiensis strain AQ5-12[J]. 3 Biotech, 2018, 8(2):108.
doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1123-4 URL |
| [21] |
KARAMBA K I, AHMAD S A, ZULKHARNAIN A, et al. Optimisation of biodegradation conditions for cyanide removal by Serratia marcescens strain AQ07 using one-factor-at-a-time technique and response surface methodology[J]. Rendiconti lincei, 2016, 27(3):533-545.
doi: 10.1007/s12210-016-0516-8 URL |
| [22] | 王俞苹, 孔令新, 郑涛, 等. 假单胞菌Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf0-1中转录调控因子SpfB负调控DNA磷硫酰化修饰[J]. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(5):851-862. |
| [23] |
BORGGAARD O K, GIMSING A L. Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: a review[J]. Pest management science, 2008, 64(4):441-456.
pmid: 18161065 |
| [24] |
HOVE-JENSEN B, ZECHEL D L, JOCHIMSEN B. Utilization of glyphosate as phosphate source: biochemistry and genetics of bacterial carbon-phosphorus lyase[J]. Microbiol mol biol rev, 2014, 78(1):176-197.
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-13 URL |
| [25] |
SVIRIDOV A V, SHUSHKOVA T V, ZELENKOVA N F, et al. Distribution of glyphosate and methylphosphonate catabolism systems in soil bacteria Ochrobactrum anthropi and Achromobacter sp.[J]. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 2012, 93(2):787-796.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3485-y URL |
| [26] |
DELANEY B, ZHANG J, CARLSON G, et al. A gene-shuffled glyphosate acetyltransferase protein from Bacillus licheniformis (GAT4601) shows no evidence of allergenicity or toxicity[J]. Toxicological sciences an official journal of the society of toxicology, 2008, 102(2):425.
doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfm304 URL |
| [27] |
YU X M, YU T, YIN G H, et al. Glyphosate biodegradation and potential soil bioremediation by Bacillus subtilis strain Bs-15[J]. Genetics and molecular research, GMR, 2015, 14(4):14717-14730.
doi: 10.4238/2015.November.18.37 URL |
| [28] |
KRYUCHKOVA Y V, BURYGIN G L, GOGOLEVA N E, et al. Isolation and characterization of a glyphosate-degrading rhizosphere strain, Enterobacter cloacae K7[J]. Microbiological research, 2014, 169(1):99-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.03.002 URL |
| [1] | 苏林贺, 黄东, 曾伟民, 张彦龙. 黑木耳凝集素的提取优化及体外抗肿瘤活性的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(9): 143-150. |
| [2] | 刘颖, 耿丹丹, 韩永胜, 魏敏, 刘柳. 环保型农林保水剂研制、性能与应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(7): 86-90. |
| [3] | 白苇, 胡杨, 胡卿卿, 崔金丽, 张宝英, 杨素梅. 冀北油葵主要栽培因素对产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(5): 17-22. |
| [4] | 李佳欢, 王晓慧, 姜明国, 宋福强, 常伟. 基于响应面法优化印度梨形孢培养基[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(3): 102-109. |
| [5] | 刘淑娟, 张翠萍, 李淑英, 杨小燕, 周元清, 李元. 草本植物根际微生物降解地表水环境邻苯二甲酸酯的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(3): 44-51. |
| [6] | 刘宝海, 李晓军, 高世伟, 吴立成, 肖明纲. 黑龙江省2025年粮食产能优化分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(28): 13-20. |
| [7] | 郭东森, 王琳, 魏启舜, 崔联明, 周影, 郭成宝. 羽毛生物降解液对盐胁迫下小白菜生长的生理调控作用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(25): 25-29. |
| [8] | 高岩, 李志斐, 刘阳, 王广军, 谢骏, 郭照良. 草型湖泊水生植物残体的生物降解研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(15): 53-59. |
| [9] | 魏语宁, 刘春光, 付海燕, 吴桐, 宋福强, 马玉堃, 杨峰山. 有机磷类农药微生物修复研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(12): 131-137. |
| [10] | 屈会娟, 李明, 沈学善, 朱玲, 蒲志刚, 冯俊彦, 张聪. 食用型甘薯‘川M1422’综合优化栽培技术研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(1): 1-6. |
| [11] | 赵记军, 于显枫, 张绪成. 地膜源头减量化技术可行路径探讨[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(9): 57-63. |
| [12] | 朱海云, 马瑜, 柯杨, 李勃. 抗猕猴桃细菌性溃疡病蜡样芽孢杆菌MA23培养基及发酵条件优化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(7): 112-118. |
| [13] | 柴娇娇, 杨柳, 索萌萌. 基于复杂网络的民族地区农村居民点布局优化——以贵州省黎平县为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(5): 156-164. |
| [14] | 李婷, 王玥, 刘中珊, 刘奇, 徐赫男, 李冲伟. 一株降解纤维素的低温放线菌Streptomyces azureus及产酶条件优化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(32): 25-33. |
| [15] | 于振旭, 李逸凡, 秦光华, 宋玉民, 乔玉玲, 马玲. 刺槐无性系速生丰产林施肥方案优化研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(25): 35-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||