
中国农学通报 ›› 2026, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 84-91.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2025-0347
收稿日期:2025-05-09
修回日期:2025-10-25
出版日期:2026-01-15
发布日期:2026-01-15
通讯作者:
作者简介:汪锦,女,1995年出生,四川德阳人,实习研究员,硕士,研究方向为花卉育种与栽培。通信地址:610066 四川省成都市锦江区静居寺路20号 四川省农业科学院园艺研究所,Tel:028-84504173,E-mail:jinwang0529@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Jin1( ), WAN Bin1, TU Xunliang1, JIANG Yu1(
), WAN Bin1, TU Xunliang1, JIANG Yu1( ), DENG Jiahong2
), DENG Jiahong2
Received:2025-05-09
Revised:2025-10-25
Published:2026-01-15
Online:2026-01-15
摘要:
花色是兰花观赏价值与商业价值的核心,其形成与花色素的种类、含量及沉着模式密切相关。为系统解析兰花花色素沉着的调控机理,本文综述了兰花花色的主要物质基础(类黄酮、类胡萝卜素、叶绿素),重点归纳了花青素与类胡萝卜素合成途径中结构基因和调节基因的分子调控机制,包括结构基因通过表达类型与表达量决定花色类型(红、紫、黄等)和颜色强度;调节基因通过时空特异性表达,调控花瓣底色、斑点、斑块、脉纹等着色模式,其中MYB与bHLH转录因子的协同作用是着色模式形成的关键。同时,分析了光、温度、外源化学物质等环境因子通过调控关键基因表达间接影响花色素代谢的机制。文章对未来的研究方向提出展望,认为可在花色分类体系、视觉信号和着色模型构建的基础上,进一步完善兰花花色素合成的分子动态调控网络,并在着色模式的特异性调控机制上深入探索。研究旨在为未来兰花定向育种及基因编辑提供理论参考和应用支撑。
汪锦, 万斌, 涂勋良, 蒋彧, 邓家洪. 兰花花色素沉着调控机理的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2026, 42(1): 84-91.
WANG Jin, WAN Bin, TU Xunliang, JIANG Yu, DENG Jiahong. Research Progress on Regulatory Mechanism of Flower Color Pigmentation in Orchid[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2026, 42(1): 84-91.
| 种类 | 色系 | 主要色素类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 蝴蝶兰 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素[ |
| 菲律宾蝴蝶兰 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素、天竺葵素和飞燕草素[ |
| 铁皮石斛 | 黄色 | 类胡萝卜素[ |
| 金钗石斛 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素[ |
| 金钗石斛 | 白色 | 黄酮醇[ |
| 密花石斛 | 淡黄色 | 叶黄素[ |
| 球花石斛 | 金黄色 | 叶黄素[ |
| 鼓槌石斛 | 明黄色 | 玉米黄质、花药黄质、叶黄素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 粉红色 | 天竺葵素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 白色 | 不含花青素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 黄色 | 叶黄素、β-胡萝卜素、新黄质等[ |
| 文心兰‘Gower Ramsey’ | 黄色 | 紫黄质、新黄质[ |
| 文心兰‘Gower Ramsey’ | 橙色 | 紫黄质、新黄质、β-胡萝卜素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Big Chief Kirawee’ | 绿色 | 叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Vanguard Mas Beauty’ | 绿色 | 叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Jungfrau dos Pueblos’ | 白色 | 黄酮醇,极少量花青素,不含类胡萝卜素和叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Virgin’ | 白色 | 黄酮醇,极少量花青素,不含类胡萝卜素和叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘福韵红霞’ | 红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素[ |
| 杂交兰‘玉凤’ | 黄色 | 芍药花素、飞燕草素、黄酮醇[ |
| 建兰 | 红色 | 矢车菊素、天竺葵素[ |
| 建兰 | 黄绿色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 墨兰 | 紫色、黄色 | 芍药花素、矮牵牛素、飞燕草素[ |
| 春兰‘金黔缘’ | 暗黄色 | 飞燕草素、黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘黔明素’ | 亮黄色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘矢蝉’ | 黄白色 | 矢车菊素、飞燕草素、黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘阳明素’ | 乳白色 | 黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘锦绣黔缘’ | 红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素[ |
| 春兰‘凝香紫’ | 紫红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 寒兰 | 紫红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 寒兰 | 白色 | 黄酮醇,缺少花青素[ |
| 四川独蒜兰 | 玫瑰紫 | 矢车菊素、飞燕草素[ |
| 杏黄兜兰 | 黄色 | 玉米黄质、叶黄素[ |
| 硬叶兜兰 | 粉色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、叶黄素、玉米黄质[ |
| 种类 | 色系 | 主要色素类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 蝴蝶兰 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素[ |
| 菲律宾蝴蝶兰 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素、天竺葵素和飞燕草素[ |
| 铁皮石斛 | 黄色 | 类胡萝卜素[ |
| 金钗石斛 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素[ |
| 金钗石斛 | 白色 | 黄酮醇[ |
| 密花石斛 | 淡黄色 | 叶黄素[ |
| 球花石斛 | 金黄色 | 叶黄素[ |
| 鼓槌石斛 | 明黄色 | 玉米黄质、花药黄质、叶黄素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 紫色 | 矢车菊素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 粉红色 | 天竺葵素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 白色 | 不含花青素[ |
| 蝴蝶兰型石斛 | 黄色 | 叶黄素、β-胡萝卜素、新黄质等[ |
| 文心兰‘Gower Ramsey’ | 黄色 | 紫黄质、新黄质[ |
| 文心兰‘Gower Ramsey’ | 橙色 | 紫黄质、新黄质、β-胡萝卜素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Big Chief Kirawee’ | 绿色 | 叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Vanguard Mas Beauty’ | 绿色 | 叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Jungfrau dos Pueblos’ | 白色 | 黄酮醇,极少量花青素,不含类胡萝卜素和叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘Virgin’ | 白色 | 黄酮醇,极少量花青素,不含类胡萝卜素和叶绿素[ |
| 杂交兰‘福韵红霞’ | 红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素[ |
| 杂交兰‘玉凤’ | 黄色 | 芍药花素、飞燕草素、黄酮醇[ |
| 建兰 | 红色 | 矢车菊素、天竺葵素[ |
| 建兰 | 黄绿色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 墨兰 | 紫色、黄色 | 芍药花素、矮牵牛素、飞燕草素[ |
| 春兰‘金黔缘’ | 暗黄色 | 飞燕草素、黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘黔明素’ | 亮黄色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘矢蝉’ | 黄白色 | 矢车菊素、飞燕草素、黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘阳明素’ | 乳白色 | 黄酮醇[ |
| 春兰‘锦绣黔缘’ | 红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素[ |
| 春兰‘凝香紫’ | 紫红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 寒兰 | 紫红色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、黄酮醇[ |
| 寒兰 | 白色 | 黄酮醇,缺少花青素[ |
| 四川独蒜兰 | 玫瑰紫 | 矢车菊素、飞燕草素[ |
| 杏黄兜兰 | 黄色 | 玉米黄质、叶黄素[ |
| 硬叶兜兰 | 粉色 | 矢车菊素、芍药花素、叶黄素、玉米黄质[ |
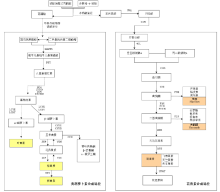
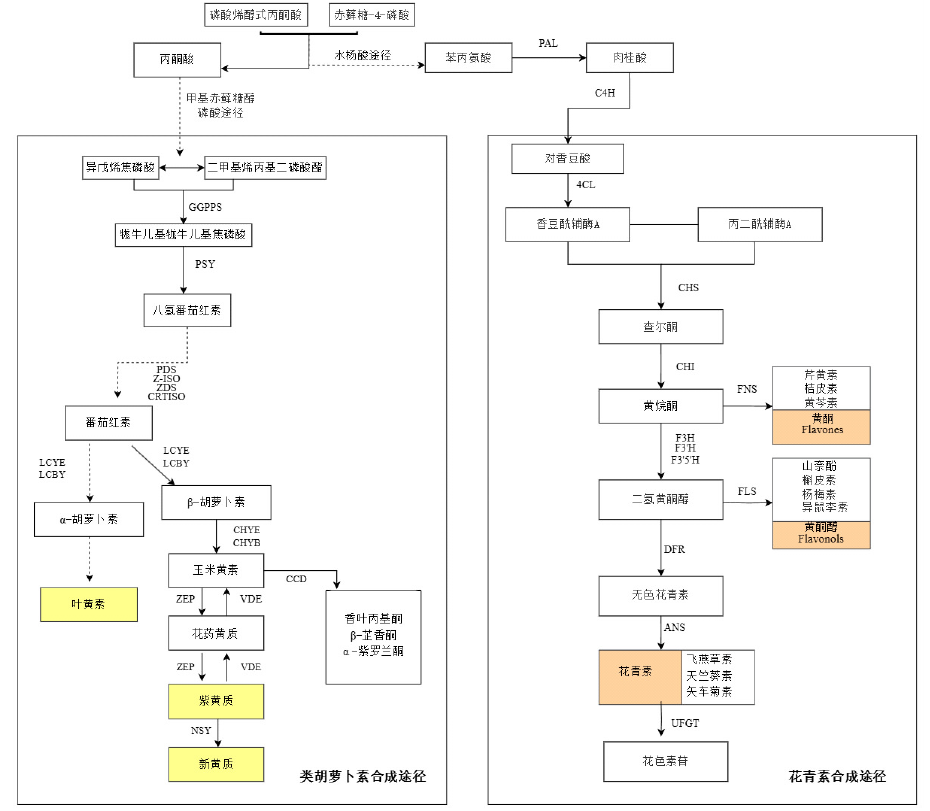
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2009.06.017 URL |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1222-x URL |
| [27] |
兰孔, 林榕燕, 樊荣辉, 等. 杂交兰花瓣类黄酮成分分析及其对花色的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(10):1711-1719.
|
| [28] |
李文建, 沈永宝, 史锋厚, 等. 建兰花色形成的成分检测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4):57-62.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201806041 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v19.12 URL |
| [30] |
doi: 10.32604/phyton.2024.051652 URL |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
刘恺媛, 王茂良, 辛海波, 等. 植物花青素合成与调控研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(14):41-51.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0390 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.4308/hjb.31.2.382-391 URL |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1616-z URL |
| [38] |
李冬梅, 朱根发, 操君喜, 等. 兜兰查尔酮合成酶基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2012, 33(4):655-662.
|
| [39] |
李文建, 冯景, 贾文庆, 等. 建兰花色形成的分子调控机理研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(4):615-623.
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.2503/hortj.MI-020 URL |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1007/s12374-011-9158-7 URL |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1007/s13562-016-0379-1 URL |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2023.05.014 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112013 URL |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr100 URL |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.3390/biology13050329 URL |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2152-9 URL |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1186/s43897-022-00023-2 pmid: 37789426 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.10.002 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-020-01058-z |
| [14] |
doi: 10.3390/plants12020304 URL |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v17.11 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9275-3 URL |
| [17] |
黄昕蕾, 王雁, 张辉. 3种石斛属植物类胡萝卜素成分及代谢途径分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(5):107-113.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1007/s00344-019-10025-y |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1006-1 URL |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
杨玉霞, 孙菲菲, 张昌伟. 蝴蝶兰全长cDNA文库构建及F3′H基因克隆[J]. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(9):1731-1738.
|
| [49] |
doi: 10.1111/plb.2016.18.issue-2 URL |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-6910-0 URL |
| [51] |
许传俊, 黄珺梅, 黄雯, 等. 不同花色品种蝴蝶兰花色素苷含量分析及相关基因表达研究[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 47(3):93-99.
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1007/s12374-022-09352-7 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03256-3 |
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.134.1.88 URL |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00205 URL |
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms20010042 URL |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.254599 URL |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01382-0 |
| [62] |
郑燕, 赵凯, 曹映辉, 等. 建兰R2R3-MYB转录因子家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(7):2089-2099.
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
doi: 10.1007/s11240-009-9649-0 URL |
| [69] |
丁灵. 蝴蝶石斛兰花色和花香形成相关基因的表达与分析[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2016.
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
doi: 10.1007/s11105-013-0617-9 URL |
| [73] |
|
| [21] |
刘红, 魏晓羽, 马辉. 几种兰属地生种花瓣花色素组成分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(6):1657-1677.
|
| [22] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
王世尧, 张果, 杨书才, 等. 基于表型的蝴蝶兰花色数量分类[J]. 热带作物学报, 2023, 44(11):2227-2235.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2023.11.011 |
| [76] |
殷涵泰, 尹俊梅, 廖易, 等. 基于秋石斛花朵颜色、色素分布及表皮细胞形态的表型分类[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10):1907-1920.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0406 |
| [1] | 赵桂龙, 唐佳琦, 黄烁淇, 李荣田, 卜庆云, 鲁振强. 植物冷胁迫下ICE-CBF-COR耐冷调控分子机理的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(9): 132-139. |
| [2] | 苏芸芸, 徐梦馨, 欧晓彬, 龚磊, 张魁, 郭倩. 外源硒响应植物高温胁迫机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(33): 113-120. |
| [3] | 黄礼佳, 张招娟, 郭玉春, 张鑫. 14个彩色马铃薯品种主要性状表现及其SSR遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(32): 17-22. |
| [4] | 廖慧, 张金凤, 张华, 张西西, 宋利娜, 张华丽, 舒健骅. 月季花器官变异的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(19): 49-55. |
| [5] | 李火建, 许誉芝, 陈珺, 张池, 伍玉玲, 魏乙斌, 姜春秀, 曾力方, 张木清. 低温胁迫后甘蔗新品种的光合变化及其抗寒性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(16): 1-8. |
| [6] | 杨星莹, 胡昌雄, 李莎, 李镇刚, 杨文, 李平平. 39份桑葚品种花青素含量分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(13): 158-164. |
| [7] | 杜念芝. AM真菌对桑树类胡萝卜素及黄酮类化合物的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(11): 90-99. |
| [8] | 江珊, 吴龙英, 赵宝生, 黄佳惠, 蒋宇喆, 焦元, 黄进. 植物耐受高温胁迫的分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(9): 132-138. |
| [9] | 肖雯丽, 王含瑞, 王梦亮, 王俊红. 盐碱胁迫下植物响应机制的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(33): 78-85. |
| [10] | 高婧, 秦梦凡, 李坤, 李武. 玉米双胚遗传机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(29): 1-7. |
| [11] | 崔瀚元, 张越, 宋兆伟, 陈颖, 丁舒, 张宇微, 张峻, 陈晓明. 紫玉米花青素研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(28): 157-164. |
| [12] | 王莹, 李娟, 孙雪梅. 菊芋HtMYB2基因VIGS体系构建与功能验证[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 116-121. |
| [13] | 罗秀芹, 韦卓文, 蔡杰, 安飞飞, 陈松笔, 薛晶晶. 转录组和代谢组联合分析阐释木薯叶片花青素合成机制[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(24): 100-106. |
| [14] | 陈伊航, 唐朝臣, 张荣, 姚祝芳, 金晶炜, 王章英. 132份甘薯地方种质遗传多样性和群体结构分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 22-30. |
| [15] | 张凯, 程彦弟, 胡皓楠, 冯海萍, 吴宏亮, 康建宏. 不同轮作模式通过改善西兰花土壤养分和真菌群落在土壤健康中的应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(18): 73-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||