
中国农学通报 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (16): 21-27.doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2024-0475
张楠( ), 张士昌, 彭义峰, 李亚青, 李孟军(
), 张士昌, 彭义峰, 李亚青, 李孟军( ), 史占良
), 史占良
收稿日期:2024-07-27
修回日期:2025-03-25
出版日期:2025-06-05
发布日期:2025-06-05
通讯作者:
作者简介:张楠,女,1989年出生,河北石家庄人,农艺师,学士,主要从事作物分子生物学研究。通信地址:050041 石家庄市正定县三里屯街道正定新区商务中心东门C区308室,Tel:0311-86839186,E-mail:zhangnan-89@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Nan( ), ZHANG Shichang, PENG Yifeng, LI Yaqing, LI Mengjun(
), ZHANG Shichang, PENG Yifeng, LI Yaqing, LI Mengjun( ), SHI Zhanliang
), SHI Zhanliang
Received:2024-07-27
Revised:2025-03-25
Published:2025-06-05
Online:2025-06-05
摘要:
为推动高黄色素小麦分子标记辅助育种工作,测定46个小麦品种(系)的面粉黄色素含量,对黄色素生物合成途径的关键酶(PSY、PDS、ZDS、LCYE)基因,及对面粉具有漂白作用的氧化酶(LOX、POD)基因的相关分子标记进行有效性验证。研究结果显示,不同基因位点的分子标记呈现出不同的情况。Psy-A1和Psy-B1位点的功能标记YP7A和YP7B2,Lox-B1位点的显性互补功能标记LOX16和LOX18,在46个小麦品种(系)中均检测到不同的等位变异,不同等位变异间面粉黄色素含量平均值的差异达极显著水平(P<0.01)。Pds-B1位点的共显性功能标记YP4B1和YP4B2,在46个小麦品种(系)中检测到的不同等位变异之间面粉黄色素含量相关性未达到显著水平(P=0.063)。Pod-A1位点的共显性功能标记POD3A1和POD3A2,在46个小麦品种(系)中检测到的不同等位变异之间面粉黄色素含量无显著差异,但Pod-A1a型材料(低POD活性)面粉黄色素含量均值略高于Pod-A1b型材料(高POD活性)。功能标记YP7A、YP7B2、LOX16和LOX18可用于高黄色素小麦分子标记辅助育种,而共显性功能标记YP4B1和YP4B2、POD3A1和POD3A2在高黄色素小麦分子标记辅助育种时应谨慎使用。
张楠, 张士昌, 彭义峰, 李亚青, 李孟军, 史占良. 小麦黄色素相关分子标记的有效性验证[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(16): 21-27.
ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Shichang, PENG Yifeng, LI Yaqing, LI Mengjun, SHI Zhanliang. Validation of Molecular Markers Related to Yellow Pigment Content of Wheat Flour[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2025, 41(16): 21-27.
| 标记名称 | 引物序列(5'→3') | 扩增片段/bp | 等位变异 | 表型 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | R | |||||
| YP7A | GGACCTTGCTGATGACCGAG | TGACGGTCTGAAGTGAGAATGA | 194 | Psy-A1a | 高YP含量 | [ |
| 231 | Psy-A1b | 低YP含量 | ||||
| YP7A-2 | GCCAGCCCTTCAAGGACATG | CAGATGTCGCCACACTGCCA | 1686 | Psy-A1a/b | 不确定 | [ |
| 1001 | Psy-A1c | 不确定 | ||||
| YP7B2 | GCCACCCACTGATTACCACTA | CCAAGGTGAGGGTCTTCAAC | 482 | Psy-B1c | 高YP含量 | [ |
| YP4B1 | AAGTTGGTGGGAGTTCCTGTC | TGTCAGCAATGACAAAAGGATGCA | - | Pds-B1a | 不确定 | [ |
| 652 | Pds-B1b | 不确定 | ||||
| YP4B2 | AAGTTGGTGGGAGTTCCTGTC | GTGAACTCCTGAAACAGAAAGATTG | 382 | Pds-B1a | 不确定 | [ |
| - | Pds-B1b | 不确定 | ||||
| LOX16 | CCATGACCTGATCCTTCCCTT | GCGCGGATAGGGGTGGT | 489 | Lox-B1a | 高LOX活性 | [ |
| - | Lox-B1b | 低LOX活性 | ||||
| LOX18 | ACGATGTGAGTTGTGACTTGTGA | GCGCGGATAGGGGTGC | - | Lox-B1a | 高LOX活性 | [ |
| 791 | Lox-B1b | 低LOX活性 | ||||
| POD3A1 | ACGGGAGACGACGAGAAGCAAAG | TCGTGGAAGTGTAGGCGAAGA | 291 | Pod-A1a | 低POD活性 | [ |
| - | Pod-A1b | 高POD活性 | ||||
| POD3A2 | GTGGCGCAGGGCCTGTCA | TCGTGGAAGTGTAGGCGAAGA | - | Pod-A1a | 低POD活性 | [ |
| 766 | Pod-A1b | 高POD活性 | ||||
| 标记名称 | 引物序列(5'→3') | 扩增片段/bp | 等位变异 | 表型 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | R | |||||
| YP7A | GGACCTTGCTGATGACCGAG | TGACGGTCTGAAGTGAGAATGA | 194 | Psy-A1a | 高YP含量 | [ |
| 231 | Psy-A1b | 低YP含量 | ||||
| YP7A-2 | GCCAGCCCTTCAAGGACATG | CAGATGTCGCCACACTGCCA | 1686 | Psy-A1a/b | 不确定 | [ |
| 1001 | Psy-A1c | 不确定 | ||||
| YP7B2 | GCCACCCACTGATTACCACTA | CCAAGGTGAGGGTCTTCAAC | 482 | Psy-B1c | 高YP含量 | [ |
| YP4B1 | AAGTTGGTGGGAGTTCCTGTC | TGTCAGCAATGACAAAAGGATGCA | - | Pds-B1a | 不确定 | [ |
| 652 | Pds-B1b | 不确定 | ||||
| YP4B2 | AAGTTGGTGGGAGTTCCTGTC | GTGAACTCCTGAAACAGAAAGATTG | 382 | Pds-B1a | 不确定 | [ |
| - | Pds-B1b | 不确定 | ||||
| LOX16 | CCATGACCTGATCCTTCCCTT | GCGCGGATAGGGGTGGT | 489 | Lox-B1a | 高LOX活性 | [ |
| - | Lox-B1b | 低LOX活性 | ||||
| LOX18 | ACGATGTGAGTTGTGACTTGTGA | GCGCGGATAGGGGTGC | - | Lox-B1a | 高LOX活性 | [ |
| 791 | Lox-B1b | 低LOX活性 | ||||
| POD3A1 | ACGGGAGACGACGAGAAGCAAAG | TCGTGGAAGTGTAGGCGAAGA | 291 | Pod-A1a | 低POD活性 | [ |
| - | Pod-A1b | 高POD活性 | ||||
| POD3A2 | GTGGCGCAGGGCCTGTCA | TCGTGGAAGTGTAGGCGAAGA | - | Pod-A1a | 低POD活性 | [ |
| 766 | Pod-A1b | 高POD活性 | ||||
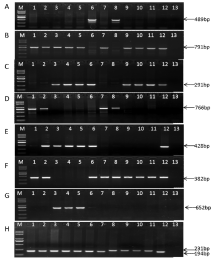
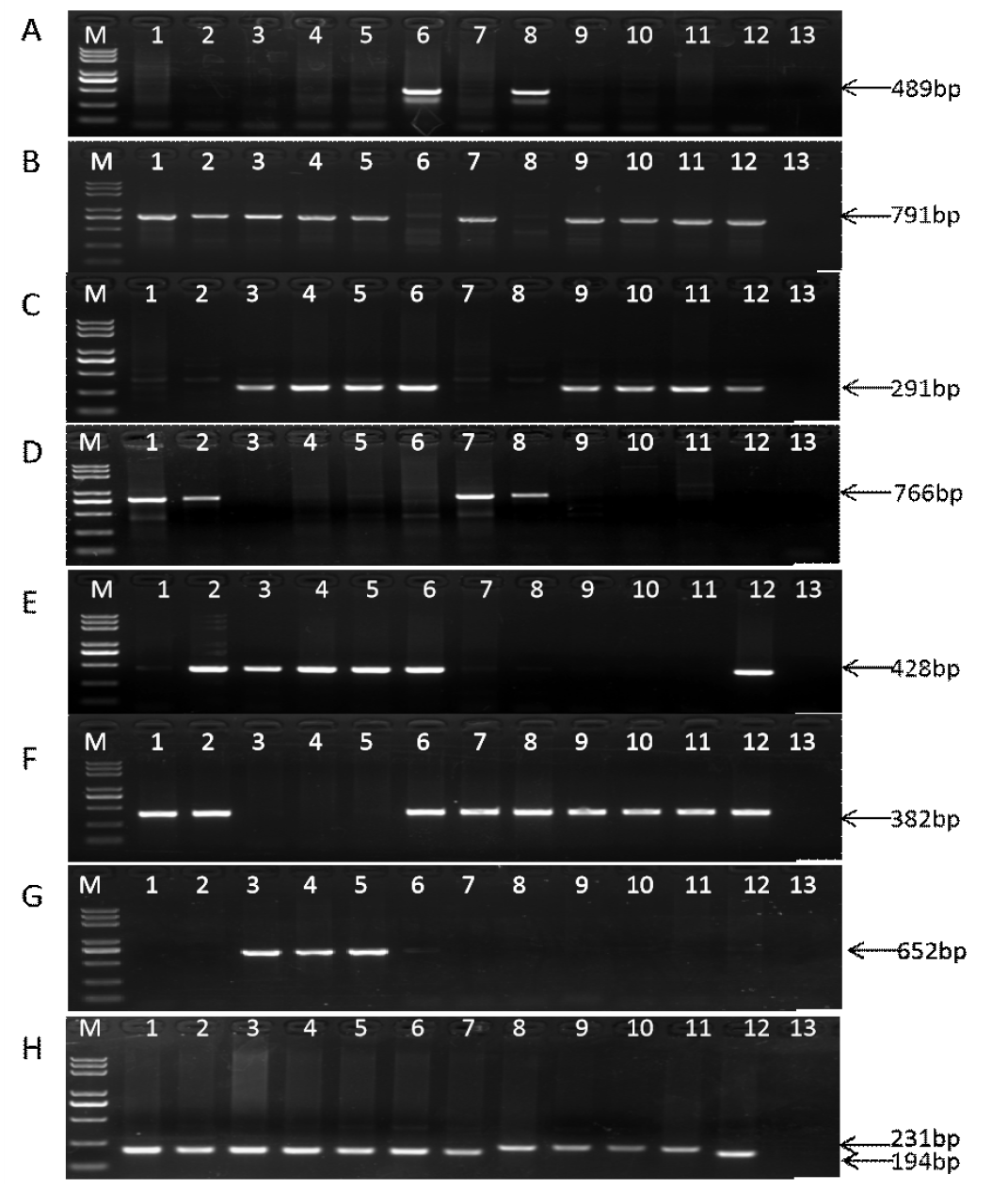
| 编号 | 品种(系) | 等位变异类型 | 黄色素含量/(mg/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP7A | YP7B2 | YP4B1 | YP4B2 | LOX16 | LOX18 | POD3A1 | POD3A2 | |||
| 1 | C1002 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 8.76±0.02 | |||||
| 2 | C1001 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 7.53±0.03 | |||
| 3 | 山农48 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 5.96±0.06 | ||||
| 4 | 济麦8040 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.48±0.10 | ||||
| 5 | 石U5012 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 5.78±0.01 | |||
| 6 | 济麦22 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 3.16±0.08 | ||||
| 7 | 徐18164 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.58±0.08 | |||
| 8 | 周麦22 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 5.66±0.21 | |||
| 9 | 济南18 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 3.46±0.20 | |||
| 10 | 乐麦558 | Psy-A1b | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.39±0.08 | |||
| 11 | 改良鲁麦8号 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 3.55±0.13 | |||
| 12 | 衡0816 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 5.36±0.10 | ||||
| 13 | 运97154 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 5.27±0.08 | ||||
| 14 | 邯原1号 | Psy-A1b | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.24±0.16 | |||
| 15 | 龙麦1号 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 5.27±0.13 | ||||
| 16 | 徐18174 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 4.48±0.10 | |||
| 17 | 河农638 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.36±0.07 | ||||
| 18 | 金丰5129 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 4.39±0.17 | |||
| 19 | 山农1355 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 4.33±0.13 | ||||
| 20 | 衡4399 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 3.46±0.13 | |||
| 21 | 藁麦5号 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.33±0.17 | ||||
| 22 | 淮0432 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.27±0.24 | |||
| 23 | 鲁研217 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.21±0.30 | |||
| 24 | 哈高6号 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 3.34±0.17 | ||||
| 25 | 淮阴9701 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 3.31±0.30 | ||||
| 26 | 运旱21-30 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 5.60±0.27 | |||
| 27 | 齐丰1号 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.83±0.24 | ||||
| 28 | 邯02-6018 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 2.71±0.23 | ||||
| 29 | 冀师02-1 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 2.62±0.21 | ||||
| 30 | 860955 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 2.53±0.27 | ||||
| 31 | 冀麦585 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.50±0.10 | ||||
| 32 | 新农1718 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.35±0.35 | ||||
| 33 | 冀麦185 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.35±0.08 | ||||
| 34 | 河农4361 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 2.29±0.03 | ||||
| 35 | 河农6049 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.29±0.27 | ||||
| 36 | 济麦262 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 1.96±0.25 | ||||
| 37 | 山农2149 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 1.93±0.24 | ||||
| 38 | 临麦4号 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 1.90±0.13 | ||||
| 39 | 鲁麦16 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 1.75±0.01 | ||||
| 40 | 石新828 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 1.35±0.10 | |||||
| 41 | 良星99 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 3.94±0.08 | ||||
| 42 | 鲁原502 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.18±0.13 | ||||
| 43 | 临资5126 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 3.10±0.23 | ||||
| 44 | 徐18170 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 6.32±0.17 | |||
| 45 | 淮麦32 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 6.26±0.11 | |||
| 46 | 徐18173 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 6.17±0.28 | |||
| 编号 | 品种(系) | 等位变异类型 | 黄色素含量/(mg/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP7A | YP7B2 | YP4B1 | YP4B2 | LOX16 | LOX18 | POD3A1 | POD3A2 | |||
| 1 | C1002 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 8.76±0.02 | |||||
| 2 | C1001 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 7.53±0.03 | |||
| 3 | 山农48 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 5.96±0.06 | ||||
| 4 | 济麦8040 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.48±0.10 | ||||
| 5 | 石U5012 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 5.78±0.01 | |||
| 6 | 济麦22 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 3.16±0.08 | ||||
| 7 | 徐18164 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.58±0.08 | |||
| 8 | 周麦22 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 5.66±0.21 | |||
| 9 | 济南18 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 3.46±0.20 | |||
| 10 | 乐麦558 | Psy-A1b | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.39±0.08 | |||
| 11 | 改良鲁麦8号 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 3.55±0.13 | |||
| 12 | 衡0816 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 5.36±0.10 | ||||
| 13 | 运97154 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 5.27±0.08 | ||||
| 14 | 邯原1号 | Psy-A1b | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.24±0.16 | |||
| 15 | 龙麦1号 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 5.27±0.13 | ||||
| 16 | 徐18174 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 4.48±0.10 | |||
| 17 | 河农638 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.36±0.07 | ||||
| 18 | 金丰5129 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 4.39±0.17 | |||
| 19 | 山农1355 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 4.33±0.13 | ||||
| 20 | 衡4399 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 3.46±0.13 | |||
| 21 | 藁麦5号 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.33±0.17 | ||||
| 22 | 淮0432 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.27±0.24 | |||
| 23 | 鲁研217 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 4.21±0.30 | |||
| 24 | 哈高6号 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 3.34±0.17 | ||||
| 25 | 淮阴9701 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 3.31±0.30 | ||||
| 26 | 运旱21-30 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 5.60±0.27 | |||
| 27 | 齐丰1号 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.83±0.24 | ||||
| 28 | 邯02-6018 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 2.71±0.23 | ||||
| 29 | 冀师02-1 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 2.62±0.21 | ||||
| 30 | 860955 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 2.53±0.27 | ||||
| 31 | 冀麦585 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.50±0.10 | ||||
| 32 | 新农1718 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.35±0.35 | ||||
| 33 | 冀麦185 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.35±0.08 | ||||
| 34 | 河农4361 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 2.29±0.03 | ||||
| 35 | 河农6049 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 2.29±0.27 | ||||
| 36 | 济麦262 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 1.96±0.25 | ||||
| 37 | 山农2149 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 1.93±0.24 | ||||
| 38 | 临麦4号 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1b | 1.90±0.13 | ||||
| 39 | 鲁麦16 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 1.75±0.01 | ||||
| 40 | 石新828 | Psy-A1b | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | 1.35±0.10 | |||||
| 41 | 良星99 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 3.94±0.08 | ||||
| 42 | 鲁原502 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1b | 4.18±0.13 | ||||
| 43 | 临资5126 | Psy-A1a | Pds-B1a | Lox-B1a | Pod-A1a | 3.10±0.23 | ||||
| 44 | 徐18170 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 6.32±0.17 | |||
| 45 | 淮麦32 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 6.26±0.11 | |||
| 46 | 徐18173 | Psy-A1a | Psy-B1c | Pds-B1b | Lox-B1b | Pod-A1a | 6.17±0.28 | |||
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
魏景欣. 小麦籽粒过氧化物酶活性QTL分析及相关基因克隆和功能标记开发[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015:27.
|
| [24] |
American Association of Cereal Chemists International 2000. Approved Methods of AACC[S]. Method 14-50. AACCI: St. Paul, MN,2000:14-50.
|
| [25] |
杨芳萍, 何心尧, 何中虎, 等. 中国小麦品种黄色素含量基因等位变异分子检测及其分布规律研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(10):2923-2930.
|
| [26] |
芦静, 胡钰, 周安定, 等. 新疆小麦黄色素含量基因等位变异的分子检测及其分布[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2012, 32(2):234-239.
|
| [27] |
胡凤灵, 何中虎, 葛建贵, 等. 小麦品种黄色素含量和多酚氧化酶活性基因的分子标记检测[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2011, 31(1):47-53.
|
| [28] |
叶石. 陕西小麦籽粒PPO活性基因和YP含量基因的等位变异检测和分布分析[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学,2010:22-23.
|
| [29] |
杨淑萍, 张宏纪, 张举梅, 等. 俄引及黑龙江春小麦黄色素含量相关基因分析[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2015, 35(10):1347-1354.
|
| [30] |
朵茂惠, 赵池铭, 汪军成, 等. 甘肃省新育成小麦品种(系)面粉色度相关基因分子检测[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(2):163-170.
|
| [31] |
张钰玉, 张晓科, 蒋雷, 等. 陕西小麦黄色素含量基因TaZds-A1和TaZds-D1的组成与分布[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2013, 33(6):1144-1148.
|
| [32] |
张福彦, 陈锋, 程仲杰, 等. 小麦TaLox-B等位变异对脂肪氧化酶活性和面粉色泽的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(8):1370-1377.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.08.002 |
| [33] |
白璐, 禹飞雄, 茹仙古丽·牙生, 等. 新疆小麦TaLox-B1、TaLox-B2、TaLox-B3位点的等位变异及其分布规律[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2016, 36(11):1456-1463.
|
| [34] |
陈杰, 张星宇, 张福彦, 等. 黄淮麦区(南片)小麦新品系脂肪氧化酶活性分析及其等位基因检测[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(10):1219-1227.
|
| [35] |
陈杰, 张星宇, 白冬, 等. 黄淮麦区(南片)小麦籽粒过氧化物酶活性分析及其等位基因检测[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(9):1073-1080.
|
| [36] |
王丽丽, 战帅帅, 谢磊, 等. 新疆小麦籽粒过氧化物酶(POD)活性检测及其基因等位变异检测[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(10):1765-1774.
doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2020.10.001 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
马乐, 闫少芳, 黄旸木, 等. 叶黄素干预对早期老年黄斑变性患者生活质量的影响[J]. 营养学报, 2012, 34(4):327-331.
|
| [4] |
马骋. 小麦叶黄素合成关键酶基因ε-LCY的克隆及遗传转化[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学,2012:2-3.
|
| [5] |
翟胜男, 郭军, 刘成, 等. 小麦类胡萝卜素合成途径关键基因Lcye功能分析[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(10):1485-1495.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.01013 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
朱长甫, 陈星, 王英典. 植物类胡萝卜素生物合成及其相关基因在基因工程中的应用[J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2005,30:609-618.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
张立平, 阎俊, 夏先春, 等. 普通小麦籽粒黄色素含量的QTL分析[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(1):41-45.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
何心尧. 普通小麦及其近缘种籽粒多酚氧化酶活性与黄色素含量相关基因的克隆与功能标记开发[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院,2008:58-62.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
董长海. 普通小麦特粒黄色素含量相关基因的克隆与功能标记开发[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学,2011:19-22.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [1] | 田翠玲, 田家良. 不同生育期喷施海藻酸增效液对冬小麦光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(9): 25-31. |
| [2] | 任庆国, 吴广俊, 林平, 张继雨, 张鑫, 张永珊, 海涛. 小麦新品种‘菏麦26’的产量及品质特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(9): 32-37. |
| [3] | 薛远赛, 王锡久, 邹士国, 张守福, 刘光亚, 韩伟, 孙显. 复合寡糖对山东典型作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(8): 50-56. |
| [4] | 陶媛, 何亚玲, 张倩, 孙倩, 刘永亮, 李前荣. 调整播期对宁夏春小麦产量与品质性状的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(6): 10-21. |
| [5] | 范华, 程敦公, 刘建军, 刘爱峰. 不同筋力小麦品种混播的理化品质特性变化及对面包面条品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(6): 148-152. |
| [6] | 夏彦, 刘凯文, 叶佩, 邓艳君, 肖潇, 耿一风, 吴启侠. 基于优化播期的江汉平原冬小麦种植气象适宜性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(4): 102-107. |
| [7] | 吴月娥, 段海燕, 姜恭好. 有色稻米及其相关基因研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(4): 19-24. |
| [8] | 张新刚. 气候变暖对豫北地区冬小麦生长发育和产量的影响——以河南省沁阳市为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(3): 98-106. |
| [9] | 刘立伟, 刘静, 王静, 易媛, 朱雪成, 张娜, 张会云, 马红勃, 刘东涛, 冯国华. 2004—2022年徐州地区气候因子及小麦区域试验品系性状演变分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(3): 76-83. |
| [10] | 赵彦坤, 李彩华, 班进福, 李占坤, 单子龙, 曹巧, 王秀堂, 高新梅, 傅晓艺, 何明琦, 马龙, 高振贤. 节水灌溉条件下小麦新品种‘石麦34’的抗倒性和品质分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(15): 1-6. |
| [11] | 陈宏州, 张海波, 周晨, 朱友理, 杨红福, 徐超, 郭晓萌, 朱凤. 小麦籽粒DON积累动态及其影响因素相关性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(15): 7-14. |
| [12] | 钱晨诚, 王君, 仇景涛, 马泉, 丁锦峰. 不同小麦品种在里下河地区产量水平及品质的差异分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(14): 1-7. |
| [13] | 茹淑华, 王雪晴, 赵欧亚, 刘蕾, 侯利敏, 肖广敏, 王策, 王凌, 孙世友. 河北山前平原区不同小麦品种镉吸收差异研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(14): 74-80. |
| [14] | 王国权, 逯盼盼, 李俊超, 王岩岩, 郭梦诚, 徐于倩, 岳礼洋, 李卫国, 周锋, 刘润强. 3种植物生长调节剂对小麦幼苗生长性状及产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(13): 1-6. |
| [15] | 蔡金华. 长江中下游麦区小麦种质资源的产量和品质性状及其相关性分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2025, 41(12): 19-25. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||